Chapter: Engineering Chemistry: Surface Chemistry and Catalysis
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis
Homogeneous
and Heterogeneous Catalysis
The phenomenon of catalysis can be divided into two
main types – homogeneous and heterogeneous catalysis, on the bases of the
number of phases present in the reaction mixture (A phase is a homogeneous part
of a system).
(a) Homogeneous Catalysis
When the
catalyst is present in the same phase as the reactants, the phenomenon is
called homogeneous catalysis. For
example :
(i) Nitric oxide catalyses the oxidation of sulphur
dioxide to sulphur trioxide in the lead chamber process.
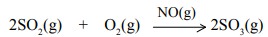
(ii)
Hydrogen ions catalyse the inversion
of cane sugar
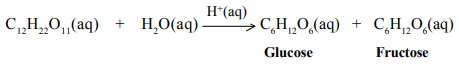
(b) Heterogeneous Catalysis
When the
catalyst is present in a phase other than that of reactants the phenomenon is
called heterogeneous catalysis. For
example :
(i) Iron (s) catalyses the formation of NH3 gas.
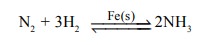
(ii) In contact process for the manufacture of
sulphuric acid, platinized asbestos is used as the catalyst

Related Topics