Chapter: 9th Social Science : Civics: Human Rights
Fundamental Rights in India
Fundamental Rights in India
Fundamental rights are
required for the all round development of a human being. They make the life of
people meaningful by giving them rights like speech and to live in an area of
their choice.
The fundamental rights are :
·
Right to Equality
·
Right to Freedom
·
Right against Exploitation
·
Right to Freedom of Conscience and Religion
·
Cultural and Educational Rights for minorities
·
Right to Constitutional Remedies
Right to Equality
It refers to equality
before law and equal protection of law. Prohibition or discrimination on the
grounds of religion, caste, races, gender or place of birth is offensive and
one can seek justice from court.

Right to Freedom
Six different types of
freedom are mentioned in the Constitution. They are:
a.
Freedom of speech and expression.
b.
Freedom to assemble peacefully without arms.
c.
Freedom to form associations and unions.
d.
Freedom to reside and settle in any part of India.
e.
Freedom to move freely throughout the territory of India.
f.
Freedom to practice any profession and carry on any occupation,
trade or business.
Right against Exploitation
It is against the law to
employ children below 14 years of age in mines, factories or other occupations.
Neither contractor nor an employer can force a worker to do a job against the
their will.

Right to Freedom of Conscience and Religion
This right gives the
citizens freedom to follow and practice a religion of their choice.

All citizens have the
freedom of conscience or ideas. The citizens also have the freedom to follow
their own ways for practicing any religion.
Cultural and Educational Rights
The Constitution gives
us the right to preserve, protect and promote culture. We have the right to
open schools, associations and societies to preserve and promote our tradition
and culture. Similarly a group of people may open a school for imparting
religious education to children. The government also promotes such activities
by giving grants. However, such institutions cannot deny admission to anyone
based on their caste, colour, creed or even religion.
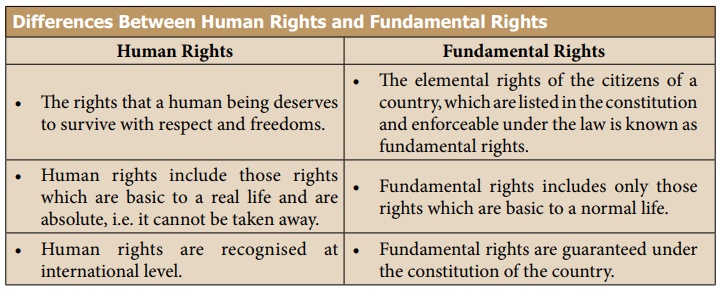
Human rights as declared
by the UN, suggest minimum standards of rights to be adopted by Government and
these serve more or less like Directive Principles.
Right to Constitutional Remedies
Fundamental Rights are
guaranteed by the Constitution. By this right, a person can adopt
Constitutional means and approach a court if he is denied the Fundamental
Rights. The court then issues orders which are called ‘Writs’ to the government
to restore the rights to the citizen. The Constitutional Remedies put to right
anything which may be wrong in terms of the Constitution. This right therefore
protects and safeguards all other rights.

Related Topics