Book Back Important Questions Answers | Choose the Correct Answers | Short, brief Answers | Zoology - Microbes in Human Welfare: Questions and Answers (Evaluation) | 12th Zoology : Chapter 9 : Microbes in Human Welfare
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 9 : Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes in Human Welfare: Questions and Answers (Evaluation)
Evaluation
1. Which of the following microorganism is used for production of citric acid in industries?
a) Lactobacillus bulgaris
b) Penicillium citrinum
c) Aspergillus niger
d) Rhizopus nigricans
Answer: c)
Aspergillus niger
2. Which of the following pair is correctly matched for the product produced by them?
a) Acetobacter aceti - Antibiotics
b) Methanobacterium - Lactic acid
c) Penicilium notatum - Acetic acid
d) Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Ethanol
Answer: d)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae - Ethanol
3. The most common substrate used in distilleries for the production of ethanol is_________
a) Soyameal
b) Groundgram
c) Molasses
d) Corn meal
Answer: c) Molasses
4. Cry toxins obtained from Bacillus thuringiensis are effective against for______
a) Mosquitoes
b) Flies
c) Nematodes
d) Bollworms
Answer: d) Bollworms
5. Cyclosporin – A is an immunosuppressive drug produced from _______
a) Aspergillus niger
b) Manascus purpureus
c) Penicillium notatum
d) Trichoderma polysporum
Answer: d)
Trichoderma polysporum
6. Which of the following bacteria is used extensively as a bio-pesticide?
a) Bacillus thurigiensis
b) Bacillus subtilis
c) Lactobacillus acidophilus
d) Streptococcus lactis
Answer: a) Bacillus
thurigiensis
7. Which of the following is not involved in nitrogen fixation?
a) Pseudomonas
b) Azotobacter
c) Anabaena
d) Nostac
Answer: a)
Pseudomonas
8. CO2 is not released during
a) Alcoholic fermentation
b) Lactate fermentation
c) Aerobic respiration in animals
d) Aerobic respiration in plants
Answer: b) Lactate
fermentation
9. The purpose of biological treatment of waste water is to _______
a) Reduce BOD
b) Increase BOD
c) Reduce sedimentation
d) Increase sedimentation
Answer: a) Reduce BOD
10. The gases produced in anaerobic sludge digesters are
a) Methane, oxygen and hydrogen sulphide.
b) Hydrogen sulphide, methane and sulphur dioxide.
c) Hydrogen sulphide, nitrogen and methane.
d) Methane, hydrogen sulphide and CO2.
Answer: d) Methane,
hydrogensulphide and CO2
11. How is milk converted into curd? Explain the process of curd formation.
a) It is prepared by
the action of LAB (Lactic Acid Bacteria)
b) It grows in milk and
digesting the milk protein casein and converts it into curd.
Process of curd formation :
1. A small amount of
curd added to fresh milk as starter or inoculum
2. It contains
millions of Lactobacilli
3. Under suitable
temperature ie 40 ° C
4. They partially
digest the milk proteins casein
5. Curd is more
nutritious than milk as it contains a number of organic acids and vitamins
(Vit-B12)
12. Give any two bioactive molecules produced by microbes and state their uses.
1. Streptokinase 2. Cyclosporin A
1. Streptokinase :
• Produced by the
bacterium streptococcus and genetically engineered streptococci.
• It is used as
"clot buster" for removing clots from the blood vessels of patients
who have undergone myocardial infraction.
2. Cyclosporin :
• It is produced from
the fungus Trichoderma polysporium
• It is used as an
immuno suppressant in organ transplantation.
• It is also used for
its antiinflammatory anti - fungal and anti - parasitic properties.
13. What is biological oxygen demand?
• BOD refers to the amount
of the oxygen that would be consumed, if all the organic matter in one litre of
water were oxidized by bacteria.
• The greater the BOD of
the waste water more is its polluting potential.
14. Explain the role of cry-genes in genetically modified crops.
• Bacillus thuringiensis
is a soil dwelling bacteria.
• It is an example of
mircobial bio control agents that can be introduced in order to control
butterfly caterpillars.
• It is used as a
biopesticide
• It contains a toxin
called cry toxin.
• Scientists have
introduced this toxin producing genes into plants and have raised genetically
engineered insect resistant plants. eg:- Bt - Cotton
• During sporulation
Bacillus thuringiensis produces crystal proteins called Delta - end otoxin which
is encoded by "cry genes'.
• When the insects
ingest the toxin crystals their alkaline digestive tract denatures the
insoluble crystals making them soluble.
• The 'crytoxin' then gets
inserted into the gut cell membrance and paralyzes the digestive tract.
• The insect then stops
eating and starves to death.
• This toxin can kill
certain insects of the order Lepidoptera, Diptera, Coleoptera and Hymenoptera.
15. Write the key features of organic farming.
Key features of organic farming :-
• Protecting soil
quality using organic materials and encouraging biological activity.
• Indirect provision of
crop nutrients using soil micro organisms.
• Nitrogen fixation in
soil using legumes.
• Weed and pest control
based on methods like crop rotation, biological diversity, natural predators,
organic manures and suitable chemical, thermal and biological intervention.
16. Justify the role of microbes as a bio-fertilizer.
• Bio fertilizers are
living micro organism that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil.
• They increase physico
- chemical properties of soil such as structure, water holding capacity, and PH
by providing several nutrients, and sufficient organic matter.
• The main sources of
biofertilizers are bacteria fungi and cyano bacteria.
• Rhizobium is a
classical example for symbiotic Nitrogen fixing bacteria that infects the root
nodules of leguminous plants and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms.
• A symbiotic
association between a fungus and the roots of the plant called mycorrhiza
absorbs the phosphorous from soil and transfers to the plant. e.g. Genus Glomus
form mycorrhiza
• Plants with such
association also show other benefits such as resistance to root born pathogens,
tolerence, to salinity, drought, enhances plant growth and developments.
• Cyanobacteria or blue
green algae can fix molecular nitrogen.e.g.:- oscillatoria, Nostoc, Anabaena,
Tolypothrix.
• They secrete growth
promoting substances like indole - 3 -acetic acid, indole - 3 - butyric acid
naphthalene acetic acid, amino acids, proteins, vitamins, which promotes plant
growth and production.
• Thus biofertilizers
are used in organic farming methods which involves cultivation of plants and
rearing of animals in natural ways, avoiding synthetic substances.
17. Write short notes on the following.
a) Brewer's yeast b) Ideonella sakaiensis c) Microbial fuel cells
a) Brewer's yeast:
• Saccharomyees
cerevisiae used for bread making and commonly called brewer's yeast
• It is used for
fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices to produce various alcoholic beverages.
• Wine and beer are
produced without distillation.
• Whisky, brandy and rum
are obtained by fermentation and distillation.
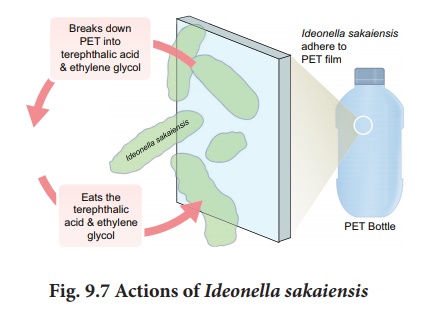
b) Ideonella sakaiensis
• It is currently tried for recycling of PET plastics.
• These bacteria use
PETase and MHETase enzymes to break down PET plastic into terephthalic acid and
ethylene glycol.
c) Microbial fuel cells
• It is a bio -
electrochemical system that drives an electric current by using bacteria.
• If mimicks bacterial
interaction found in nature.
• Bacterial respiration
involves redox reaction in which
electrons are being moved around.
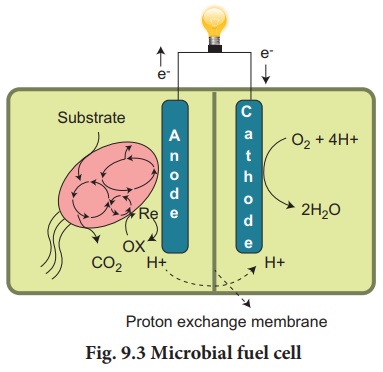
• MFC consists of an
anode and a cathode separated by a proton exchange membrane.
• Microbes at the anode
oxidize the organic fuel.
• It generates protons
which pass through the membrane to the cathode.
• Electrons pass through
the anode to the external circuit to generate current.
18. List the advantages of biogas plants in rural areas.
• Biogas can be produced
from raw materials such as agricultural wastes, manure, municipal water, plant
material, sewage, food waste etc.
• Cattle dung is
available in large quantities in rural areas where cattle are used for a
variety of purposes.
• The organic materials
are converted into gas and organic fertilizer under microbial reactions.
• It is a renewable
natural gas.
• It provides reliable,
clean and cheap energy.
• It has high calorific
value.
• Creating a bio gas
system for a rural home is much simple.
• This system produces
methane gas which flows through a PVC pipe to the home where we can turn it on
when we need to use it.
• It also produces
manure that is free of pathogens which farmers can use as fertilizer.
• People need not
collect large amounts of fire wood and the emission of smoke from burning fire
wood is also reduced.
• A bio gas system can
replace approximately the related 4 tons of annual green house gas emission
according to world wild life fund.
• Using the biogas
resource materials available in our daily life when used as a fuel source reduces
the amount of methane released into the atmosphere.
• Thus turning the waste
into biogas could solve both the energy problem and the sanitation problem.
• Once people do have
biogas systems in their homes they can live healthier and comfortable while also
reducing their impacts on the environment.,
• So Biogas plants are
more often built in rural areas.
19. When does antibiotic resistance develop?
• Antibiotic resistance
occurs when bacteria develop the ability to defeat the during designed to kill
or inhibit their growth.
• Now a days, it is one
of the most acute threat to public health.
• It may be due to
misuse and overuse of antibiotics also due to poor infection prevention
control.
• Antibiotics prescribed
by a certified health professional alone should be used.
• Narrow spectrum
antibiotics are preferred over broad spectrum antibiotics.
• They accurately target
specific pathogens and are less likely to cause resistance.
• When the bacteria
become resistant antibiotics cannot fight against them and the bacteria
multiply.
• "Superbug"
is a term used to describe strains of bacteria that are resistant to the
majority of antibiotics commonly used today.
20. What is the key difference between primary and secondary sewage treatment?
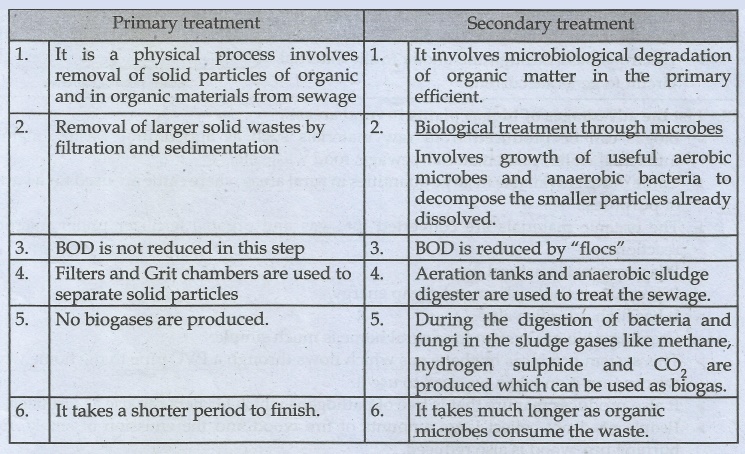
Primary treatment
1. It is a physical
process involves removal of solid particles of organic and in organic materials
from sewage
2. Removal of larger
solid wastes by filtration and sedimentation
3. BOD is not reduced
in this step
4. Filters and Grit
chambers are used to separate solid particles
5. No biogases are
produced.
6. It takes a shorter
period to finish.
Secondary treatment
1. It involves
microbiological degradation of organic matter in the primary efficient.
2. Biological
treatment through microbes
Involves growth of
useful aerobic microbes and anaerobic bacteria to decompose the smaller
particles already dissolved.
3. BOD is reduced by
"flocs"
4. Aeration tanks and
anaerobic sludge digester are used to treat the sewage.
5. During the
digestion of bacteria and fungi in the sludge gases like methane, hydrogen
sulphide and CO2 are produced which can be used as biogas.
6. It takes much
longer as organic microbes consume the waste.
Extra One mark Questions and Answers
1. When domestic sewage mixes with river water
a) Small animals like rat will die after drinking river water
b) The increased microbial activity releases micronutrients such as iron.
c) The increased microbial activity uses up dissolved oxygen.
d) The river water is still suitable for drinking as impurities are only about 0.1 per cent
2. Select the correct statement from the following.
a) Biogas is produced by the activity of aerobic bacteria on animal waste.
b) Methanobacterium is an aerobic bacterium found in rumen of cattle.
c) Biogas, commonly called gober gas, is pure methane.
d) Activated sludge-sediment in settlement tank of sewage treatment plant is a right source of aerobic bacteria.
3. Read the following four statements (A to D):
A) Colostrums is recommended for the new born because it is rich in antigen.
B) Chikungunya is caused by a gram negative bacterium.
C) Tissue culture has proved useful in obtaining virus-free plants.
D) Beer is manufactured by distillation of fermented grape juice
How many of the above statements are wrong?
a) Three
b) Four
c) One
d) Two
4. Which of the following are likely to be present in deep sea water?
a) Archaebacteria
b) Eubacteria
c) Blue – green algae
d) Saprophytic fungi
5. During sewage treatment, biogas are produced which includes
a) Methane, hydrogen sulphide, carbon dioxide
b) Methane, oxygen, hydrogen sulphide
c) Hydrogen sulphide, methane, sulphur dioxide
d) Hydrogen sulphide, nitrogen, methane
6. What gases are produced in anaerobic sludge digesters?
a) Methane and CO2 only
b) Methane, hydrogen sulphide and CO2
c) Methane, hydrogen sulphide and O2
d) Hydrogen sulphide and CO2
e) Consumption of organic matter in the water is higher by the microbes
7. Match the following list of microbes and their importance:
a)Saccharomyces cerevisiae (i)Production of immunosuppressive agents
b)Monasus purpureus (ii)Ripening of Swiss cheese
c)Trichoderma polysporum (iii)Commercial production of ethanol
d)Propionibacterium shermanii (iv)Production of blood- cholesterol lowering agents.
a) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
b) (iv) (ii) (i) (iii)
c) (iii) (i) (iv) (ii)
d) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
8. Which of the following is wrongly matched in the given table?
(a) Microbe: Trichoderma polysporum, Product: Cyclosporin A , Application: Immunosuppressive drug
(b) Microbe:Monascus purpureus, Product: Statins, Application: Lowering of blood cholesterol
(c) Microbe:Streptococcus, Product: Sterptockinase , Application: Removal of clot from blood vessel
(d) Microbe: Clostridium, Product: butylicum Lipase , Application: Removal of oil stains
9. Match Column – I with Column – II and select the correct options using the codes given 9.below:
Column I :
A.Citric acid
B.Cyclosporin A
C.Statins
D.Butyric acid
Column II :
1. Trichoderma
2. Clostridium
3. Aspergillus
4. Monoscus
a) A:3, B:1, C:4, D:2
b) A:1, B:4, C:2, D:3
c) A:3, B:4, C:1, D:2
d) A:3, B:1, C:2, D:4
Related Topics