Chapter: Programming and Data Structures : Sorting And Searching
Extendible Hashing
EXTENDIBLE HASHING:
When open address hashing or separate chaining
hashing in used ,collisions could causes several blocks to be examined during a
find even for a well distributed hashtable .Furtermore,when the table gets too
full, an extremely expensive rehashing steps must be performed,which require
O(N) disk accesses.
These
problem can be overcome by using
extendible hashing.
Extendible hashing, allows a find to be performed in
two disk accesses come.Insertion also requires few disk accesses.
Let us suppose,consider our data consist of several
six bit intergers.The root of the tree contains four pointers determied by the
leading two bits of the data.Ecah leaf has upto M=4 element.In each leaf the
first two bits are indentified, this is indicated by the number in parenthesis
.
D will be represent the
number of bits used by the root,also know as the directory.The number of
entries in the directory 2D.dl is the number of leading
bits that all the elements of some leaf L have in common .dL <
D.The extendible hashing scheme for this data is given below.
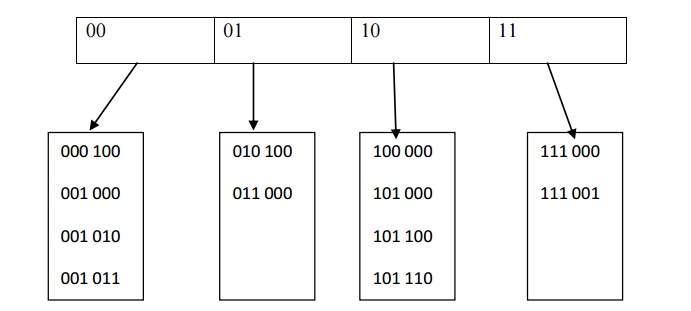
Suppose that we want to
insert the key 100100.This would go into the leaf,But as the third leaf is
already full there is no room.We thus split this leaf into two leaves,which are
now determined by the first three bit. Now the directory size is increased to 3.
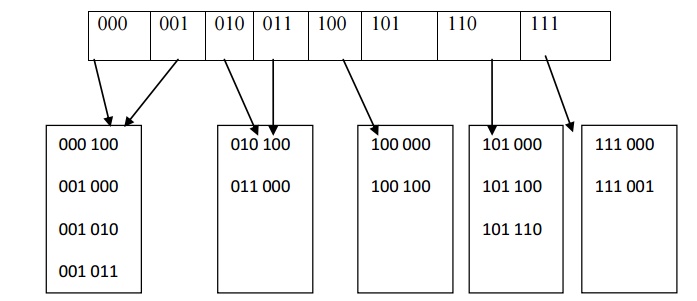
Similarly,if the key
000000 is inserted ,then the first leaf split generating two leaves with dL=3.The
000 and 001 pointers are updated
ADVANTAGE:
àProvides
quick access time for insert and find operation are large data bases.
DISADVANTAGES:
àThis
algorithm does not work if there are more then M duplicates.
àIf
the elements in a leaf occurs in more then D+1 leading bits ,several directory
split is possible the expected size of directory is O (Nl+l/M/M).
Related Topics