Zoology - Microbes as bio control agents and biofertilisers | 12th Zoology : Chapter 9 : Microbes in Human Welfare
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 9 : Microbes in Human Welfare
Microbes as bio control agents and biofertilisers
Microbes as bio
control agents and biofertilisers
Large scale application of chemical insecticides and pesticides have a
deleterious effect on the health of human beings and pollute our environment.
Biocontrol is a method of controlling pest by use of
microbes such as fungi, bacteria, viruses or by naturally occurring substances
derived from plants and animals.
The use of a
microbes or other biological agents to control a specific pest is called a biopesticide.
Biopesticides are used to control insect pests.
The lady bird beetle and dragonflies are useful to control aphids and mosquito
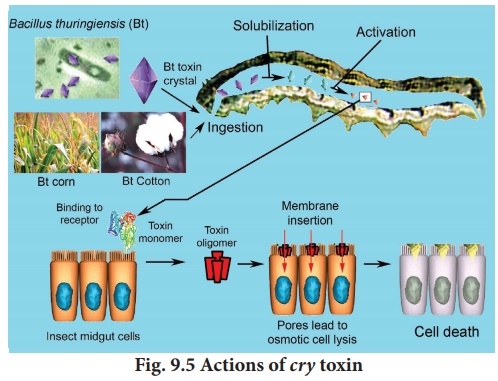
larvae respectively. soil dwelling bacterium which is commonly used as a
biopesticide and contains a toxin called cry toxin (Fig. 9.5). Scientists have
introduced this toxin producing genes into plants and have raised genetically
engineered insect resistant plants. E.g. Bt-cotton.
During sporulation Bacillus thuringiensis
produces crystal proteins called Delta-endotoxin which is encoded by cry genes.
Delta-endotoxins have specific activities against the insects of the orders
Lepidoptera, Diptera, Coleoptera and Hymenoptera. When the insects ingest the
toxin crystals their alkaline digestive tract denatures the insoluble crystals
making them soluble. The cry toxin then gets inserted
into the gut cell membrance and paralyzes the digestive tract. The insect then
stops eating and starves to death.
Weedicides are substances, which destroy weeds
withoutharming the useful plants. Bioweedicides are compounds and
secondary metabolites derived from microbes such as fungi, bacteria or
protozoa. The first bioherbicide developed in 1981 was a Mycoheribicide
derived from the fungus Phytophthora
palmivora. It controls
the growth of strangler vine in citrus crops. Trichoderma species are
free living fungi that are very common in the root ecosystem. They are
effective biocontrol agents for several plant pathogens. Buculoviruses are
pathogens that
The genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus
is used as a biocontrol agent. These viruses are species specific
and have narrow spectrum insecticidal applications.
Biofertilisers
Biofertilisers are formulation of living
microorganisms that enrich the nutrient quality of the soil. They increase
physico – chemical properties of soils such as soil structure, texture, water
holding capacity, cation exchange capacity and pH by providing several
nutrients and sufficient organic matter. The main sources of biofertilisers are
bacteria, fungi and cyanobacteria. Rhizobium is a classical example for
symbiotic nitrogen fixing bacteria. This bacterium infects the root nodules of
leguminous plants and fixes atmospheric nitrogen into organic forms. Azospirillum
and Azotobacter are free living bacteria that fix atmospheric nitrogen
and enrich the nitrogen content of soil.
A symbiotic association between a fungus and the
roots of the plants is called mycorrhiza. The fungal symbiont in these
associations absorbs the phosphorus from soil and transfers to the plant.
Plants having such association show other benefits such as resistance to
root-borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity, drought, enhances plant growth and
developments. For example, many members of the genus Glomus form
mycorrhiza. Cyanobacteria (or) blue green algae (BGA) are prokaryotic
free-living organisms which can fix nitrogen. Oscillatoria, Nostoc,
Anabaena, Tolypothrix are well known nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria.
Their importance is realized in the water logged paddy fields where Cyanobacteria
multiply and fix molecular nitrogen. Cyanobacteria secrete growth
promoting substances like indole-3-acetic acid, indole-3-butyric acid,
naphthalene acetic acid, amino acids, proteins, vitamins which promotes plant
growth and production.
Biofertilisers are commonly used in organic
farming methods. Organic farming is a technique, which involves cultivation of
plants and rearing of animals in natural ways. This process involves the use of
biological materials, avoiding synthetic substances to maintain soil fertility
and ecological balance thereby minimizing polluteon and wastage.
Key features of organic farming
·
Protecting soil quality using organic materials and encouraging
biological activity.
·
Indirect provision of crop nutrients using soil microorganisms.
·
Nitrogen fixation in soils using legumes.
·
Weed and pest control based on methods like crop rotation,
biological diversity, natural predators, organic manures and suitable chemical,
thermal and biological interventions.
Related Topics