Statistical Methods and Econometrics - Data | 12th Economics : Chapter 12 : Introduction to Statistical Methods and Econometrics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 12 : Introduction to Statistical Methods and Econometrics
Data
Data
Data is the information about facts or numbers collected to be
examined and used to help with decisions. Data are the basic raw materials of statistics.
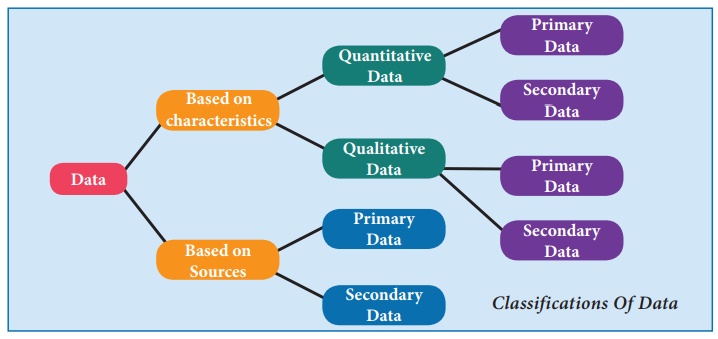
In statistics, data are classified into two broad categories:
1.Quantitative data and Qualitative data.
1. Quantitative data are those that can be quantified in definite units of
measurement. These refer to characteristics whose successive measurements yield
quantifiable observations. Eg. Age, income, number of firms etc
2. Qualitative data refer to qualitative characteristics of a
subject or an object. A characteristic is qualitative in nature when its
observations are defined and noted in terms of the presence or absence of a
certain attribute in discrete numbers. These data are further classified as
nominal and rank data. Eg. Gender, Community, honesty…
(i) Nominal data are the outcome of classification into
two or more categories of
items or units comprising a sample or a population according to some quality
characteristic. Classification of students according to their sex (as
males and females), Workers according to their skill (as skilled, semi-skilled, and unskilled), and of
employees according to their level of education (as matriculates,
undergraduates, and post-graduates).
(ii) Rank data, on the other hand, are the result of
assigning ranks to specify order in terms of the integers 1,2,3, ..., n. Ranks
may be assigned according to the level of performance in a test, a contest, a
competition, an interview, or a show. The candidates appearing in an interview,
for example, may be assigned ranks in integers ranging from I to n, depending
on their performance in the interview.
Sources of Collection of data
Based on the data sources, data could be seen as of two types,
viz., secondary data and primary data. The two can be defined as under:
(i) Primary data: Those data which do not already exist in
any form, and thus have to be collected for the first time from the primary
source(s). By their very nature, these data are fresh and first-time collected
covering the whole population or a sample drawn from it
(ii) Secondary data: They already exist in some form:
published or unpublished in an identifiable secondary source. They are,
generally, available from published source(s), though not necessarily in the
form actually required. Eg. Data from CSO, NSSO, RBI….
Related Topics