Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Beta-Lactam & OtherCell Wall- & Membrane-Active Antibiotics
Monobactams - Beta Lactam Drugs
MONOBACTAMS
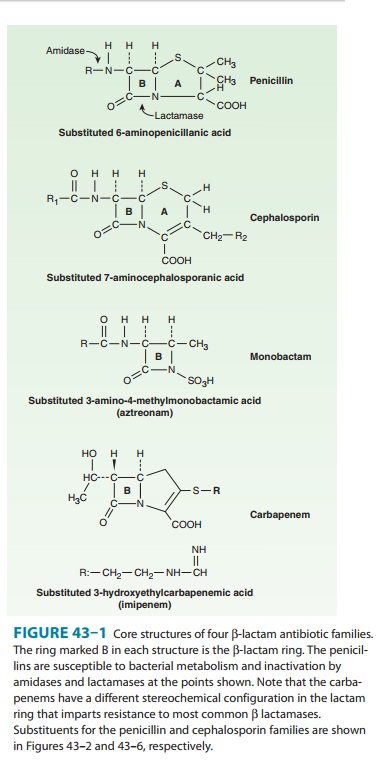
Monobactams are drugs with a monocyclic β-lactam ring (Figure 43–1). Their spectrum of activity is limited to aerobic gram-negative rods (including P aeruginosa). Unlike other β-lactam antibiotics, they have no activity against gram-positive bacteria or anaerobes. Aztreonam is the only monobactam available in the USA. It has structural similarities to ceftazidime; hence, its gram-negative spectrum is similar to that of the third-generation cepha-losporins. It is stable to many β lactamases with the notable exceptions being AmpC β lactamases and extended-spectrum lactamases.
It penetrates well into the cerebrospinal fluid. Aztreonam is given
intravenously every 8 hours in a dose of 1–2 g, providing peak serum levels of
100 mcg/mL. The half-life is 1–2 hours and is greatly prolonged in renal
failure.
Penicillin-allergic
patients tolerate aztreonam without reaction. Occasional skin rashes and
elevations of serum aminotransferases occur during administration of aztreonam,
but major toxicity is uncommon. In patients with a history of penicillin
anaphylaxis, aztre-onam may be used to treat serious infections such as
pneumonia, meningitis, and sepsis caused by susceptible gram-negative
pathogens.
Related Topics