Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio zoology Human Body higher secondary school
List of Plant Cell Organelles
Cell Organelles
The internal architecture of cells and central metabolic pathways are similar in all plants, animals and unicellular eukaryotic organisma (eg. Yeast) All eukaryotic cells contain a membrane bound nucleus and numerous other organelles in their cytosol. Unique proteins in the interior and membranes of each type of organelle largely determine it's specific functional characteristics.
A Typical plant cell contains the following organelles and parts:
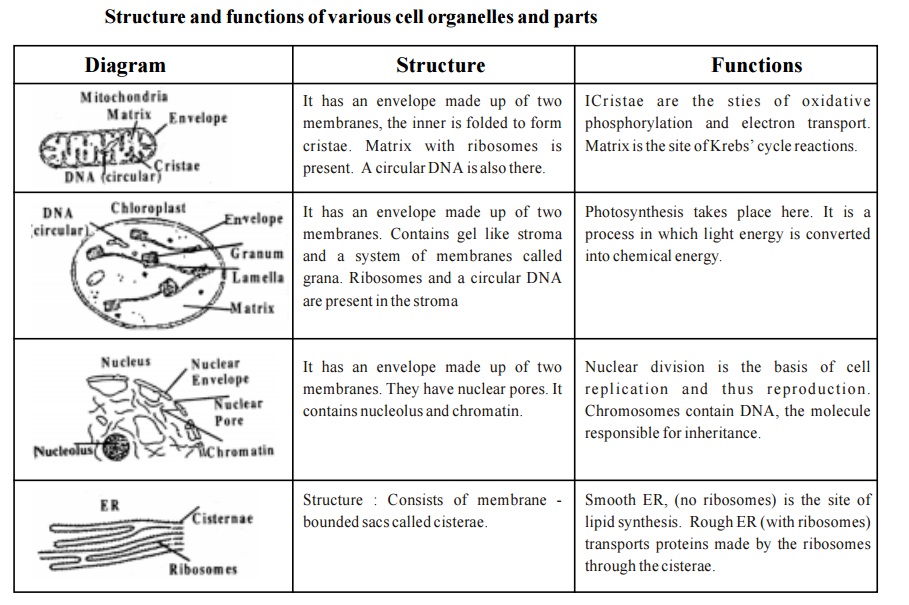
1. Mitochondria
They are bounded by two membranes with the inner one extensively folded. Enzymes in the inner mitochondrial membrane and central matrix carry out terminal stages of sugar and lipid oxidation coupled with ATP synthesis.
2. Chloroplasts
They are the sites of Photosynthesis. They are found only in plant cells. They are surrounded by an inner and outer membrane, a complex system of thylakoid membranes in their interior contains the pigments and enzymes that absorb light and produce ATP.
3. Nucleus
It is surrounded by an inner and outer membrane. These contain numerous pores through which materials pass between the nucleus and cytosol. The outer nuclear membrane is continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum. The nuclear membrane resembles the plasma membrane in its function. The nucleus mainly contains DNA organized into linear structures called chromosomes.
4. Endoplasmic reticulum
These are a network of inter connected membranes. Two types of Endoplasmic Reticulum are recognised. 1.Rough E.R 2.Smooth E.R
a. Rough ER
In this kind of ER, ribosomes are present on the surface. The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for protein synthesis in a cell. Ribosomes are sub organelles in which the amino acids are actually bound together to form proteins. There are spaces within the folds of ER membrane and they are known as Cisternae.
b. Smooth ER
This type of ER does not have ribosomes.
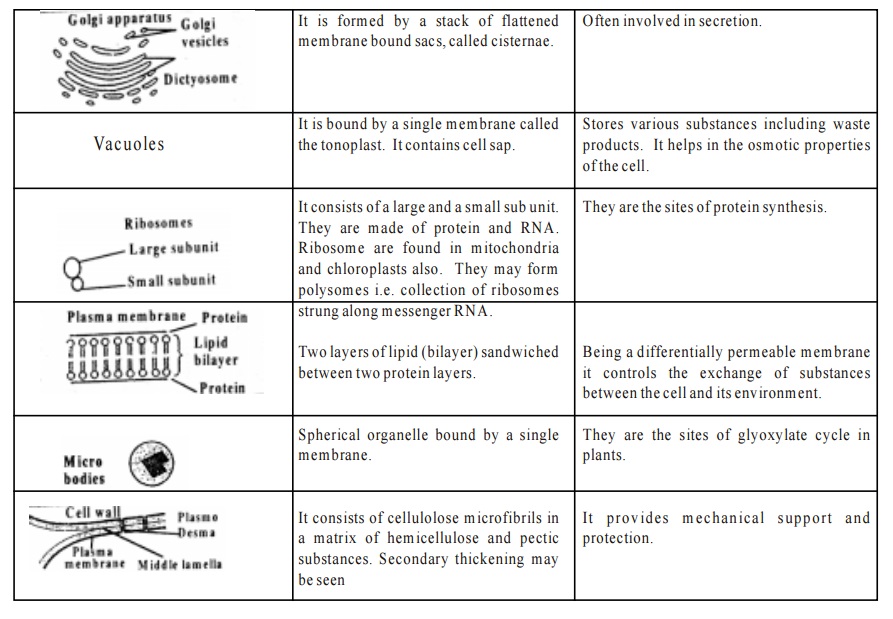
5. Golgi Body or Golgi Apparatus(G.A.) (Dictyosomes)
Golgi body is a series of flattened sacs usually curled at the edges. Proteins which were formed on ribosomes of rough endoplasmic reticulum are processed in G.A. After processing, the final product is discharged from the G.A. At this time the G.A. bulges and breaks away to form vesicle known as secretory vesicle. The vesicles move outward to the cell membrane and either insert their protein contents in the membrane or release these contents outside the cell.
6. Vacuoles
The Vacuoles form about 75% of the plant cell. In the vacuole the plant stores nutrients as well as toxic wastes. If pressure increases within the vacuole it can increase the size of the cell. In this case the cell will become swollen. If the pressure increases further the cell will get destroyed.
7. Ribosomes
Ribosomes are found in cells, both prokaryotic and eukaryotic except in mature sperm cells and RBCs. In eukaryotic cells they occur freely in the cytoplasm and also found attached to the outer surface of rough ER. Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis
8. Plasma Membrane
In all the cells the plasma membrane has several functions to perform. These include transporting nutrients into and metabolic wastes out of the cell. It is formed of lipids and proteins.
9. Microbodies
These are spherical organelles bound by a single membrane. They are the sites of glyoxylate cycle in plants.
10. Cell wall
The cells of all plants have cell wall. It has three parts. 1. Middle lamella 2. Primary wall 3. Secondary wall.It gives definite shape to the plant cell.
Structure and functions of various cell organelles and parts
Related Topics