Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Geography earth space Higher secondary school College Notes
Human-made ecosystems : settlement systems
HUMAN-MADE ECOSYSTEMS : SETTLEMENT
SYSTEMS
When we observe a town from a high, vantage point at night, we see the
lights from the houses and the streets reflecting a pattern of the settlement.
The light from them gives an expression to the town form. When the light is
wider, it is likely the town is large. Where we see a few lights and often dim
light, it could be either a village or more open spaces and fields. Thus, the
light at night in a town gives us an idea of the shape and form of the town.
Such shapes and forms have been classified by the geographers. The forms of
settlements have been ordered on the basis of their functions. A settlement's
morphology depends upon the mountains, water bodies and such physical features
around it. We cannot see a specific type of settlements in all regions of the
world. They differ from place to place. For the differences that we see among
settlements, there are several causes. But before we analyse these causes, it
is necessary to understand the reasons for the settlements' forms.
Origin of Settlements
For the
nomads to transform themselves into permanent settlers, religion, culture,
army, politics and economics were the essential causes. First, to bury their dead
and to perform the rituals connected with it, the nomads created some permanent
locations. In course of time, these places had become places of religious or
ritualistic importance. And when the men moved about from place to place in
search for food, the aged, women and children stayed put in a locality and
produced things that were needed to run the families. Such localities then
became places of cultural importance. In order to protect the religious heads,
teachers, women and children who were now settled almost permanently, the
settlers built walls around such places. Army of soldiers were trained and
separate settlements for them were built. Hence, settlements of political and
military importance began to appear in the beginning of settlements.
It was necessary that a large number of settlers
had to go in search of food for those who lived in permanent settlements. It
was often difficult to gather adequate food for all settlers for all seasons.
In consequence to such needs, godowns and storages were built to store food
when it was available in good quantity. Such places over time became
economically important settlements. Over time, people had renounced the nomadic
way of life to become permanent settlers in given places. It was thus the
permanent settlements originated earlier.
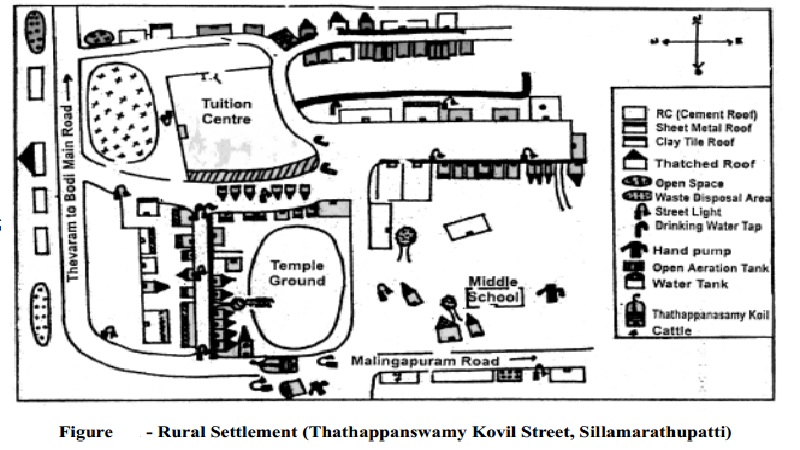
Settlements
Places where humans live are called the settlements. Each of them is a
reflection of the human intervention in, and impact on, the earth and its
environment. All settlements have locations. It is the characteristics of such
locations which provide for patterns of the settlements.
Site and Situation
The location of a settlement is defined by two
factors. They are: the site and the situation.
The settlements with similar sites and situation are similar in characteristics,
too. One of the purposes of settlement geography is to make possible an
understanding of the locational characteristics and distribution of
settlements. Hill slopes, summits, hillocks, river valleys, river beds ,
springs, ponds, road confluences and religious sites are some of the locations
conducive for settlements.
Site. The
location of a settlement is considered a site. If we understand the importance and amenities of a place, we could
understand the cause behind the setttlement. Such causes are helpful in finding
the origin of settlements. However, once the settlements are developed, they
may lose their significance. For instance, because there is water at the site,
a settlement could come about around a pond. A pond which was of some importance
earlier may lose its importance, with the growth of population, in course of
time. Nevertheless, such settlements do not relocate themselves, over time.
They may develop other sources of water. For example, new wells and ponds may
be created in response to developments.
Commercial Site. In subsistence agriculture, products were stored close to the fields. Hence, farmsteads were developed keeping the
fields as the site. In mechanised agriculture, however, there arose a need to
sell the surplus. Consequently, the bags of grains had to be taken to distant
places. The surpluses from several villages were collected at a central
village. Consequently, with an orderly commercial activity, the central village
turned itself into a commercial site. In the commercial villages, transport
lines were needed to transfer commodities to places far away. In response,
several commercial villages had emerged in areas of surplus agricultural
production. This was how settlements along the river banks, broad roads, at the
confluence of several roads and railway lines had developed with commerce as
their functional base.
Situation.
Situation of settlements refers to the landscapes and the environments around them. Apart from the landscapes, sunshine,
water, land hazards, social relations and the like are parts of the situation.
As the European countries are in the high latitude, temperate lands, the people
of these countries require temperature. Therefore, they build their houses
facing east, to take advantage of sunshine. In India, houses are mostly built
facing south as it is a monsoon land.
Similarly, water bodies are a cause for the
construction of houses. Several large cities of today have been in the vicinity
of water bodies. London on the Thames River is a good example. Conversely,
settlements are away and at high elevations in the riverine floodplains and
alluvial fans prone to inundations. In India, settlements developed on the
elevated lands in the midst of the valleys of the Yamuna and the Chambal
floodplains.
It is recognised that due to the unique characteristics of the site and
situation, settlements acquire special characteristics. Just as the natural
landscapes of hills, valleys and rivers, the cultural features developed by
human beings are also considered as significant among the landscapes.
Thus far, we have seen how site and situation
determine the settlement pattern. Based on the functions of settlements, they
may be divided into two basic types: rural settlement and urban settle-ment.
Related Topics