Chapter: Mobile Networks : Cellular Wireless Network
Introduction to Cellular Network
INTRODUCTION
TO CELLULAR NETWORK
Cellular
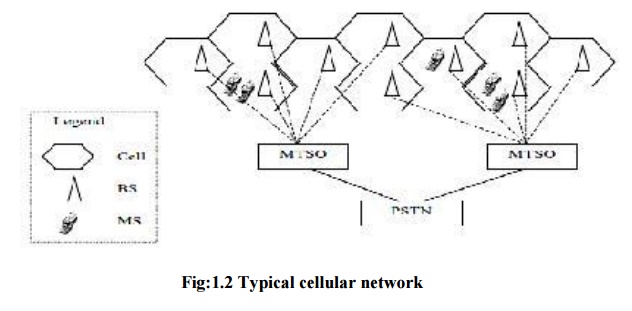
network or mobile network is a radio network scattered over land areas called cells. A cell is coverage of base
station connected to other stations via wire or fiber or wirelessly through
switching centre. Cellular network employ
Space division multiplexing (SDM) Cellular
network consist of
Cellular Base station.
Mobile telephone switching offices
(MTSO).
Mobile communication devices.
Base station: Each cell
is served by at least one fixed-location transceiver, known as a cell site or base station. It contains a radio transceiver
and controller and provides radio communication to mobile units located in
cell.
Mobile telephone switching
offices (MTSO): The MTSO links calls together using traditional copper, fiber optic, or microwave technology. It
also allows mobile communication devices in the cell to dial out and alerts
devices in the cell of incoming calls. The MTSO monitors the quality of the
communications signal and transfers the call to another base station which is
better suited to provide communication to the mobile device.
Mobile communication devices: The
mobile communication devices consist of hand
held phones, car phones, notebook computers, palm-top computers, and portable
data collection devices. When these mobile units communicate to the network,
they must register with the system by subscribing to a carrier service.
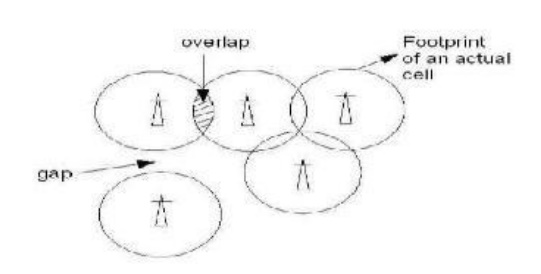
If the
cell size is preferred as circle, then a overlap and gap occurs. The cell which
gives the actual radio coverage is called footprint
of a cell. It might so happen that either there may be an overlap between
any two such side by side circles or there might be a gap between the coverage
areas of two adjacent circles. In a cellular radio system, a land region to be
supplied with radio service is divided into regular shaped cells, even though
hexagonal cells are conventional. A regular shape for cellular design over a
territory which can be served by 3 regular Polygons, namely, equilateral
triangle, square and regular hexagon, which can cover the entire area without
any overlap and gaps.
Along
with its regularity, a cell must be designed such that it is most reliable too,
i.e., it supports even the weakest mobile with occurs at the edges of the cell.
For any distance between the center and the farthest point in the cell from it,
a regular hexagon covers the maximum area. In a cellular network, each cell
uses a dissimilar set of frequencies from neighboring cells, to avoid
interference and provide assured bandwidth within each cell.
Cell
radius differs from tens of meters in buildings, and hundreds of meters in
cities, up to tens of kilometers in the landscape. The set of frequencies can
be reused in other cells, provided that the same frequencies are not reused in
adjacent nearby cells as that would cause co-channel interference.
Related Topics