Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Virology, Virus: Arboviruses
Hepatitis A Virus: Properties of the Virus
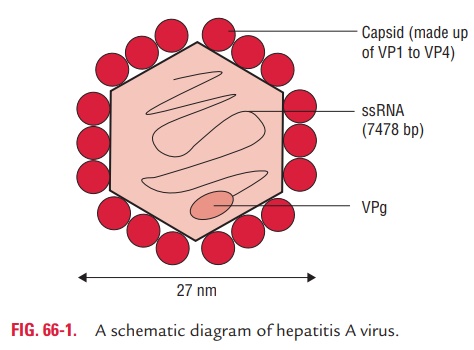
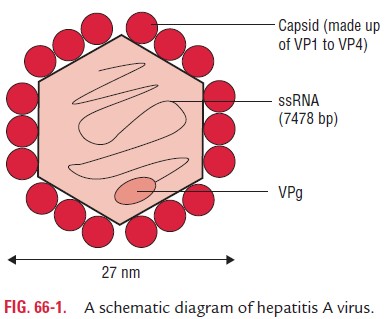
Hepatitis A Virus
Hepatitis A virus (HAV) is a picornavirus that is most commonly transmitted by fecaloral route. It has a relatively short
Properties of the Virus
◗ Morphology
Hepatitis A virus shows following morphological features:
· It is a typical enterovirus in the family Picornaviridae.
· It is a small, nonenveloped virus measuring 27 nm in diameter (Fig. 66-1).
· It has a single-stranded positive-sense RNA genome. The HAV was originally designated as enterovirus, but it is recognized as a prototype of Hepatovirus. The naked capsid is more stable than other picornaviruses to acid and other treatment.
◗ Viral replication
Hepatitis A virus replicates in the cytoplasm of the infected cell. It has a replicative cycle similar to that of other picornaviruses. Briefly, it combines specifically with a receptor expressed on liver cells and few other cells. However, unlike other picornavi-ruses, it is not cytolytic and is released by exocytosis.
◗ Antigenic and genomic properties
There is only one serotype in HAV. The virus does not show any antigenic relationship with hepatitis B or other hepatitis viruses.
◗ Other properties
Hepatitis A virus is highly resistant to environmental factors. It is stable at 60°C for 1 hour, 56°C for 30 minutes, and 4°C for weeks. It is stable to acidic pH, at pH 1. It is resistant to inactivation by lipid solvents, such as ether and chloroform, to action of detergents, and to drying.
The virus is inactivated by formalin (0.35%) at 37°C during a period of 24 hours and by treatment with peracetic acid (2%) for 4 hours and beta-propiolactone (0.25%) for 1 hour. It is also inac-tivated by exposure to ultraviolet radiation (2 mW/cm2/minute). The virus is inactivated by routine chlorine treatment of drink-ing water.
Virus Isolation and Animal Susceptibility
Hepatitis A is the only virus that can be grown in human and simian cell culture. However, it is difficult to grow routinely from feces of infected patients.
Related Topics