Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment of Respiratory Function
Endoscopic Procedures - Diagnostic Evaluation
ENDOSCOPIC PROCEDURES
Bronchoscopy
Bronchoscopy is
the direct inspection and examination of thelarynx, trachea, and bronchi
through either a flexible fiberoptic bronchoscope or a rigid bronchoscope. The
fiberoptic scope is used more frequently in current practice.
The
purposes of diagnostic bronchoscopy are: (1) to examine tissues or collect
secretions, (2) to determine the location and ex-tent of the pathologic process
and to obtain a tissue sample for di-agnosis (by biting or cutting forceps,
curettage, or brush biopsy),to determine if a tumor can be resected surgically,
and (4) to diagnose bleeding sites (source of hemoptysis).
Therapeutic
bronchoscopy is used to: (1) remove foreign bod-ies from the tracheobronchial
tree, (2) remove secretions ob-structing the tracheobronchial tree when the
patient cannot clear them, (3) treat postoperative atelectasis, and (4) destroy
and ex-cise lesions.
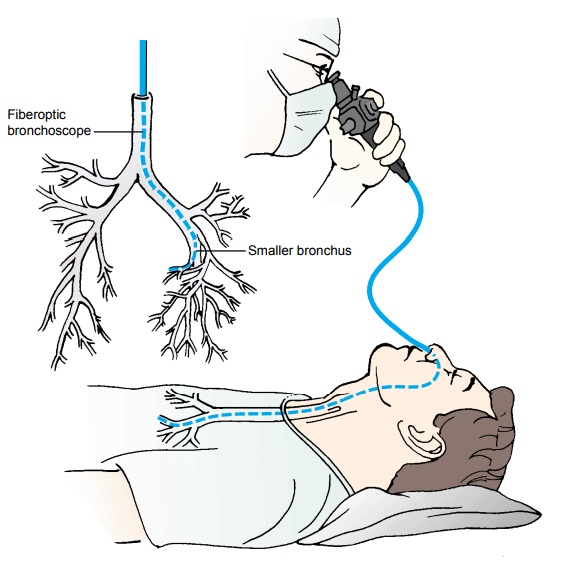
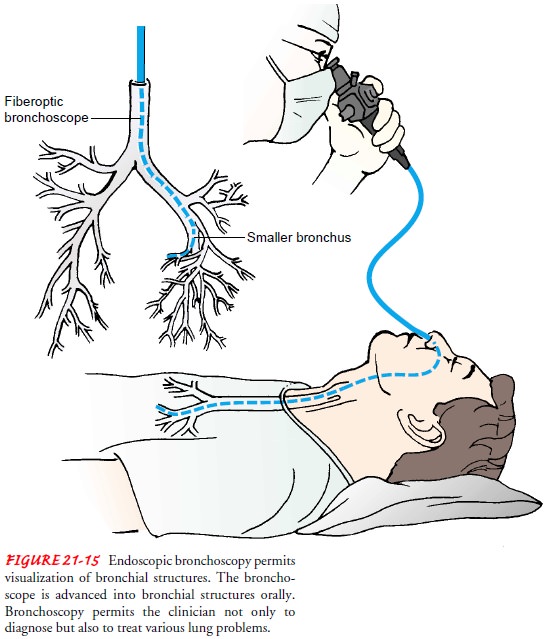
The fiberoptic bronchoscope is a thin,
flexible bronchoscope that can be directed into the segmental bronchi (Fig.
21-15). Be-cause of its small size, its flexibility, and its excellent optical
system, it allows increased visualization of the peripheral airways and is
ideal for diagnosing pulmonary lesions. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy allows biopsy
of previously inaccessible tumors and can be per-formed at the bedside. It also
can be performed through endotra-cheal or tracheostomy tubes of patients on
ventilators. Cytologic examinations can be performed without surgical
intervention.
The rigid bronchoscope is a hollow metal
tube with a light at its end. It is used mainly for removing foreign
substances, inves-tigating the source of massive hemoptysis, or performing
endo-bronchial surgical procedures. Rigid bronchoscopy is performed in the
operating room, not at the bedside.
Possible complications of bronchoscopy
include a reaction to the local anesthetic, infection, aspiration,
bronchospasm, hyp-oxemia (low blood
oxygen level), pneumothorax, bleeding, andperforation.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Before
the procedure, a signed consent form is obtained from the patient, and food and
fluids are withheld for 6 hours before the test to reduce the risk of
aspiration when the cough reflex is blocked by anesthesia. The nurse explains
the procedure to the patient to reduce fear and decrease anxiety and
administers pre-operative medications (usually atropine and a sedative or
opioid) as prescribed to inhibit vagal stimulation (thereby guarding against
bradycardia, dysrhythmias, and hypotension), suppress the cough reflex, sedate
the patient, and relieve anxiety.
The patient must remove dentures and
other oral prostheses. The examination is usually performed under local
anesthesia, but general anesthesia may be needed for rigid bronchoscopy. A
top-ical anesthetic such as lidocaine (Xylocaine) may be sprayed on the pharynx
or dropped on the epiglottis and vocal cords and into the trachea to suppress
the cough reflex and minimize discom-fort. Sedatives or opioids are administered
intravenously as pre-scribed to provide moderate sedation.
After the procedure, it is important that the patient takes nothing by mouth until the cough reflex returns, because the pre-operative sedation and local anesthesia impair the protective la-ryngeal reflex and swallowing for several hours. Once the patient demonstrates a cough reflex, the nurse may offer ice chips and eventually fluids. The nurse assesses for confusion and lethargy in the elderly, which may be due to the large doses of lidocaine given during the procedure.
The nurse also monitors the patient’s respiratory
status and observes for hypoxia, hypotension, tachycar-dia, dysrhythmias,
hemoptysis, and dyspnea. Any abnormality is reported promptly. The patient is
not discharged from the re-covery area until adequate cough reflex and
respiratory status are present. The nurse instructs the patient and family
caregivers to report any shortness of breath or bleeding immediately.
Thoracoscopy
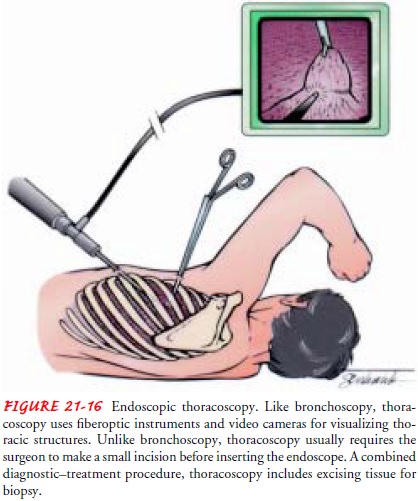
Thoracoscopy
is a diagnostic procedure in which the pleural cav-ity is examined with an
endoscope (Fig. 21-16). Small incisions are made into the pleural cavity in an
intercostal space; the loca-tion of the incision depends on the clinical and
diagnostic find-ings. After any fluid present in the pleural cavity is
aspirated, the fiberoptic mediastinoscope is inserted into the pleural cavity,
and its surface is inspected through the instrument. After the proce-dure, a
chest tube may be inserted, and the pleural cavity is drained by
negative-pressure water-seal drainage.
Thoracoscopy
is primarily indicated in the diagnostic evalua-tion of pleural effusions,
pleural disease, and tumor staging. Biop-sies of the lesions can be performed
under visualization for diagnosis.
Thoracoscopic procedures have expanded with the availabil-ity of video monitoring, which permits improved visualization of the lung. Such procedures also have been used with the carbon dioxide laser in the removal of pulmonary blebs and bullae and in the treatment of spontaneous pneumothorax.
Lasers have also been
used in the excision of peripheral pulmonary nodules. Al-though the laser does
not replace the need for thoracotomy in the treatment of some lung cancers, its
use continues to expand be-cause it is less invasive.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Follow-up
care in the health care facility and at home involves monitoring the patient
for shortness of breath (which might in-dicate a pneumothorax), and minor
activity restrictions, which vary depending on the intensity of the procedure.
If a chest tube is in place, monitoring the chest drainage system and chest
tube insertion site is essential.
Related Topics