Chapter: Medical Physiology: Digestion and Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract
Digestion of the Various Foods by Hydrolysis
Digestion of the Various Foods by Hydrolysis
Hydrolysis of Carbohydrates. Almost all the carbohydrates of the diet are eitherlarge polysaccharides or disaccharides, which are combinations of monosaccha-rides bound to one another by condensation. This means that a hydrogen ion(H+) has been removed from one of the monosaccharides, and a hydroxyl ion (-OH) has been removed from the next one. The two monosaccharides then combine with each other at these sites of removal, and the hydrogen and hydroxyl ions combine to form water (H2O).
When carbohydrates are digested, the above process is reversed and the car-bohydrates are converted into monosaccharides. Specific enzymes in the diges-tive juices of the gastrointestinal tract return the hydrogen and hydroxyl ions from water to the polysaccharides and thereby separate the monosaccharides from each other. This process, called hydrolysis, is the following (in which R'-R'' is a disaccharide):
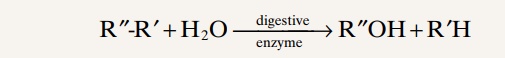
Hydrolysis of Fats. Almost the entire fat portion of the diet consists of triglyc-erides (neutral fats), which are combinations of three fatty acid molecules con-densed with a single glycerol molecule. During condensation, three molecules of water are removed.
Digestion of the triglycerides consists of the reverse process: the fat-digesting enzymes return three molecules of water to the triglyceride molecule and thereby split the fatty acid molecules away from the glycerol. Here again, the digestive process is one ofhydrolysis.
Hydrolysis of Proteins. Proteins are formed from multipleamino acidsthat arebound together by peptide linkages. At each linkage, a hydroxyl ion has been removed from one amino acid and a hydrogen ion has been removed from the succeeding one; thus, the successive amino acids in the protein chain are also bound together by condensation, and digestion occurs by the reverse effect: hydrolysis. That is, the proteolytic enzymes return hydrogen and hydroxyl ions from water molecules to the protein molecules to split them into their con-stituent amino acids.
Therefore, the chemistry of digestion is simple because, in the case of all three major types of food, the same basic process ofhydrolysis is involved. The only difference lies in the types of enzymes required to promote the hydrolysis reactions for each type of food.
All the digestive enzymes are proteins.
Related Topics