Atomic Structure | Chapter 12 | 8th Science - Laws of chemical combinations | 8th Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
Laws of chemical combinations
Laws of chemical combinations
By studying quantitative
measurements of many reactions, it was observed that the reactions taking place
between various substances are governed by certain laws. They are called as the
ŌĆśLaws of chemical combinationsŌĆÖ. They are given below.
1. Law of conservation of mass
2. Law of constant proportion
3. Law of multiple proportions
4. Gay LussacŌĆÖs law of gaseous volumes
In this lesson, we will study about
the first two laws. You will study about Law of multiple proportions and Gay
LussacŌĆÖs Law of gaseous volumes in standard IX.
1. Law of conservation
of mass
The law of conservation of mass
which relates the mass of the reactants and products during the chemical change
was stated by a French chemist Lavoisier
in 1774. It states that during any
chemical change, the total mass of the products is equal to the total mass of the reactants. In other
words the law of conservation of mass means that mass can neither be created
nor be destroyed during any chemical reaction. This law is also known as Law of indestructibility of mass.
Activity 5
Take some ice cubes in
an air tight container and note the weight of the container with ice cubes.
Wait for a while for the ice cubes to become water. It is a physical change
ie., ice cubes melt and they are converted into liquid. Now weigh the container
and compare the weight before and after the melting of ice cubes. It remains
the same. Hence it is proved that during a physical change, the total mass of
matter remains the same.
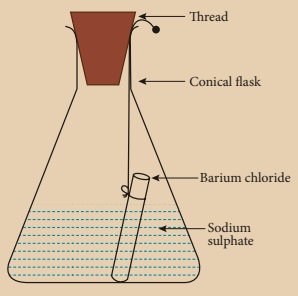
Activity 6
Prepare 5% of barium
chloride (5g of BaCl2 in 100 ml of water) and sodium sulphate
solutions separately. Take some solution of sodium sulphate in a conical flask
and some solution of barium chloride in a test tube. Hang the test tube in the
conical flask. Weigh the flask with its contents. Now mix the two solutions by
tilting and swirling the flask. Weigh the flask after the chemical reaction is
occurred. Record your observation. It can be seen that the weight of the flask
and the contents remainsthe same before and after the chemical change. Hence,
it is proved that during a chemical change, the total mass of matter remains
the same.
Consider the formation of ammonia (HaberŌĆÖs process) from the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen
N2 ŌĆā + 3H2ŌĆā ŌåÆŌĆā
ŌĆā 2NH3
28gŌĆā+ 6g ŌĆā ŌåÆŌĆā 34g
During HaberŌĆÖs process the total
mass of the reactant and the product are exactly same throughout the reaction.
Now, it is clear that mass is neither
created nor destroyed during physical or chemical change. Thus, law of
conservation of mass is proved.
2. Law of constant
proportions
Law of constant proportions was
proposed by the scientist Joseph Proust
in 1779. He states that in a pure
chemical compound the elements are always present in definite proportions by
mass. He observed all the compounds with two or more elements and noticed
that each of such compounds had the same elements in same proportions,
irrespective of where the compound came from or who prepared it. For example,
water obtained from different sources like rain, well, sea, and river will
always consist of the same two elements hydrogen and oxygen, in the ratio 1:8
by mass. Similarly, the mode of preparation of compounds may be different but
their composition will never change. It will be in a fixed ratio. Hence, this
law is also known as ŌĆśLaw of definite proportionsŌĆÖ.
Related Topics