Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Beta-Lactam & OtherCell Wall- & Membrane-Active Antibiotics
Carbapenems - Beta Lactam Drugs
CARBAPENEMS
The carbapenems are structurally related to β-lactam antibiotics (Figure 43–1). Doripenem, ertapenem, imipenem, and meropenem are licensed for use in the USA. Imipenem, the firstdrug of this class, has a wide spectrum with good activity against many gram-negative rods, including P aeruginosa, gram-positive organisms, and anaerobes.
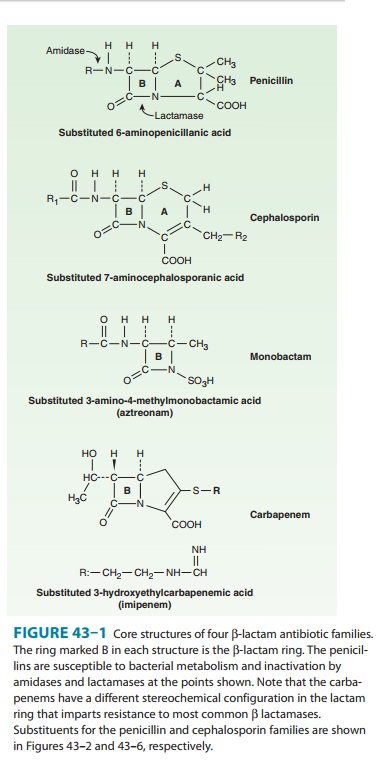
It is resistant to most β lactamases but not carbapenemases or metallo-β lactamases. Enterococcus faecium,
methicillin-resistant strains of staphylococci, Clostridium difficile, Burkholderia
cepacia, and Stenotrophomonas
maltophilia are resis-tant. Imipenem is inactivated by dehydropeptidases in
renal tubules, resulting in low urinary concentrations. Consequently, it is
administered together with an inhibitor of renal dehydropepti-dase, cilastatin, for clinical use. Doripenem
and meropenem are similar to imipenem but have slightly greater activity
against gram-negative aerobes and slightly less activity against
gram-positives. They are not significantly degraded by renal dehydro-peptidase
and do not require an inhibitor. Ertapenem is less active than the other
carbapenems against P aeruginosa and Acinetobacter species. It is not
degraded by renal dehydropeptidase.
Carbapenems penetrate
body tissues and fluids well, including the cerebrospinal fluid. All are
cleared renally, and the dose must be reduced in patients with renal
insufficiency. The usual dosage of imipenem is 0.25–0.5 g given intravenously
every 6–8 hours (half-life 1 hour). The usual adult dosage of meropenem is
0.5–1 g intravenously every 8 hours. The usual adult dosage of doripenem is 0.5
g administered as a 1- or 4-hour infusion every 8 hours. Ertapenem has the
longest half-life (4 hours) and is administered as a once-daily dose of 1 g
intravenously or intramuscularly. Intramuscular ertapenem is irritating, and
for that reason the drug is formulated with 1% lidocaine for administration by
this route.
A carbapenem is
indicated for infections caused by susceptible organisms that are resistant to
other available drugs, eg, P aeruginosa,
and for treatment of mixed aerobic and anaerobic infections. Carbapenems are
active against many penicillin-non-susceptible strains of pneumococci.
Carbapenems are highly active in the treatment of enterobacter infections
because they are resistant to destruction by the β lactamase produced by these organisms.
Clinical experience suggests that carbapenems are also the treat-ment of choice
for infections caused by extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing gram-negative bacteria.
Ertapenem isinsufficiently active against P
aeruginosa and should not be used to treat infections caused by that
organism. Imipenem, meropenem, or doripenem, with or without an aminoglycoside,
may be effec-tive treatment for febrile neutropenic patients.
The
most common adverse effects of carbapenems—which tend to be more common with
imipenem—are nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, skin rashes, and reactions at the
infusion sites. Excessive levels of imipenem in patients with renal failure may
lead to seizures. Meropenem, doripenem, and ertapenem are much less likely to
cause seizures than imipenem. Patients allergic to penicil-lins may be allergic
to carbapenems as well.
Related Topics