Chapter: English
Effective use of SMS
Effective use of SMS
Introduction
Short
message service is a mechanism of delivery of short messages over the mobile
networks. It is a store and forward way of transmitting messages to and from
mobiles. The message (text only) from the sending mobile is stored in a central
short message center (SMS) which then forwards it to the destination mobile. This
means that in the case that the recipient is not available, the short message
is stored and can be sent later. Each short message can be no longer than 160
characters. These characters can be text (alphanumeric) or binary Non-Text
Short messages. An interesting feature of SMS is return receipts. This means
that the sender, if wishes, can get a small message notifying if the short
message was delivered to the intended recipient. Since SMS used signaling
channel as opposed to dedicated channels, these messages can be sent/received
simultaneously with the voice/data/fax service over a GSM network. SMS supports
national and international roaming. This means that you can send short messages
to any other GSM mobile user around the world. With the PCS networks based on
all the three technologies, GSM, CDMA and TDMA supporting SMS, SMS is more or
less a universal mobile data service.
Note: The
actual limit of size of SMS is 160 characters if Latin alphabets are used. If non-Latin
alphabets like Chinese or Arabic are used, the limit is 70 characters.
How does SMS work
The
figure below shows a typical organization of network elements in a GSM network
supporting SMS.
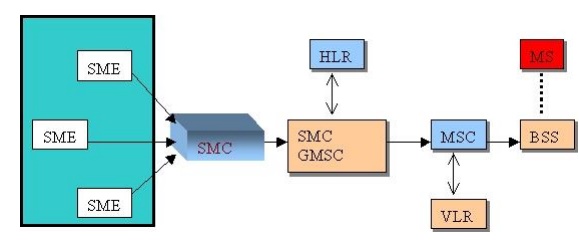
The SMC
(Short Message Center) is the entity which does the job of store and forward of
messages to and from the mobile station. The SME (Short Message Entity) which
can be located in the fixed network or a mobile station, receives and sends
short messages.
The SMS
GWMS (SMS gateway MSC) is a gateway MSC that can also receive short messages.
The gateway MSC is a mobile network’s point of contact with other networks.
On
receiving the short message from the short message center, GMSC uses the SS7
network to interrogate the current position of the mobile station form the HLR,
the home location register.
HLR is
the main database in a mobile network. It holds information of the subscription
profile of the mobile and also about the routing information for the
subscriber, i.e. the
area
(covered by a MSC) where the mobile is currently situated. The GMSC is thus
able to pass on the message to the correct MSC.
MSC
(Mobile Switching Center) is the entity in a GSM network which does the job of
switching connections between mobile stations or between mobile stations and
the fixed network.
A VLR
(Visitor Location Register) corresponds to each MSC and contains temporary
information about the mobile, information like mobile identification and the
cell (or a group of cells) where the mobile is currently situated. Using
information form the VLR the MSC is able to switch the information (short
message) to the corresponding BSS (Base Station System, BSC + BTSs), which
transmits the short message to the mobile. The BSS consists of transceivers,
which send and receive information over the air interface, to and from the
mobile station. This information is passed over the signaling channels so the
mobile can receive messages even if a voice or data call is going on.
Applications
Some of
the common applications of SMS are:
Exchanging small messages like "See you at
8.30 tonight at xyz". SMS is particularly suited for these kinds of short
messages because SMS is much cheaper than calling someone and giving the same
message. Calling some one to give the same message would invariably take more
time and hence more cost.
Many operators offer e-mail service over SMS. Every
user is assigned an e-mail address at signup and any message delivered to that
email is converted to short messages and delivered to the mobile.
It is possible to send e-mail messages (less than
160 characters) from a mobile phone to any e-mail address via SMS.
Information services like news, weather,
entertainment and stock prices etc. can be availed just by sending a keyword
like NEWS, WEATH etc to the short message center number.
SMS can be used by the network operators to provide
services like balance enquiry in case of prepaid cards using SMS.
Mobile chatting is one more hot application of SMS
SMS can be used to notify users that they have
received new voice-mail or fax messages.
It provides an alternative to alphanumeric paging
services
Using SIM-Toolkit, now a part of GSM
specifications, SMS can be used to have on the air activation of features. By
sending codes embedded in short messages from the server network operators can
remotely provision the user's wireless terminal
Internet e-mail alerts.
Downloading new ring tones.
Limitations of SMS
There is no doubt that SMS has been very popular.
The figures in the section above support this. What is more interesting to
observe is that this popularity has been inspite of many limitations of SMS.
Many of these limitations are the driving force behind the developments and
initiatives being taken in the field of short messaging. Some of the
limitations of SMS are:
Messages
are plain vanilla in nature. You can only send simple text messages. There is
no scope for any graphics or audio.
The messages are limited by size. An SMS message
can’t exceed 160 characters.
(BTW this limitation is due to the limitation in
the MAP protocol in GSM) In case of longer e-mails or information service
messages like news, the messages need to
broken down into more than one message. The need to break the messages
into several smaller segments could make SMS comparatively costlier in
comparison to GPRS (for the same kind of service). Also, This doesn’t look very
appealing on a mobile device! The limitation of easy input mechanisms in mobile
devices makes it very uncomfortable sending messages larger than even 5-6
words.
Many
proprietary protocols are used by SMS operators and application developers need
to implement different interfaces for making their applications work with
different SMS centers. X.25 is used as a popular protocol for connecting with
SMS centers.
SMS
protocol data units as defined in GSM 03.40 are also not very efficient. The
various header fields in the PDU are fixed which puts a constraint on the
scenarios that can be indicated. 3G specifications are being looked up to look
and address these constraints.
Data
rate and latency. GPRS and USSD provide better data rates and lower latency
compared to SMS. This is because SMS uses the slow signaling channel, which is
used for many other things also in GSM.
The store and
forward nature of SMS, though useful in many applications makes SMS not very
suitable for WAP
SMS, WAP, and GPRS?
Where
does SMS go with services like WAP and GPRS? Well, The first thing to
understand is that SMS is a bearer service. It is a mechanism of sending short
messages. WAP provides the user with services and protocols that can be used on
top of SMS. With the increased use of WAP, the SMS traffic in networks should
see considerable increase.
GPRS, on
the other hand, is a packet based data service that provides much higher
throughput. Unlike SMS, it provides a real time data bearer. The users always
stay connected to the network. But GPRS and SMS don’t really compete with each
other in the real sense. The costs involved in sending small messages for an
end user in case of SMS are expected to be lower than that in GPRS (packet
data) service because the responsibility for sending the message to the
recipient in case of SMS lies entirely on the short message center as opposed
to the user in GPRS. In GPRS there is no concept of storage. Confirmation of delivery
is a unique feature of SMS because of the very nature of short message service.
Simultaneous transmission with GSM voice, data, and fax services is another
distinguishing characteristic of SMS.
True,
GPRS will be a much better option to use for services like WAP, but the
availability of GPRS and GPRS-compliant handsets will take some time to pickup.
Also, SMS needs no special network elements and handsets. It is something that
almost every mobile user has and can use to send messages to any other mobile
user without worrying about the capabilities of that mobile and its network!
Tips for sending SMS Target your Message
To get
the best response rate target, target, target! Find who you want to contact,
and then target them using the language they use and with solutions / offers
they would want to receive.
Timing
As most
people have their phone with them over 90% of the day, timing is not much of an
issue. However, it has being found that if you are sending business text
messages are mid to late afternoon.
Doesn’t Use Text Speak!
Always
remember you are sending a business marketing message. U won’t rite text spoke
on ur website wud u? So don't do it because it is a text message.
Keep it Clear & Simple!
The
easier you keep the message the more likely your contacts are to respond. You
only have 160 characters to get your message across, so keep it to one simple
single offer or news with a clear call to action.
Be Complete
Ensure
you include everything you want, as well as full instructions on what the
receiver needs to do. If they have to call ensure you give the phone number. If
they need to keep and show the text, tell them.
Use a friendly name your Customers will recognize.
When you
begin to send business sms text marketing messages you will be able to choose a
friendly name. This friendly name will be shown on your contacts mobile phone
when they receive the text message.
Now this
is pretty obvious but always ensures you choose a name your customers will
recognize. Even if you want to do a gimmick and promote an event or music band
- use their name.
Grab Attention Straight Away
Just like
any other piece of marketing, try to grab attention straight away. Start your
message with the word NEWS, OFFER or any of those other words we all like to
see. This is the part of the message that will also show if the receiver has
text preview on their mobile phone and will entice them more to open the SMS
text message.
Test, Revise, Test, Revise and Test Again
Mobile is
no different than any other marketing communication method you would use in
your Business. Always send a test message to your own mobile phone first as
this will give you a chance to see it on the small screen. However, after that
test also keep testing and revising the messages you send to your contacts.
Each time change a small aspect of the SMS message and test if it gets a better
response.
Conclusions
SMS,
because of its very nature has unique advantages that other non voice services
do not have. It provides a very convenient method of exchanging small bits of
information between mobile users. The reasons for the enormous popularity of
SMS have been the fact that this mechanism of sending and receiving messages
not only saves time but costs less as well. In many situations one is relatively
much more comfortable sending a message via SMS than talking over phone. With
new information services and unique value added services being used by the
operators the popularity of SMS is increasing further. SMS is also uniquely
positioned as a very attractive advertisement medium. SMS should no longer be
treated as a value added service in mobile networks. SMS is not only providing
a useful mechanism for a host of innovative services over mobile networks but
it acting as a point of entry for new data services like WAP in mobile
networks.
Abbreviations
Related Topics