Chapter: Mobile Networks : Cellular Wireless Network
Fundamental Concept In Cellular Technology
FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPT IN CELLULAR
TECHNOLOGY
The radio
spectrum contains many bands that are allocated and used for commercial,
personal, and military applications. Fifty (50) MHz of spectrum allocated to
cellular networks exists in the 824-849 MHz and the 869-894 MHz bands (Pagett,
1995). These bands are then further subdivided into 832 channels allowing many
users in the same area to simultaneously access the network. Types of cellular
network access are:
Advanced mobile phone system
(AMPS).
Time division multiple access
(TDMA).
Code division multiple access
(CDMA).
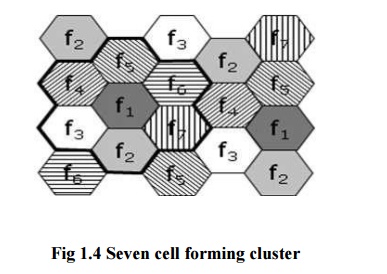
Cells are combined together to form
clusters. There are 2 types of formation of clusters
·
Three
cells forming a cluster.
·
Seven
cells forming a cluster.
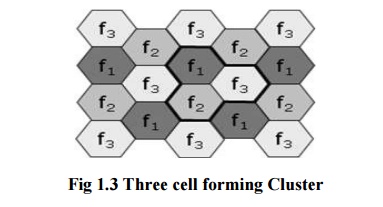
The set
of frequencies can be reused in other cells, provided that the same frequencies
are not reused in adjacent nearby cells as that would cause co-channel
interference. So never use same frequencies at same time with in the
interference range.
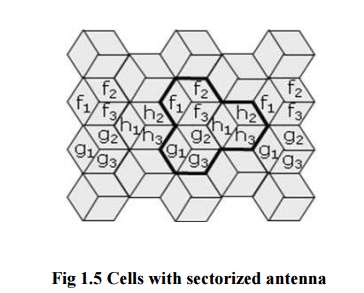
Sectorized
antenna is an another method to reduce the interference.
Channel Assignment Strategies:
Fixed frequency assignment.
Dynamic
frequency assignment.
Fixed frequency assignment:
If certain frequency are assigned to certain cells
then it is called fixed channel allocation (FCA). In fixed
channel assignment strategy each cell is
allocated a fixed number of voice channels. The problem related is
dissimilar traffic load occurs in dissimilar cell.
Dynamic frequency assignment:
If the frequency is borrowed and assigned to cells
then it is called dynamic channel
allocation(DCA). In dynamic channel assignment strategy channels are temporarily assigned for use in cells for the
duration of the call. As the frequencies are recurring, the transmission power
is restricted to stay away from interference with subsequent cell using the
same frequency.
If the
cell has heavy traffic and its neighboring cell has less load then the
frequencies can be borrowed and assigned to the cell having heavy load. This is
called borrowing channel
allocation(BCA).The idea of breathe is that the cell can cover bulky area
under light load and its size shrink under heavy load.CDM system faces a
problem of cell size depending upon load.
Handoff process:
Handoff is an important task in cellular network.
when a MS moves into another cell, while the conversation is still in progress,
the MSC automatically transfers the call to a new FDD channel without
disturbing the conversation. This process is called as handoff.
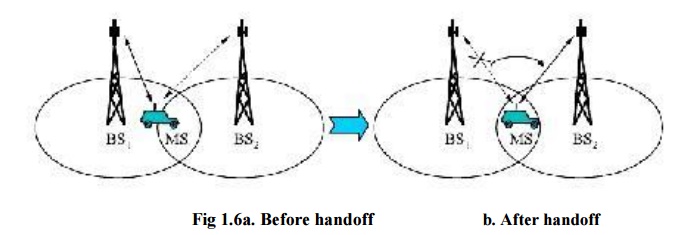
Handoff performance metrics:
The probability of a new call
being blocked is referred as call blocking Probability.
The probability that the call is
ended due to handoff is the call dropping probability.
The probability that a admitted
call is not dropped before ended is the call completion probability.
The probability that a handoff is
executed while the response conditions are inadequate is referred as
Probability of unsuccessful handoff.
The probability that a handoff
cannot be effectively completed is the handoff blocking probability.
The probability that a handoff
occur earlier than call termination is the handoff probability.
The
number of handoffs per unit time is referred as rate of handoff.
The
duration of moment during a handoff in which a mobile is not connected to
either base station is the Interruption duration.
Distance
the mobile moves from the point at which the handoff should occur to the point
at which it does occur is the handoff delay.
Handoff strategy used to determine instant of
handoff:
Relative signal strength
Prediction techniques
Relative signal strength with
hysteresis and threshold
Relative signal strength with
hysteresis
Relative signal strength with
threshold
Frequency reuse:
Frequency reuse, or, frequency planning, is a
technique of reusing frequencies and channels within a communication system to
improve capacity and spectral efficiency.
The characteristic of a cellular network is the
ability to re-use frequencies to increase both coverage and capacity. Adjacent
cells must use different frequencies to avoid interference, however there is no
difficult with two cells sufficiently far apart in use on the same frequency.
10 to 50 frequencies are assigned to each cell. The elements that determine
frequency reuse are the reuse distance and the reuse factor. The reuse
distance, D is calculated as
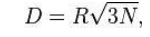
R - Cell radius and
N- number of cells per
cluster.
The rate
at which the same frequency can be used in the network is called frequency
reuse factor. It is 1/K
K - Number of
cells which cannot use the same frequencies for transmission.
Common
values for frequency reuse factor are 1/3, 1/4, 1/7, 1/9 and 1/12.Factors
limiting Frequency reuse are co-channel interference and adjacent channel
interference.
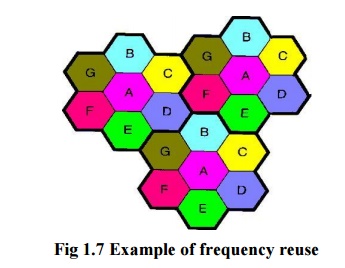
Each
Colour/letter uses the same frequency band.
Related Topics