Chapter: Linear Integrated Ciruits : IC Fabrication and Circuit Configuration for Linear ICs
Current Mirror and Current Sources
CURRENT MIRROR AND CURRENT
SOURCES:
Constant current source(Current Mirror):
A
constant current source makes use of the fact that for a transistor in the
active mode of operation, the collector current is relatively independent of
the collector voltage. In the basic circuit shown in fig 1
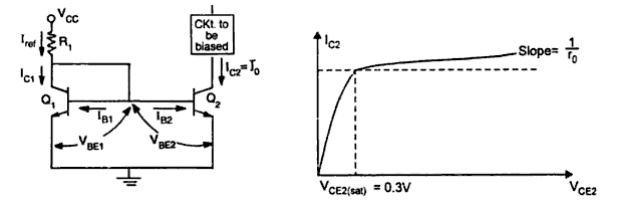
Transistors
Q1&Q2 are matched as the circuit is fabricated using IC technology. Base
and emitter of Q1&Q2 are tied together and thus have the same VBE. .In
addition, transistor Q1 is connected as a diode by shorting it s collector to
base. The input current Iref flows through the diode connected transistor Q1
and thus establishes a voltage across Q1.
This
voltage in turn appears between the base and emitter of Q2 .Since Q2 is
identical to Q1, the emitter current of Q2 will be equal to emitter current of
Q1 which is approximately equal to Iref
As long
as Q2 is maintained in the active region ,its collector current IC2=Io will be
approximately equal to Iref .
Since the
output current Io is a reflection or mirror of the reference current Iref, the
circuit is often referred to as a current mirror.
Analysis:
The
collector current IC1 and IC2 for the transistor Q1 and
Q2 can be approximately expressed as
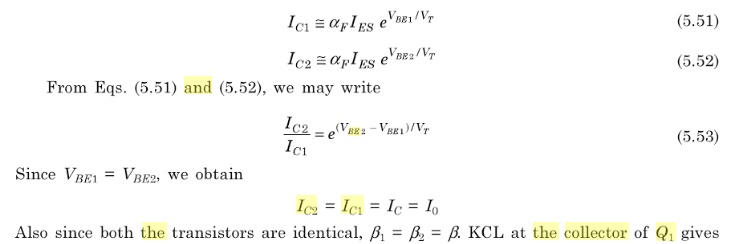

From equations b>>1, b/(b+2) is almost unity and the output current I0 is equal to the reference current, Iref which for a given R1 is constant. Typically Io varies by about 3% for 50 ≤ b ≤200.
It is
possible to obtain current transfer ratio other than unity simple by
controlling the area of the emitter-base junction (EBJ) of the transistor Q2 .
For example, if the area of EBJ of Q2 is 4 times that of Q1,then
IO=4 Iref
The
output resistance of the current source is the output resistance,r0 of Q2,
The
circuit however operates as a constant current source as long as Q2 remains in
the active region.
Related Topics