Meaning, Definitions, Objectives and Fiscal Instruments - Fiscal Economics - Fiscal policy | 12th Economics : Chapter 9 : Fiscal Economics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 9 : Fiscal Economics
Fiscal policy
Fiscal policy
As an instrument of macro-economic policy, fiscal policy has been
very popular among modern governments. The growing importance of fiscal policy
was due to the Great Depression and the development of ‘New Economics’ by
Keynes.
1. Meaning of Fiscal Policy
In common parlance fiscal policy means the budgetary manipulations
affecting the macro economic variables – output, employment, saving, investment
etc.
2. Definitions
“The term fiscal policy refers to a policy under which the
Government uses its expenditure and revenue programmes to produce desirable
effects and avoid undesirable effects on the national income, production and
employment” – Arthur Smithies
“By fiscal policy is meant the use of public finance or
expenditure, taxes, borrowing and financial administration to further our
national economic objectives” – Buehler
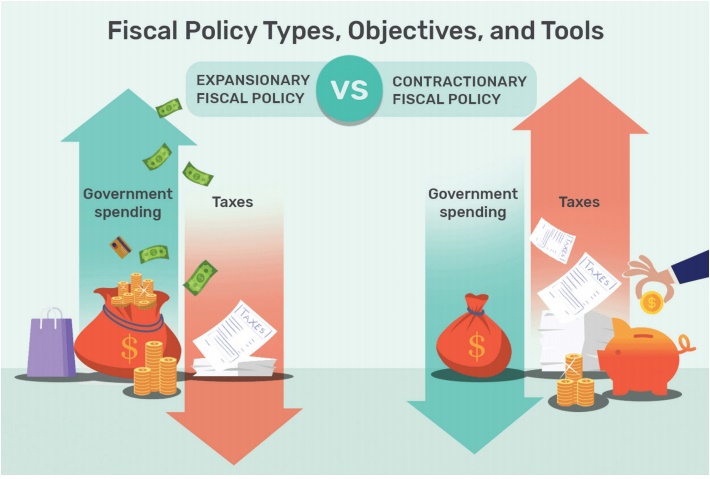
3. Fiscal Instruments
Fiscal Policy is implemented through fiscal instruments also
called ‘fiscal tools’ or fiscal levers: Government expenditure, taxation and
borrowing are the fiscal tools.
i) Taxation: Taxes transfer income from the people to the Government.
Taxes are either direct or indirect. An increase in tax reduces disposable
income. So taxation should be raised to control inflation. During depression,
taxes are to be reduced.
ii) Public Expenditure: Public expenditure raises wages and
salaries of the employees and thereby the aggregate demand for goods and
services. Hence public expenditure is raised to fight recession and reduced to
control inflation.
iii) Public debt: When Government borrows by floating a
loan, there is transfer of funds from the public to the Government. At the time
of interest payment and repayment of public debt, funds are transferred from
Government to public.
4. Objectives of Fiscal Policy:

The Fiscal Policy is useful to achieve the following objectives:
1. Full Employment
Full Employment is the common objective of fiscal policy in both
developed and developing countries. Public expenditure on social overheads help
to create employment opportunities. In India, public expenditure on rural
employment programmes like MGNREGS is aimed at employment generation.
2. Price Stability
Price instability is caused by mismatch between aggregate demand
and aggregate supply. Inflation is due to excess demand for goods. If excess
demand is caused by Government expenditure in excess of real output, the most
effective measure is to cut down public expenditure. Taxation of income is the
best measure if excess demand is due to private spending.
Taxation reduces disposable income and so aggregate demand.
To fight depression, the Government needs to increase its spending
and reduce taxation.
3. Economic Growth
Fiscal Policy is used to increase the productive capacity of the
economy. Tax is to be used as an instrument for encouraging investment. Tax
holidays and tax rebates for new industries stimulate investment. Public sector
investments are to be increased to fill the gap left by private investment.
When resource mobilization through tax measures is inadequate, the Government
resorts to borrowing both from internal and external sources to finance growth
projects.
4. Equitable distribution
Progressive rates in taxation help to reduce the gap between rich
and poor. Similarly progressive rates in public expenditure through welfare
schemes such as free education, noon meal for school children and subsidies
promote the living standard of poor people.
5. Exchange Stability
Fluctuations in international trade cause movements in exchange
rate. Tax concessions and subsidy to export oriented units help to boost
exports. Customs duties on import of non-essential items help to cut import
bill. The reduction in import duty on import of raw material and machinery
enables reduction in cost and make the exports competitive.
6. Capital formation
Capital formation is essential for rapid economic development. Tax
relief helps to increase disposable income, savings and thereby capital
formation. Government expenditure on infrastructure development like power and
transport encourages private investment.
7. Regional balance
Fiscal incentives for industries in the backward regions help to
narrow down regional imbalances. Public expenditure may be used to start
industrial estates so that industrial activity is stimulated in backward
regions.
Related Topics