Chapter: Design of Electrical Machines : Transformers
Important Short Questions and Answers: Design of Electrical Machines - Transformers
TRANSFORMERS
1.
Define transformation ratio.
It
is defined as the ratio of secondary terminal voltage to primary terminal
voltage.
It is denoted by k.
K = Vs /Vp = Ts / Tp = Ip / Is
2.
Name the types of transformer.
Based
upon construction, the types are
Core type and
shell type transformer
Based
on applications,
the types are
Ø
Distribution
transformers
Ø
Power
transformers
Ø
Special
transformers
Ø
Instrument
transformers
Ø
Electronics
transformers
Based
on the type of connection,
the types are
Ø
Single
phase transformer
Ø
Three
phase transformer
Based
on the frequency range,
the types are
Ø
Power
frequency transformer
Ø
Audio
frequency transformer
Ø
UHF
transformers
Ø
Wide
band transformers
Ø
Narrow
band transformer
Ø
Pulse
transformer
Based
on the number of windings,
the types are
Ø
Auto
transformer
Ø
Two
winding transformer
3.
Define windows space factor or
window area constant.
It is defined as the ratio of the
are of copper in the window to the window area.
Kw
= Ac / Aw < 1
Ac is the area of copper in m2
Aw is the area of window in m2
4. Define iron space factor.
It is defined as the ratio of gross
core area to the area of the circumscribing circle.
Kis
= Agi / Ace < 1
Agi
is the gross core area in m2
Ace
is the area of circumscribing circle
in m2
5.
What is a function of a transformer?
Ø
It
increases or decreases the voltage at same frequency.
Ø
It
transforms energy from one winding to other winding at constant frequency.
Ø
It
is used in electronic circuits with rectifying units to convert ac to dc.
Ø
It
provides isolation between to electrical circuits.
6.
What is the function of transformer
oil?
Ø
It
provides cooling.
Ø
It
acts as insulation.
Ø
It
protects the paper from dirt and moisture.
7.
What is the cause of noise in
transformer?
Ø
Mechanical
forces developed during working
Ø
Loosening
of stampings in the core
Ø
Expansion
and contraction of oil level
8.
What are the properties of
transformer oil?
Ø
High
dielectric strength
Ø
High
resistivity and density
Ø
Low
viscosity
Ø
Low
impurity
Ø
Reasonable
cost and flash point
9.
Difference between core type and shell type transformer.
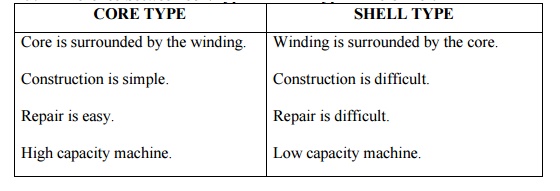
10.
Difference between distribution and power transformer.
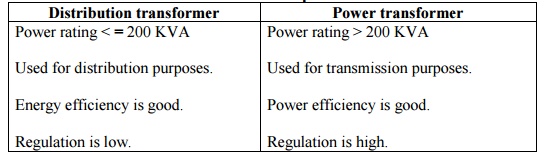
11.
Mention the important characteristics
desirable in transformer oil.
Ø
Electric
strength
Ø
Resistance
to emulsion
Ø
Viscosity
Ø
Purity
Ø
Flash
point
Ø
Sludge
formation
12.
Why is transformer oil used as
cooling medium?
When transformer oil is used as
coolant, the heat dissipation by convection is 10 times more than the
convection due to air specific heat dissipation by convection due to air = 8 W/
m2 – C.
Specific heat dissipation by
convection due to oil = 80 to 100 W/ m2 – C.
13.
Mention the factors to be considered for selecting the cooling method of a
transformer.
The choice of cooling method depends
on KVA rating of transformer, size, application and the site condition where it
has to be installed.
14.
List the different methods of
cooling of transformer.
Ø
Air
natural
Ø
Air
blast
Ø
Oil
natural
Ø
Oil
natural – air forced
Ø
Oil
natural water forced
Ø
Forced
circulation of oil
Ø
Oil
forced – air natural
Ø
Oil
forced – air forced
Ø
Oil
forced – water forced
15.
Give an expression for the heating time constant of transformer.

Where G is weight, h is specific
heat, λ is the specific heat dissipation.
16.
Why cooling tubes are are provided?
Cooling tubes are provided to
increase the heat dissipating area of the tank.
17.
Give the expression for magnetizing current.
The magnetizing current is given by
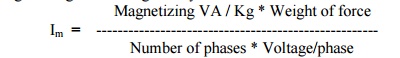
18.
Write the expression for temperature rise in plain walled tanks.
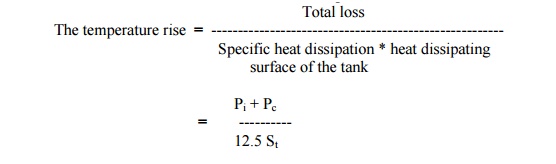
where Pi = iron loss ; Pc = copper loss ; St = Heat dissipating surface of
the tank
19.
Why plain walled tanks are not used for large output transformers?
The plain walled tanks are not used
for large output transformers as they are not sufficient to dissipate losses.
This is because volume and hence losses increase as cube of linear dimensions
while the dissipating surface increases as the square of linear dimensions.
Thus an increase in rating results in an increase in loss to be dissipated per
unit area giving a higher temperature rise.
20.
How is leakage reactance of winding estimated?
It is estimated by primarily
estimating the distribution of leakage flux and the resulting flux leakages of
the primary and the secondary windings. The distribution of the leakage flux
depends upon the geometrical configuration of the coils and the neighboring
iron masses and also on the permeability of the iron.
21.
Define stacking factor and give its typical value.

Its typical value is 0.9.
22.
Why stepped cores are used in transformers?
When stepped cores are used, the
diameters of the circumscribing circle is minimum for a given area of the core,
which helps in reducing the length of mean turn of the winding with consequent
reduction in both cost of copper and copper loss.
23.
What is the range of flux densities used in the design of a transformer?
When hot rolled silicon steel is
used,
Ø
Bm
= 1.1 to 1.4 Wb / m2 for distribution transformer
Ø
=
1.2 to 1.5 Wb / m2 for power transformer When cold rolled silicon
steel is used,
Ø
Bm
= 1.5 Wb / m2 for up to 132 KV transformer
Ø
=
1.6 Wb / m2 for 132 KV to 275 KV transformer
Ø
=
1.7 Wb / m2 for 275KV to 400 KV transformer
24.
Name the factors to be considered to
choose the type of winding for a core type transformer.
Ø
Current
density
Ø
Short
circuit current
Ø
Surge
voltage
Ø
Impedance
Ø
Temperature
rise
Ø
Transport
facilities
25.
Give typical values of core area
factor for various types of transformers.
Core area factor ( Kc )
for various transformers:
Ø
Square
core Kc = 0.45
Ø
Cruciform
core Kc = 0.56
Ø
Three
stepped core Kc = 0.6
Ø
Four
stepped core Kc = 0.62
26.
List the assumptions made for
calculation of leakage flux and leakage reactance.
Ø
The
primary and secondary windings have an equal axial length
Ø
The
flux paths are parallel to the windings along the axial height
Ø
Primary
winding mmf is equal to secondary winding mmf
Ø
Half
of the leakage flux in the duct links with each winding
Ø
The
length of the mean turn of the windings are equal
Ø
The
reluctance of flux path through yoke is negligible
27.
Define copper space factor.
For a transformer, it is the ratio
of conductor area and window area.
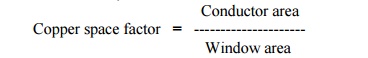
28.
Name the various types of cross section
used for core type transformer.
Ø
Square
Ø
Rectangle
Ø
Cruciform
and
Ø
Multi
stepped cores
29.
What is window space factor?
The window space factor is defined
as the ratio of copper area in window to total window
Window space factor = area. Copper area in window / Total
Window area
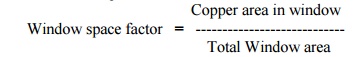
30.
How the area of window is calculated?
Are of the window (Aw) = Height of
window (Hw) * Width of window (Ww).
31.
Why are the cores of large transformers built up of circular cross-section?
The excessive leakage fluxes produced
during short circuit and over loads develop mechanical stresses in the coils.
These forces are radial in circular coils and there is no tendency for the coil
to change its shape. But in rectangular coils, these forces are perpendicular
and tend to deform the coil.
32.
Give the expression for window width that gives the maximum output.
The width of the window for maximum
output is
Ww = D - d = 0.7 d.
Where D = distance between adjacent
limbs d = width occupied by iron
33.
Give the expression for KVA rating of a single and three phase transformer.
Rating of a single phase & three
phase transformer in KVA is given as
Q
= 2.22 f Bm δ Kw Aw Ai * 10-3
Where f = frequency, Hz
Bm = maximum flux
density, Wb/m2
δ = current density, A/mm2
Kw = Window space factor
Aw = Window area, m2
Ai = Net core area, m2
34.
Mention different types of low
voltage windings.
Ø
Cylindrical
windings
Ø
Helical
winding
35.
What is the range of efficiency of a
transformer?
The efficiency will be in the range
of 94% to 99%.
36.
In transformers, why the low voltage
winding is placed near the core?
The winding & core are both made
of metals and so insulation has to be placed in between them. The thickness of
insulation depends on the voltage rating of the winding. In order to reduce the
insulation requirement the low voltage winding is placed near the core.
37.
What are the disadvantages of stepped cores?
With large number of steps a large
number of different sizes of laminations have to be used. This results in
higher labor charges for shearing and assembling different types of
laminations.
38.
What is the objective behind using
sheet steel stampings in the construction of electrical machines?
The stampings are used to reduce the
eddy current losses. The stampings are insulated by a thin coating of varnish,
hence when the stampings are stacked to form a core, the resistance for the
eddy current is very high.
39.
What type of steel is commonly used
for the core of transformer?
The hot rolled and cold rolled
silicon steel with 3 to 5%silicon are used for the laminations of the core of
transformers. The hot rolled silicon steel allows a maximum flux density of
1.45 Wb/m2 and the cold rolled silicon steel permits a maximum flux
density of 1.8 Wb/m2.
40.
What is tertiary winding?
Some three phase transformers may
have a third winding called tertiary winding apart from primary and secondary.
It is also called auxiliary winding or stabilizing winding.
The tertiary winding is provided in
a transformer for any one of the following reasons:
Ø
To
supply small additional load at a different voltage
Ø
To
give supply to phase compensating devices such as capacitors which work at
different voltage
Ø
To
limit short circuit current
Ø
To
indicate voltage in high voltage testing transformer
41.
How the tertiary winding is
connected? Why?
The tertiary winding is normally
connected in delta. When the tertiary is connected in delta, the unbalance in
the phase voltage during unsymmetrical faults in primary or secondary is
compensated by the circulating currents flowing in the closed delta.
42.
What are the salient features of
distribution transformer?
Ø
The
distribution transformers will have low iron loss and higher value of copper
loss.
Ø
The
capacity of transformers will be up to 500 KVA
Ø
The
transformers will have plain walled tanks are provided with cooling tubes or
radiators
Ø
The
leakage reactance and regulation will be low.
42.
What types of forces acts on the
coils of a transformer in the event of a short circuit on a transformer?
During short circuit conditions the
radial forces will be acting on the coil, which is due to short circuit
currents.
43.
What is the range of current
densities used in the design of transformer winding?
The choice of current density
depends on the allowable temperature rise, copper loss and method of cooling.
The range of current density for various types of transformers is given below:
Ø
δ
= 1.1 to 2.2 A/mm2 - For
distribution transformers
Ø
δ
= 1.1 to 2.2 A/mm2 - For
small power transformers with self oil cooling
Ø
δ
= 2.2 to 3.2 A/mm2 - For
large power transformers with self oil cooling
δ = 5.4 to 6.2 A/mm2 - For large power transformers
with forced circulation of oil
44.
How the heat dissipates in a transformer?
The heat dissipation in a
transformer occurs by conduction, convection and Radiation.
45.
How the leakage reactance of a transformer is reduced?
In transformers the leakage
reactance is reduced by interleaving the high voltage, and low voltage winding.
46.
How the magnetic curves are used for calculating the no-load current of a
transformer?
The B –H curve can be used to find
the mmf per metre for the flux densities in yoke and core. The loss curve can
be used to estimate the iron loss per Kg for the flux densities in yoke and
core.
47.
What is conservator?
A conservator is a small cylindrical
drum fitted just above the transformer main tank. It is used to allow the expansion
and contraction of oil without contact with surrounding atmosphere.
When conservator is fitted in a
transformer, the tank is fully filled with oil and the conservator is half
filled with oil.
48.
Why silica gel is used in breather?
The silica gel is used to absorb the
moisture when the air is drawn from atmosphere into the transformer.
49.
What are the merits and demerits of
using water for forced cooling of transformers?
The advantage in forced water
cooling is that large amount of heat can be removed quickly from the
transformer.
The disadvantage in forced water
cooling is that the water may leak into oil and the oil may be contaminated.
50.
In mines applications transformers
with oil cooling should not be used, why?
The oil used for transformer cooling
is inflammable. Hence leakage of cooling oil may create fore accidents in
mines. Therefore oil cooled transformers are not used in mines.
Related Topics