Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Pharmaceutical Chemicals: Purity and Management
Limit Tests for Lead
Limit Tests for Lead
Theory : The offcial test is based on
the conversion of traces of lead salts present in the pharmaceutical substances to lead sulphide, which is
obtained in colloidal form by the addition of sodium sulphide in an alkaline
medium achieved by a fairly high concentration of ammonium acetate. The
reaction may be expressed as follows :
PbCl2 + Na2S → PbS (Dec) + 2NaCl
The brown colour, caused due to colloidal lead sulphide
in the test solution is compared with that produced from a known amount of
lead.
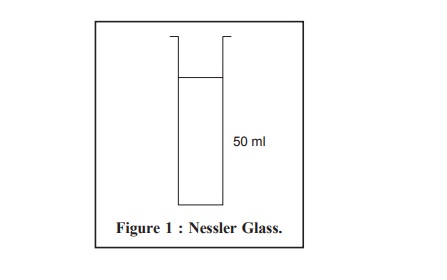
Equipment : Nessler Cylinders
(or Nessler Glasses) : According to the British Standard Specification No : 612, 966—a
pair of cylinders made of the same glass and having the same diameter with a graduation mark at the same height from the
base in both cylinders (Figure 1).
The final comparison is made
by viewing down through the solution against a light background.
Materials Required :
(i) Lead Nitrate Stock
Solution : Dissolve0.1598 g of lead nitrate in 100 ml DW to which has
been added 1 ml nitric acid, then dilute
with water to 1 Litre.
Note : The solution must be prepared
and stored in polyethylene or glass containers free from soluble lead salts.
(ii) Standard Lead Solution : On the day of
use, dilute 10.0 ml of lead nitrate stock solution with DW to 100.0 ml. Each ml
of standard lead solution contains the equivalent of 10 microgrammes of lead. A
control comparison solution prepared with 2.0 ml of standard lead solution
contains, when compared to a solution representing 1.0 g of the substance being
tested, the equivalent of 20 parts per million of lead.
(iii) Standard Solution : Into a 50 ml Nessler
Cylinder, pipette 2 ml of standard lead solution and dilute with DW to 25 ml.
Adjust with dilute acetic acid Sp. (IP)* or dilute ammonia solution Sp. (IP) to
a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with DW to about 35 ml and mix.
(iv) Test Solution : Into a 50 ml Nessler
Cylinder, place 25 ml of the solution prepared for the test as directed in the
individual monograh, dissolve and dilute with DW to 25 ml the specified
quantity of the substance being tested. Adjust with dilute acetic acid Sp. (IP)
or dilute ammonia solution Sp. to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with DW to
about 35 ml and mix.
Procedure : To each of the cylinders
containing the standard solution and test solution respectively, add l0 ml of freshly prepared hydrogen
sulphide solution, mix, dilute with water (DW) to 50 ml, allow to stand for 5
minutes and view downwards over a white surface, the colour produced in the
test solution is not darker than that produced in the standard solution.
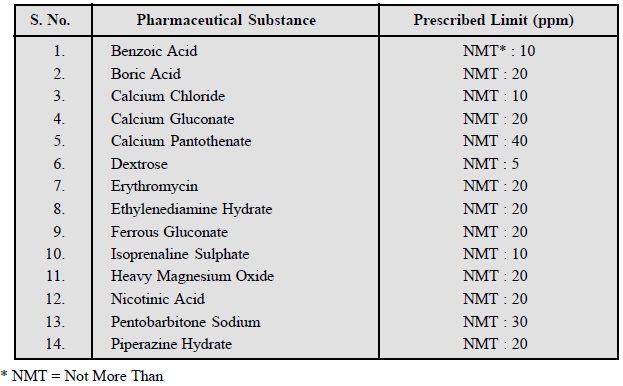
A few typical examples from the official
compendium are given below :
Related Topics