Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Assessment of Cardiovascular Function
Echocardiography - Diagnostic Evaluation of Cardiovascular Function
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY
Echocardiography
is a noninvasive ultrasound test that is used to examine the size, shape, and
motion of cardiac structures. It is a particularly useful tool for diagnosing
pericardial effusions, determining the etiology of heart murmurs, evaluating
the func-tion of prosthetic heart valves, determining chamber size, and
evaluating ventricular wall motion. It involves transmission of high-frequency
sound waves into the heart through the chest wall and recording of the return
signals. The ultrasound is gen-erated by a hand-held transducer applied to the
front of the chest. The transducer picks up the echoes, converts them to
electrical impulses, and transmits them to the echocardiography machine for
display on an oscilloscope and recording on a video-tape. An ECG is recorded simultaneously
to assist with inter-preting the echocardiogram.
M-mode
(motion), the unidimensional mode that was first introduced, provides
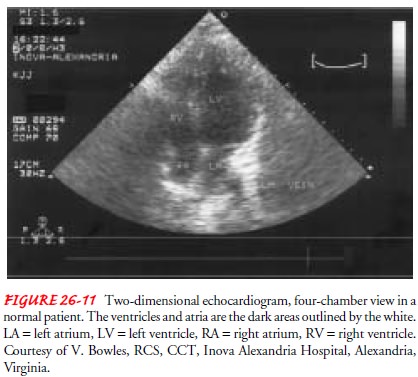
information about the cardiac structures and their motion. Two-dimensional or
cross-sectional echocardi-ography (Fig. 26-11), an enhancement of the
technique, creates a sophisticated, spatially correct image of the heart. Other
tech-niques, such as Doppler and color flow imaging echocardiogra-phy, show the
direction and velocity of the blood flow through the heart.
As
previously mentioned, echocardiography may be performed with an exercise or
pharmacologic stress test; resting and stress images are obtained. Myocardial
ischemia from decreased perfu-sion during stress causes abnormalities in
ventricular wall motion and is easily detected by echocardiography. A stress
test using echocardiography is considered positive if abnormalities in
ven-tricular wall motion are detected during stress but not during rest. These
findings are highly suggestive of CAD and require further evaluation, such as a
cardiac catheterization.
Transesophageal Echocardiography
A significant limitation of traditional echocardiography has been the poor quality of the images produced. Ultrasound loses its clar-ity as it passes through tissue, lung, and bone. Another echo-cardiographic technique involves threading a small transducer through the mouth and into the esophagus. This technique, called transesophageal echocardiography (TEE), provides clearer images because ultrasound waves are passing through less tissue. Pharma-cologic stress testing using dobutamine and TEE can also be per-formed. The high-quality imaging obtained during TEE makes this technique an important adjunct to the technology available for detecting and evaluating the severity of CAD. Complications are uncommon during TEE, but if they do occur they are serious. These complications are caused by sedation and impaired swal-lowing from topical anesthesia (respiratory depression and aspi-ration) and by insertion and manipulation of the transducer into the esophagus and stomach (vasovagal response or esophageal perforation). The patient must be assessed before TEE for a his-tory of dysphagia or radiation therapy to the chest that would increase the risk for complications.
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
Before
traditional echocardiography, the nurse informs the pa-tient about the test,
explaining that it is painless. Echocardio-graphic monitoring is performed
while a transducer that emits the sound waves is moved about the chest. Gel
applied to the skin helps transmit the sound waves. Periodically, the patient
will have to turn onto the left side or hold a breath. The test takes about 30
to 45 minutes. If the patient is to undergo an exercise or phar-macologic stress
test with echocardiography, information on stress testing is also reviewed.
In
preparation for a TEE study, the following information is reviewed:
·
The patient must fast for 6 hours
before the study.
·
An intravenous line is started for
administering a sedative and any pharmacologic stress testing medications.
·
The patient’s throat is anesthetized
before the probe is inserted.
·
BP and the ECG are monitored
throughout the study.
·
The patient will be kept comfortable
but not heavily sedated. The patient must be alert enough to follow
instructions and to report symptoms such as chest pain.
After
the study, monitoring continues for 30 to 60 minutes. The patient is to
continue fasting for 4 hours. The patient may have a sore throat for the next
24 hours.
Related Topics