Chapter: Mechanical : Manufacturing Technology : Theory Of Metal Cutting
Important Questions and Answers: Theory of Metal Cutting
THEORY OF METAL CUTTING
1. Define Metal Cutting .
Metal cutting or machining is the
process of by removing unwanted material from a block of metal in the form of
chips.
2. What are the important
characteristics of materials used for cutting tools?
High
red hardness High wear
resistance
Low
frictional co- efficient
High
toughness
High
thermal conductivity.
3. How do you define tool life?
The time period between two
consecutive resharpening, with which the cuts the material effectively is
called as tool life.
4. What is tool signature?
The various angles of tools are
mentioned in a numerical number in particular order. That is known as tool
signature.
5. What is the effect of back rack
angle and mention the types?
Back rake angle of tool is increases the strength
of cutting tool and cutting action. It can be classified in to two types.
1. Negative
Rake angle.
2. Positive
rake angle.
6. Explain the nose radius?
Joining of side and end cutting
edges by means of small radius in order to increase the tool life and better
surface finish on the work piece.
7. What are all conditions for
using positive rake angle?
1. To
machine the work hardened materials.
2. To
machine low strength ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
3. To
machine long shaft of small diameters.
4. To
machine the metal blow recommended cutting speeds.
5. Using
small machine tools with low horsepower.
8. Define the orthogonal and
oblique cutting.
Orthogonal cutting: The
cutting edge of tool is perpendicular to the work piece axis. Oblique
cutting: The cutting edge is inclined at an acute angle with normal to the
cutting velocity vector is called oblique cutting process.
9. What are the favorable factors
for discontinuous chip formation?
Maching of brittle materials. Small
rake angle
Higher depth of cut Low
cutting speeds
Excess cutting fluid.
Cutting ductile materials with low speed and small rake angle
of the tool.
10. What are the favorable factors
for continuous chip formation?
Small rake angle Low
cutting speed
Strong adhesion between chip and tool face. Coarse feed
Insufficient cutting fluid. Large
uncut thickness.
11. Define machineability of metal.
Machine ability is defined as the
ease with which a material can be satisfactorily machined.
Life of the tool before tool failure or resharpening.
12. What is shear plane?
The material of work piece is
stressed beyond its yield point under the compressive force. This causes the
material to deform plastically and shear off. The plastic floe takes place in a
localized region is called shear plane.
13. What is chip and mention its
different types?
The sheared material begins to
along the cutting tool face in the form of small pieces is called chip. The
chips are mainly classified into three types.
a. Continuous
chip.
b. Discontinuous
chip.
c. Continuous
chip with built up edge.
14. Write the factors
affecting the tool life or Write the Taylor’s tool life equation.
Taylor’s equation VT n
=
C
i. Cutting
speed
ii. Feed and
Depth of cut. iii.Tool Geometry
iv.Tool
material
v. Type of
Cutting Fluid
vi.Work
material
vii.Rigidity
of the Machine tool.
15. Define “Side relief”
and “End relief” angle.
Side relief angle: It is the
angle between the portion of the side flank immediately below the side
cutting edge and a line perpendicular to the base of the tool, and measured at
right angle to the side flank.
End relief angle: It is the
angle between the portion of the end flank immediately below the end
cutting edge and a line perpendicular to the base of the tool, and measured at
right angle to the angle.
16. What are the importance of Nose
Radius?
Nose radius is favorable to long
tool life and good surface finish. A sharp point on the end of a tool is highly
stressed, Short lived and leaves a groove in the path of cut. There is an
improvement in surface finish and permissible cutting speed as nose radius is
increased from zero value.
17. What are the differences between orthogonal
cutting and oblique cutting?
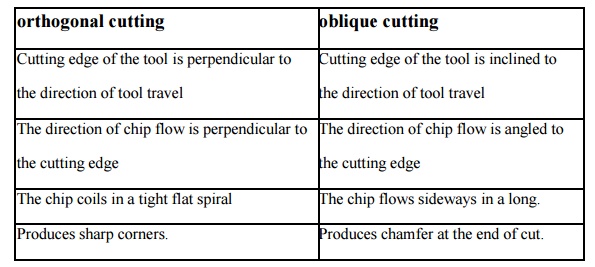
orthogonal cutting
Cutting edge of the tool is
perpendicular to the direction of tool travel
The direction of chip flow is
perpendicular to the cutting edge
The chip coils in a tight flat spiral
Produces sharp corners.
oblique cutting
Cutting edge of the tool is inclined
to the direction of tool travel
The direction of chip flow is angled
to the cutting edge
The chip flows sideways in a long.
Produces chamfer at the end of cut.
Related Topics