History - Early Civilisations | 9th Social Science : History : Ancient Civilisations
Chapter: 9th Social Science : History : Ancient Civilisations
Early Civilisations
Early Civilisations
Civilisation is seen as an advanced, organised way
of life. It instilled a way of life that could be considered as an adaptation
to particular environmental and cultural contexts. When it became necessary for
large numbers of people to live in close proximity, they brought in planning,
organisation and specialisation. Settlements were planned and laid out, a
polity emerged, society became organised and food production and craft
production were regulated. As civilisations began to take shape, huge buildings
were built, the art of writing developed and science and technology contributed
to the betterment of society.
The surplus food production by the farmers in the
fertile regions supported the livelihood of a large number of people. The
people who did not cultivate crops engaged in artisanal activities such as
making of bronze tools, ornaments and pottery. Priests, scribes, nobles,
rulers, administrators and craft persons became part of this civilisation.
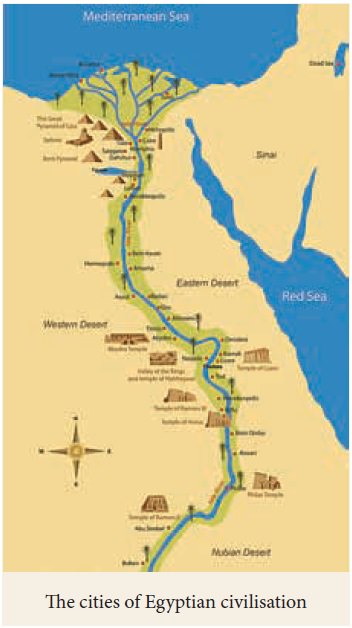
The Egyptian, Mesopotamian, the Chinese and the
Indus were the important early civilisations. While these civilisations
flourished in certain regions, people in other parts of the world lived as
hunter-gatherers and pastoralists. The hunter-gatherers and pastoralists
maintained their relationships with these civilisations through interactions.
Their history is also equally important. During the time of these
civilisations, South India witnessed the emergence of Neolithic agro -pastoral
communities and Microlith form of life by hunter-gatherers.
Related Topics