Economics - Measurement of Elasticity of Demand | 11th Economics : Chapter 2 : Consumption Analysis
Chapter: 11th Economics : Chapter 2 : Consumption Analysis
Measurement of Elasticity of Demand
Measurement of Elasticity of Demand
There are three methods of measuring price elasticity of demand.
1. The Percentage Method
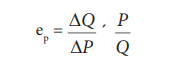
It is also known as ratio method, when we measure the ratio as:
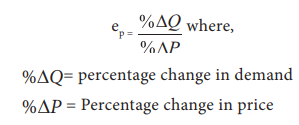
2. Total Outlay Method
Marshall suggested that the simplest way to decide whether demand is elastic or inelastic is to examine the change in total outlay of the consumer or total revenue of the firm.
Total Revenue = ( Price x Quantity Sold)
TR = (P x Q)
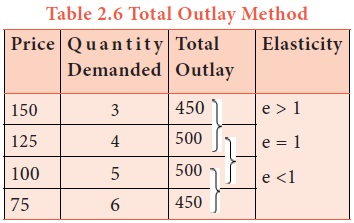
Where there is inverse relation between Price and Total Outlay, demand is elastic. Direct relation means inelastic. Elasticity is unity when Total Outlay is constant.
3. Point or Geometrical Elasticity
When the demand curve is a straight line, it is said to be linear. Graphically, the point elasticity of a linear demand curve is shown by the ratio of the segments of the line to the right and to the left of the particular point.
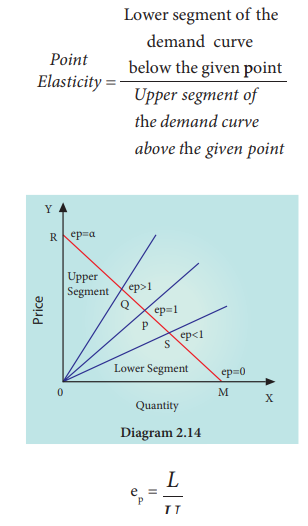
Where ‘ep’ stands for point elasticity, ‘L’ stands for the lower segment and ‘U’ for the upper segment.
Related Topics