Chapter: Mobile Networks : Cellular Wireless Network
GSM Protocol Suites
GSM PROTOCOL SUITES :
The
layers are
PHYSICAL LAYER:
The
physical layer handles all radio specific functions.
Functions :
1.
Creation of burst in any one of 5 format.
2. Multiplexing
burst into a TDMA frame.
3. Synchronization
with BTS.
4. Detection
of idle channel.
5. Channel
Quality measurement.
6. Channel
coding and error detection and correction.
The Um
interfaces use GMSK for modulation and perform encryption and decryption.
The
protocol architecture of GSM is shown below:
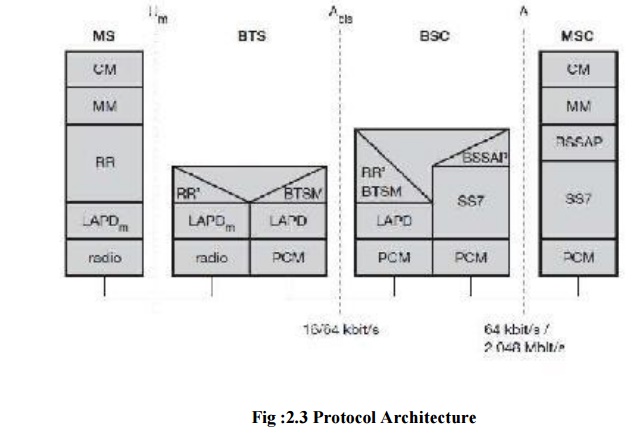
LAYER 2 :
For
signaling between entitites in GSM network this layer is used. The protocol
used is LAPDM. LAPD stands for link access procedure for D channel. LAPDM has
no buffers has to follow Um interface patterns. The functions of the layer are
namely:
1. Reliable data transfer
2. Reseqeuncing of data
3. Flow
control
LAYER 3 : NETWORK LAYER
The
network layer has sublayers. They are,
1. RADIO RESOURCE MANAGEMENT:
This is
the lowest sub layer and it‘s a part of RR and RR‘ is implemented by BSC. The
function of RR are Setup, Maintenance, Release of radio channels. RR directly
access the physical layer. It supports BTS management. The function of RR‘ are
supported by BSC via BSTM.
2. MOBILITY MANAGEMENT:
The main function of Mobility management are Registration,
Authentication, Identification, Location Updating, Providing TMSI, IMSI.
LAYER 4 : CALL MANAGEMENT:
This
layer contains three entities. They are Call control, SMS, Supplementary
services. Call control provides point to point connection between two terminals
and also used for call clearance, change of call parameters. SMS allows
messages transfer using control channels. The supplementary services discussed
already is to be reproduced here.
Related Topics