Surface Chemistry - Catalysis and Activation Energy | Engineering Chemistry: Surface Chemistry and Catalysis
Chapter: Engineering Chemistry: Surface Chemistry and Catalysis
Catalysis and Activation Energy
Catalysis
and Activation Energy
We have seen that a catalyst increases the rate of
a reaction. We explain it by considering the Fig 17.8.
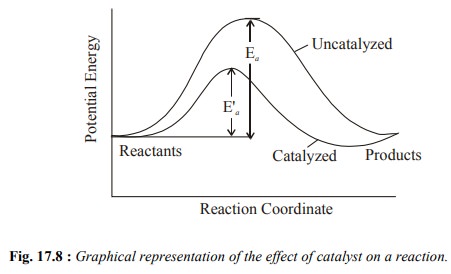
In this figure Ea is the activation
energy of uncatalysed reaction and E¢a is the
activation energy of the catalysed reaction. A catalyst lowers the activation
energy as you can see in the figure (E¢a <
Ea). The reduction in activation energy is achieved by providing an alternative
pathway of lower energy for the reaction.
You can also see in this figure that the relative
energies of reactants and products are not changed. The enthalpy change is the
same for the catalysed and uncatalysed reactions.
Related Topics