Atomic Structure | Chapter 12 | 8th Science - Ions | 8th Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 12 : Atomic Structure
Ions
Ions
In an atom, the number of protons is
equal to the number of electrons and so the atom is electricallyneutral. But, during
chemical reactions atoms try to attain stable electronic configuration (duplet
or octet) either by gaining or losing one or more electrons according to
valency. When an atom gains an electron it has more number of electrons and
thus it carries negative charge. At the same time when an atom loses an
electron it has more number of protons and thus it carries positive charge.
These atoms which carry positive or negative charges are called ions. The
number of electrons gained or lost by an atom is shown as a superscript to the
right of its symbol. When an atom loses an electron, ŌĆś+ŌĆÖ sign is shown in the
superscript and ŌĆśŌĆōŌĆÖ sign is shown if an electron is gained by an atom. Some
times, two or more atoms of different elements collectively lose or gain
electrons to acquire positive or negative charge. Thus we can say, an atom or a
group of atoms when they either lose or gain electrons, get converted into ions
or radicals.
1. Types of Ions
Ions are classified into two types.
They are cations and anions.
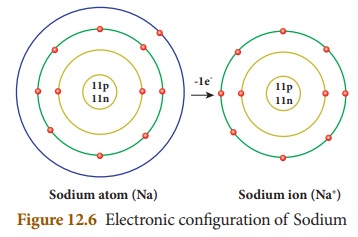
Cations
If an atom loses one or more
electrons during a chemical reaction, it will have more number of positive
charge on it. These are called cations (or) positive radicals. Sodium atom
loses one electron to attain stability and it becomes cation. Sodium ion is
represented as Na+.
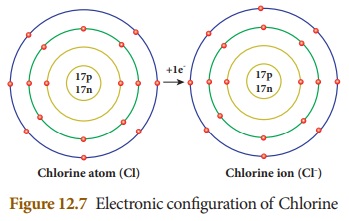
Anions
If an atom gains one or more
electrons during a chemical reaction, it will have more number of negative
charge on it. These are called anions or negative radicals. Chlorine atom
attains stable electronic configuration by gaining an electron. Thus, it
becomes anion. Chlorine ion is represented as ClŌĆō.
2. Different valent ions
During a chemical reaction, an atom
may gain or lose more than one electron. An ion or radical is classified as
monovalent, divalent, trivalent or tetravalent when the number of charges over
it is 1,2,3 or 4 respectively. Based on the charges carried by the ions, they
will have different valencies.
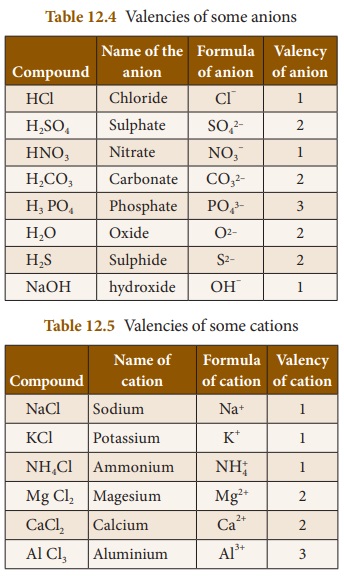
Valency
of Anions (negative radicals) and Cations (positive radicals)
The valency of an anion or cation is
a number which expresses the number of hydrogen atoms or any other monovalent
atoms (Na,K,ClŌĆ”.) which combine with them to give an appropriate compound. For
example, two hydrogen atoms combine with one sulphate ions (SO2-4)
to form sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
Activity 2
Classify the following
ions into monovalent, divalent and trivalent.
Ni2+, Fe3+,
Cu2+, Ba2+, Cs+, Zn2+, Cd2+,
Hg2+ Pb2+, Mn2+, Fe2+, Co2+,
Sr2+, Cr3+, Li+, Ca2+, Al3+
Answer:
Monovalent ions : Li+, Cs+
Divalent ions : Ni2+, Cu2+, Ba2+,
Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, Mn2+,
Fe2+, Co2+, Ca2+, Sr2 Trivalent
ions : Fe3+, Cr3+, Al3+ŌĆā
So, the valency of SO24-
is 2. One chlorine atom (Cl) combines with one ammonium ion (NH+4)
to form NH4Cl. So, the valency of NH+4 is 1. Valencies of
some anions and cations and their corresponding compounds are given below.
Related Topics