Chapter: Mobile Networks : Cellular Wireless Network
GSM
GSM
INTRODUCTION
GSM was
formally known as Groupe Speciale Mobile (found in1982) and now it is
abbreviated as Global System for mobile communications. It is a standard set
developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) to
describe protocols for second generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by
mobile phones. It became the de facto global standard for mobile communications
with over 80% market share. The GSM standard was developed as a replacement for
first generation (1G) analog cellular networks, and originally described a
digital, circuit switched network optimized for full duplex voice telephony. Further improvements were
made when the 3GPP developed third generation (3G) UMTS standards followed by
fourth generation (4G) LTE Advanced standards.
The
primary goal of GSM was to provide a mobile phone system that allows user to
roam throughout Europe and provides voice services compatible to ISDN and other
PSTN systems. GSM has initially been deployed in Europe using 890-915MHz for
uplinks and 935-960 for downlinks.
GSM 1800:
Otherwise called as
Digital cellular Systems
DCS 1800
Uplink --
>
1710 to 1785 MHz
Downlink
1805 to
1880 MHz
GSM 1900
: Otherwise called as Personal Communication Service PLS 1900
Uplink --
> 1850 to 1910 MHz
Downlink
-- > 1930 to 1990 MHz
GSM 400:
Uplink -- > 450.4 to 478 MHz
Downlink
-- > 460 to 496 MHz
GSM Rail
is used in European Countries and railroad systems.
FEATURES OF GSM RAIL
It offers 19 exclusive channels for voice and data
traffic. The special features like emergency calls, voice group call service
etc. are available. Calls are prioritized. Mostly used to control the trains,
switches, signals, gates.
GSM SERVICES
GSM allows the integration of voice and
data services and also the internetworking with the existing network.
There are
three types of services offered by GSM
Bearer
Service
Tele
Service
SupplementaryService
REFERENCE MODEL FOR GSM SERVICES
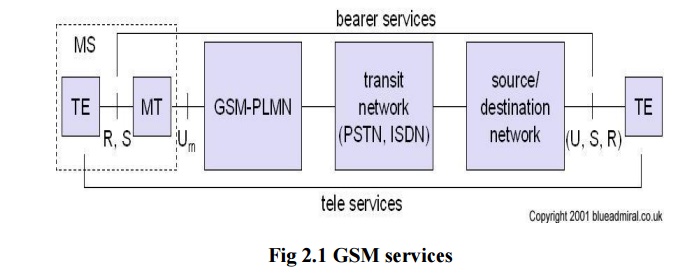
EXPLANATION:
A mobile station MS is connected to the GSM public
land mobile network PLMN via Um interface. PLMN is the infrastructure needed
for the GSM networks. This network is connected to transit
networks(eg.)PSTN,ISTN,etc. There will be additional network the source/
destinations network before another terminal TE is connected.
BEARER SERVICES:
Bearer Services comprises of all the services that
enables the transparent transmission of data between the interface to the
network. It permits transparent/non transparent , synchronous and asynchronous
data transmission.
ü
TRANSPARENT BEARER SERVICES:
This services uses the functions of physical layer
to transmit data. Data transmission has a constant delays and throughout if no
error occurs but not in real time. FEC is used to increase the transmission
quality. It does not try to recover the lost data in case of handover.
ü NON
TRANSPARENT BEARER SERVICES:
It uses the protocols of layers data link and
network to transmit data. These services uses transparent bearer service radio
link protocol (RLP). RLP has mechanisms of high level data link control HDLC.
It allows retransmission of erroneous data by using elective reject mechanisms.
TELE SERVCIES:
Tele services are application specific and need all
the 7 layers of ISO/OSI reference model. Services are specified end to end.
There tele services are voice oriented tele service. They are encrypted voice
transmission, message services and data communication with terminals from
PSTN/ISDN.
There are
some important services:
·
Telephony services: It has high quality digital
voice transmission.
·
Emergency Number: Mandatory service for all service
providers. Its of free of charge. This connection has the highest priority with
pre-emption.
·
Short Message Service: It is used fro simple
message transfer with the maximum of 160 characters. SMS does not use the
standard data channels of GSM uses the signaling channels. Sending andg receiving SMS is possible
during the data/ voice transmission.
·
Enhanced Message Service : It is used for large message size with 760 characters,
animated pictures, small images can be transmitted.
·
Multimedia Message Service : It is used to transmit large pictures of
GIF/ JPEG , video clips.
·
Group 3 fax : Fax data is transmitted as digital
data over analog telephone network using modem.
SUPPLEMENTARY SERVICES:
ü User Identification
Call Redirecting / Forwarding
Closed User Group
Multiparty
communication
GSM ARCHITECTURE
The
architecture of GSM comes in hierarchy, consisting of many entities, interfaces
and subsystems.
The GSM
system consist of three subsystems namely,
·
The
Radio Subsystems(RSS)
·
Network
and Switching
Subsystems(NSS)
·
Operation
Subsystem(OSS)
The
customer is able to notice few components of the network viz. Mobile Station
and Antenna of the Base Transceiver Station(BTS). Remaining entities are not
visible.
1.RADIO SUBSYSTEM:
As the name implies, the radio subsystem (RSS)
comprises all radio specific entities. i.e. the mobile stations(MS) and the
base station subsystem(BSS).
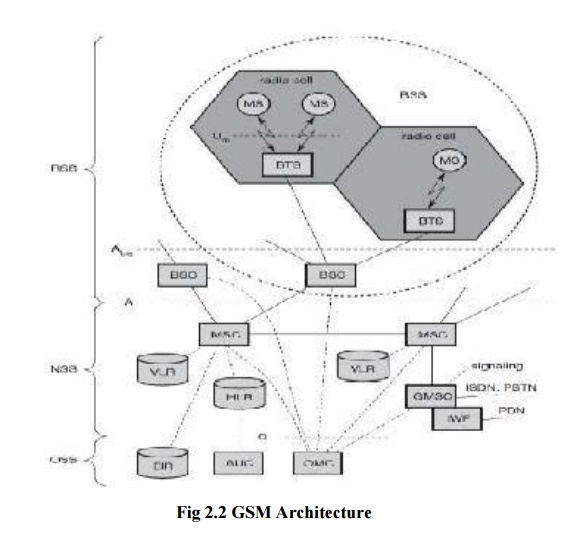
As they are in same frequency they
form a cell . The components of RSS are
Mobile
station
Base
Transceiver Station
Base
Station Subsystem
Base
Station Controller
MOBILE STATION: (MS)
MS has
all user equipment and software needed for mobile communications. It has user
independent hardware and software. Subscriber Identity Module (SIM) stores all
user specific data. Mobile Station can be identified as International Mobile
equipment identity (IMEI). The sim card Authentication key k, International
Mobile subscriber identity (IMSI). It also has Identifiers and tables. The current
location of MS is found using Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity(TMSI) . With
TMSI and Location Area Identification (LAI) the current location can be
identified.
BASE TRNSCEIVER STATION: (BTS)
BTS
contains the equipment for transmitting and receiving of radio signals,antennas
and equipment for encrypting and decrypting communications with the Base
station controller(BSC). A BTS is controlled by apparent BSC via the base
station control function(BSCF). The BCFis implemented as a discrete unit or even
incorporated in a TRX in compact base stations. The BCF provides an operations
and maintenance (O&M) connection to the Network Management System(NMS)and
manage operational state of each TRX as well as soft handling and alarm
collection.
The
function of BTS vary depending on the cellular technology used and cellula
telephone provider. There are vendors in which the BTS is a plain transceiver
which receives information from MS through Um(Air Interface) and then it
converts into TDM based interface, the Abis and it sends it towards the BSC. A
GSM cell can measure between some 100m and 35km depending on the environment.
BASE STATION SUBSYSTEM: (BSS)
The base
station subsystem is the section of traditional cellular telephone network
which is responsible for handling traffic and signaling between a mobile phone
and the network switching subsystem. The BSS carries out transcoding of speech
channels, allocation of radio channels to mobile phones, paging, quality
management of transmission and reception over the Air interface and many other
tasks related to the radio network.
BASE STATION CONTROLLER : (BSC)
The BSC
basically manages the BTSs. It reverses radio frequencies and handles the
handover from one BTS to another within BSS, and performs paging of the MS. The
BSC also multiplexes the radio channels onto the fixed network connections at A
interface.
b) NETWORK AND SWITCHING SUBSYSTEM:
This
network and switching subsystem is the heart of GSM. Their function are to
connect wireless network with standard public network, performs handover
between different BSS, localization (to locate the mobile station),Charging,
Accounting and roaming of users.The NSS contains the following switches and
databases.
MOBILE SERVIES SWITCHING CENTER(MSC):
MSC are
digital ISDN switches. It establishes connection qith other MSC and BSC via A
interfacet Gateway MSC connects to fixed networks(eg.) PSTN, ISDN. With the
help of Internet Working Functions, MSC can connect to public data Network PDN.
It handles all signaling needed for connection setup, connection release and
handover.
HOME LOCATION REGISTER : (HLR)
It is an
important database. It stores user relevant information and also has static
information and dynamic information.
Static Information:
Mobile
subscriber ISDN number is available. It has subscribed services for a
particular number. It is also an international mobile subscriber identity.
Dynamic Information :
It is a
current location area(LA) of MS. It consist of Mobile subscriber roaming number
(MSRN), VLR and MSC in it. When MS leaves the current LA, then the information
is updated in HLR. The Usage of the information is to locate the user.
VISITOR LOCATION REGISTER: (VLR)
The VLR
is associated to each MSC. It is a dynamic database. It stores all the information
needed for the MS currently in LA. If new MS comes to LA then the VLR is
responsible for copying the information needed from HLR.
c) OPERATION SUBSYSTEM :
The third
part of a GSM system is operation subsystem (OSS) which contains the necessary
functions for network operation and maintenance. The OSS possesses network
entities of its own and accesses other entities via SS7 signaling. The
following entities have been defined:
OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE CENTER (OMC):
The OMC
monitors and controls all other network entities via the O interface (SS7 with
X.25). Typical OMC management functions are traffic monitoring, status reports
of network entities, subscriber and security management, or accounting and
billing. OMCs use the concept of telecommunication management network (TMN) as
standardized by the ITU-T. Authentication centre (AuC): As the radio interface
and mobile stations are particularly vulnerable, a separate AuC has been
defined to protect user identity and data transmission. The AuC contains the algorithms
for authentication as well as the keys for encryption and generates the values
needed for user authentication in the HLR.
EQUIPMENT IDENTITY REGISTER (EIR):
The EIR
is a database for all IMEIs, i.e., it stores all device identifications registered
for this network. As MSs are mobile, they can be easily stolen. With a valid
SIM, anyone could use the stolen MS. The EIR has a blacklist of stolen (or
locked) devices. In theory an MS is useless as soon as the owner has reported a
theft. Unfortunately, the blacklists of different providers are not usually
synchronized and the illegal use of a device in another operator‟s network is
possible (the reader may speculate as to why this is the case). The EIR also
contains a list of valid IMEIs (white list), and a list of malfunctioning
devices (gray list).
Related Topics