Chapter: Graphics and Multimedia : Output Primitives
Input Techniques
Input Techniques
INPUT OF GRAPHICAL DATA
Two possible ways to see
input devices:
•
as a physical device – keyboard, mouse, trackball, etc.
•
as a logical device – from a programmer perspective – with
specified functionality, in graphics more complex
•
the separation of physical and logical levels enable us to make
programs more flexible, independent from the actual physical device
Physical input devices:
pointing device – allows to indicate position
& send signals/interrupts to the computer – relative/absolute positioning
• keyboard
device – almost
physical
keyboard – returns
character
codes to a program
Absolute positioning:
• data
tablets
• light
pen
• joystick
– variable-sensitivity
device
& haptic device
• spaceball
– up-down, left-right,
front-back
& 3 independent
twists
Logical Input Devices
Some APIs (PHIGS, GKS, Direct
xx) supports 6 classes of logical input devices – OpenGL does not take this
approach
•
Two older APIs (GKS, PHIGS) defined six types of logical input
Locator: return a position
Pick: return ID of an object
Keyboard: return strings of characters
Stroke: return array of positions
Valuator: return floating point number
Choice: return one of n items
Input Modes
•
Input devices contain a trigger
which can be used to send a signal to the operating system
Button
on mouse
Pressing
or releasing a key
•
When triggered, input devices return information (their measure) to the system
Mouse
returns position information
Keyboard
returns ASCII code
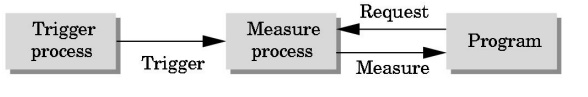
Request Mode
•
Input provided to program only when user triggers the device
•
Typical of keyboard input
Can
erase (backspace), edit, correct until enter (return) key (the trigger) is
depressed
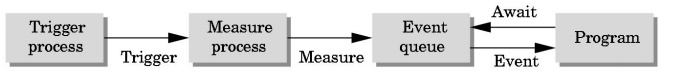
Event Mode
•
Most systems have more than one input device, each of which can be
triggered at an arbitrary time by a user
•
Each trigger generates an event
whose measure is put in an event queue
which can be examined by the user program
Event Types
•
Window: resize, expose, iconify
•
Mouse: click one or more buttons
•
Motion: move mouse
•
Keyboard: press or release a key
•
Idle: nonevent
Define what should be done if
no other event is in queue
Related Topics