Chapter: The Diversity of Fishes: Biology, Evolution, and Ecology: Sensory systems
Equilibrium and balance - Fishes
Equilibrium and balance
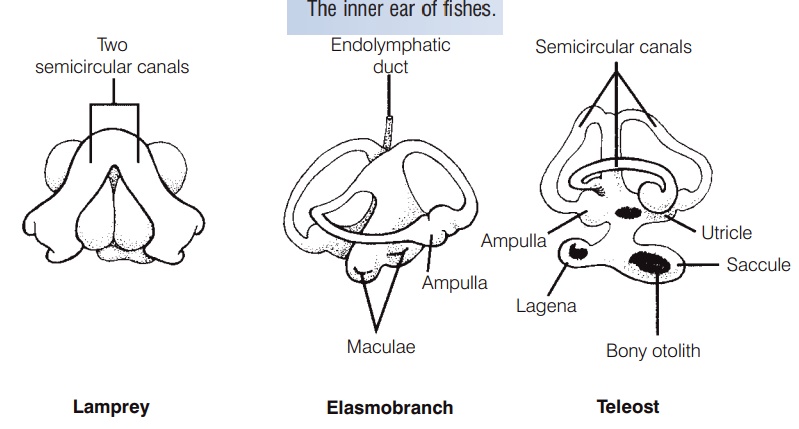
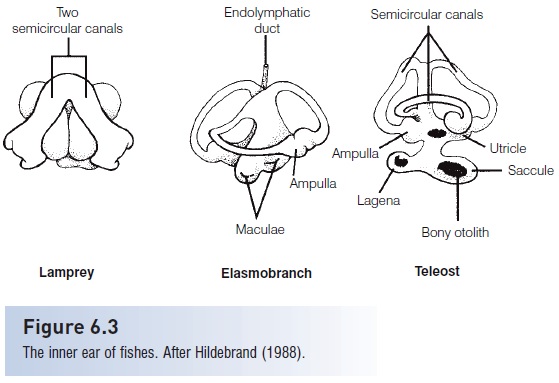
Hair cells also can detect movement of fluid or objects within organisms, and therefore play an important role in the ability of fishes to maintain their equilibrium and orientation within the water column (Schell art& Wubbels1998). Postural equilibrium and balance are maintained by the pars superior, a portion of a fish’s inner ear that, in jawed fishes, consists of three semicircular canals and an additional chamber known as the utricle (Fig. 6.3).Lampreys (Petromyzontidae) have only two semicircular canals, and hagfishes (Myxinidae) have one. The semicircular canals are filled with a fluid (endolymph) and have sensory hair cells in their terminal ampullae. Changes in acceleration or orientation set the endolymph in motion and cause displacement of a gelatinous cupula that encloses the cilia of the hair cells. Lateral displacement of the cilia results in changes in the fi ring rate of the sensory neurons innervating the hair cells, thereby signaling the fish’s brain about changes in acceleration or orientation. The utricle contains a solid deposit, or otolith (“ear stone”), the lapillus, which rests on a bed of sensory hair cells. The downward pull of gravity on the lapillus triggers impulses from the sensory cells and provides the fish with information regarding its vertical orientation in the water. The utricle works in coordination with the detection of light from above the fish by the retina of the eyes and together they help keep the fish upright in the water (the dorsal lightreflex). Goldfish with the utricle and semicircular canals removed on one side initially lost their ability to orient vertically, although this was often regained after several days (Ott & Platt 1988).
Related Topics