Chapter: Linear Integrated Ciruits : IC Fabrication and Circuit Configuration for Linear ICs
Classification of ICs
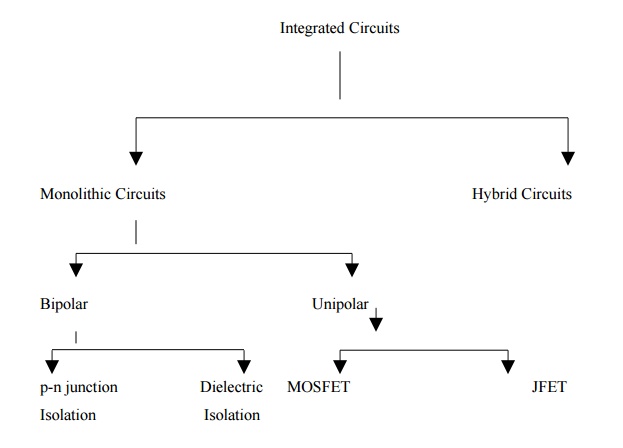
Classification of ICs:
Generations
SSI, MSI and LSI
The first
integrated circuits contained only a few transistors. Called "Small-Scale
Integration" (SSI), digital circuits containing transistors numbering in
the tens provided a few logic gates for example, while early linear ICs such as
the Plessey SL201 or the Philips TAA320 had as few as two transistors. The term
Large Scale Integration was first used by IBM scientist Rolf Landauer when describing
the theoretical concept, from there came the terms for SSI, MSI, VLSI, and
ULSI. They began to appear in consumer products at the turn of the decade, a
typical application being FMinter-carrier sound processing intelevision
receivers.
The next
step in the development of integrated circuits, taken in the late 1960s,
introduced devices which contained hundreds of transistors on each chip, called
"Medium-Scale Integration" (MSI). They were attractive economically
because while they cost little more to produce than SSI devices, they allowed
more complex systems to be produced using smaller circuit boards, less assembly
work (because of fewer separate components), and a number of other advantages.
VLSI
The final
step in the development process, starting in the 1980s and continuing through
the present, was "very large-scale integration" (VLSI).The
development started with hundreds of thousands of transistors in the early
1980s, and continues beyond several billion transistors as of 2007.
In 1986
the first one megabit RAM chips were introduced, which contained more than one
million transistors. Microprocessor chips passed the million transistor mark in
1989 and the billion transistor mark in 2005
ULSI, WSI, SOC and 3D-IC
To
reflect further growth of the complexity, the term ULSI that stands for
"Ultra-Large Scale Integration" was proposed for chips of complexity
of more than 1 million transistors.
Wafer-scale
integration (WSI)is a system of building very-large integrated circuits that
uses anentire silicon wafer to produce a single "super-chip". Through
a combination of large size and reduced packaging, WSI could lead to
dramatically reduced costs for some systems, notably
massively
parallel supercomputers. The name is taken from the term Very-Large-Scale
Integration, the current state of the art when WSI was being developed.
System-on-a-Chip
(SoCorSOC) is an integrated circuit in which all the components needed for
acomputer or other system are included on a single chip. The design of such a
device can be complex and costly, and building disparate components on a single
piece of silicon may compromise the efficiency of some elements.
However,
these drawbacks are offset by lower manufacturing and assembly costs and by a
greatly reduced power budget: because signals among the components are kept
on-die, much less power is require. Three Dimensional Integrated Circuit
(3D-IC) has two or more layers of active electronic components that are
integrated both vertically and horizontally into a single circuit.
Communication between layers uses on-die signaling, so power consumption is
much lower than in equivalent separate circuits. Judicious use of short
vertical wires can substantially reduce overall wire length for faster
operation.
Related Topics