Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Pharmacology
Metabolism - Pharmacokinetics
Metabolism
·
Water soluble: excreted unchanged
through the kidney
·
Lipid soluble: Can‟t be excreted
by kidneys (reabsorbed straight away) so conjugated or metabolised ® water
soluble ® excretion
·
Metabolism:
o May result in activation of a pro-drug, active metabolites or inactive
metabolites
o Phase 1: oxidation, reduction, hydrolysis
o Phase 2: conjugation, eg methylation, acetylation, glutamine, etc
o Occurs in mainly in the liver, also in the lung, kidney, blood, small
intestine, gut bacteria
·
1st pass metabolism: high > 70%,
e.g. lignocaine, GTN (no use taking them orally)
·
Examples of drug metabolic
reactions:
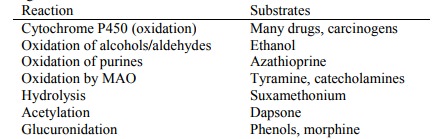
·
Factors affecting metabolism:
genetics, ethnicity, age, gender, pregnancy, liver disease, time of day,
environment, diet, malnutrition, alcohol, other drugs
Related Topics