Atomic Structure | Chapter 12 | 8th Science - Fundamental Particles | 8th Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
Fundamental Particles
Fundamental Particles
In 1878, Sir William Crookes, while
conducting an experiment using a discharge tube, found certain visible rays
travelling between two metal electrodes. These rays are known as CrookesŌĆÖ Rays
or Cathode Rays. The discharge tube used in the experiment is now referred as
Crookes tube or more popularly as Cathode Ray Tube (CRT).
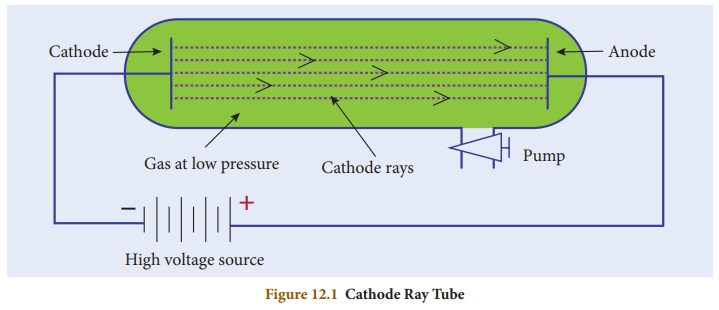
Cathode Ray Tube is a long glass
tube filled with gas and sealed at both the ends. It consists of two metal
plates (which act as electrodes) connected with high voltage. The electrode
which is connected to the negative terminal of the battery is called the
cathode (negative electrode). The electrode connected to the positive terminal
is called the anode (positive electrode). There is a side tube which is
connected to a pump. The pump is used to lower the pressure inside the discharge
tube.
Electricity, when passes
through air, removes the electrons from the gaseous atoms and produces cations.
This is called electrical discharge.
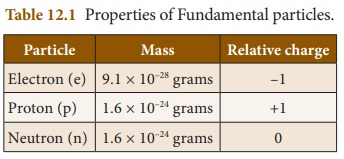
1. Discovery of Electrons
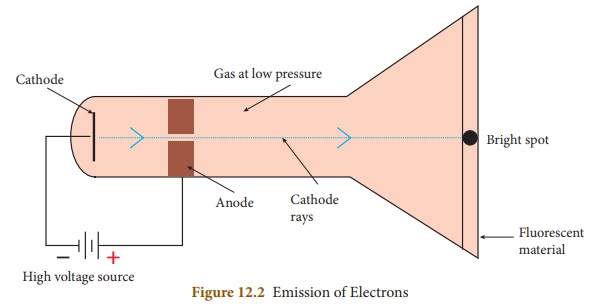
When a high electric voltage of
10,000 volts or more is applied to the electrode of a discharge tube containing
air or any gas at atmospheric pressure, no electricity flows through the air.
However, when the high voltage of 10,000 volts is applied to the electrodes of
discharge tube containing air or any gas at a very low pressure of about 0.001
mm of mercury, a greenish glow is observed on the walls of the discharge tube
behind anode. This observations clearly show some invisible ray coming from
thecathode. Hence, these rays are called cathode rays. Later, they were named
as electrons.
The fact that air is a
poor conductor of electricity is ablessing in disguise for us. Imagine what
would happen if air had been a good conductor of electricity. All of us would
have got electrocuted, when a minor spark was produced by accident.
Properties of Cathode rays
ŌĆó Cathode rays travel in straight
line from cathode towards anode.
ŌĆó Cathode rays are made up of material
particles which have mass and kinetic energy.
ŌĆó Cathode rays are deflected by both
electric and magnetic fields. They are negatively charged particles.
ŌĆó The nature of the cathode rays
does not depend on the nature of the gas filled inside the tube or the cathode
used.
In television tube
cathode rays are deflected by magnetic fields. A beam of cathode rays is
directed toward a coated screen on the front of thetube, where by varying the
magnetic field generated by electromagnetic coils, the beam traces a
luminescent image.
2. Discovery of Protons
The presence of positively charged
particles in the atom has been precisely predicted by Goldstein based on the
conception that the atom being electrically neutral in nature, should
necessarily possess positively charged particles to balance the negatively
charged electrons.
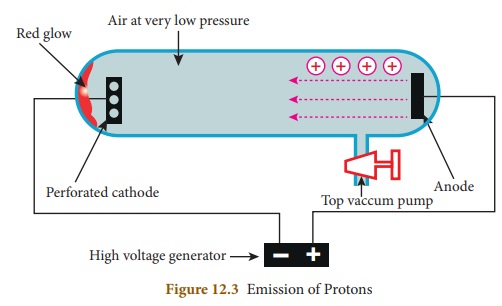
Goldstein repeated the cathode ray
experiment by using a perforated cathode. On applying a high voltage under low
pressure, he observed a faint red glow on the wall behind the cathode. Since
these rays originated from the anode, they were called anode rays or canal rays
or positive rays. Anode rays were found as a stream of positively charged
particles.
When invisible radiation
falls on materials like zinc sulphide, they emit a visible light (or glow).
These materials are called fluorescent materials.
Properties of Anode rays
ŌĆó Anode rays travel in straight
lines.
ŌĆó Anode rays are made up of material
particles.
ŌĆó Anode rays are deflected by
electric and magnetic fields. Since, they are deflected towards the negatively
charged plate, they consist of positively charged particles.
ŌĆó The properties of anode rays
depend upon the nature of the gas taken inside in the discharge tube.
ŌĆó The mass of the particle is the
same as the atomic mass of the gas taken inside the discharge tube.
When hydrogen gas wastaken
in a discharge tube, the positively charged particles obtained from the
hydrogen gas were called protons. Each of these protons are produced when one
electron is removed from one hydrogen atom. Thus, a proton can be defined as an
hydrogen ion (H+).
HŌĆā ŌåÆŌĆā H+ + eŌĆō
3. Discovery of Neutrons
At the time of J.J.Thomson, only two
fundamental particles (proton and electron) were known. In the year 1932, James
Chadwick discovered another fundamental particle, called neutron. But, the
proper position of these particles in an atom was not clear till Rutherford described
the structure of atom. You will study about RutherfordŌĆÖs atom model in your
higher classes.
Properties of Neutrons
ŌĆó Neutron carries no charge. It is a
neutral particle.
ŌĆó It has mass equal to that of a
proton, that is 1. 6 ├Ś 10ŌĆō24 grams.
Activity 1
Collect more
information about the properties of fundamental particles and prepare a chart.
Related Topics