Chapter: Data Warehousing and Data Mining
Data Mining
DATA MINING
Introduction
Data
mining refers to extracting or ―mining‖ knowledge from large amounts of data.
Many
other terms carry a similar or slightly different meaning to data mining, such
as knowledge mining from data, knowledge extraction, data/pattern analysis,
another popularly used term, Knowledge Discovery from Data, or KDD.
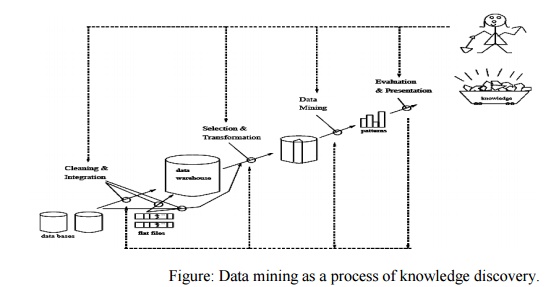
Essential
step in the Process of knowledge discovery. Knowledge discovery as a process is
depicted in Figure consists of an iterative sequence of the following steps:
Data
cleaning: to remove noise and inconsistent data
Data
integration: where multiple
data sources may be combined
Data
selection: where data relevant to the analysis task are
retrieved from the database
Data
transformation: where data are transformed or consolidated into
forms appropriate for mining by
performing summary or aggregation operations, for instance
Data
mining: an essential process where intelligent methods are applied in order to
extract data patterns
Pattern
evaluation to identify the truly interesting patterns
representing knowledge based on some
interestingness measures;
Knowledge presentation where
visualization and knowledge representation techniques are used to present the mined knowledge to the
user
The
architecture of a typical data mining system may have the following major components
Database, data warehouse, Worldwide Web, or other information repository: This
is one or a set of databases, data warehouses, spreadsheets, or other kinds of
information repositories. Data cleaning and data integration techniques may be
performed on the data.
Database
or data warehouse server: The database or data warehouse server is responsible
for fetching the relevant data, based on the user’s data mining request.
Knowledge base: This is
the domain knowledge that is used to guide the search or evaluate the interestingness of resulting patterns.
Such knowledge can include concept hierarchies, used to organize attributes or
attribute values into different levels of abstraction. Other examples of domain
knowledge are additional interestingness constraints or thresholds, and
metadata (e.g., describing data from multiple heterogeneous sources).
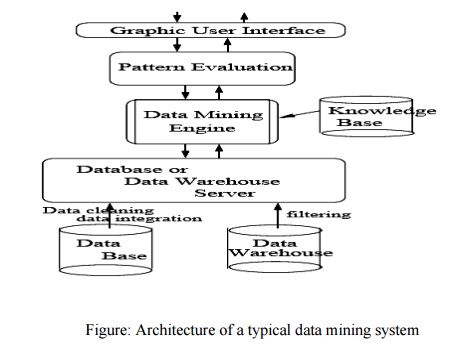
Data mining engine: This is
essential to the data mining system and ideally consists of a set of functional modules for tasks such as
characterization, association and correlation analysis, classification,
prediction, cluster analysis, outlier analysis, and evolution analysis.
Pattern evaluation module: This
component typically employs interestingness measures (and interacts with the data mining modules so as to focus the search toward interesting
patterns. It may use interestingness thresholds to filter out discovered
patterns. Alternatively, the pattern evaluation module may be integrated with
the mining module, depending on the implementation of the data mining method
used..
User interface: This
module communicates between users and the data mining system, allowing the user to interact with the system
by specifying a data mining query or task, providing information to help focus
the search, and performing exploratory data mining based on the intermediate
data mining results. In addition, this component allows the user to browse
database and data warehouse schemas or data structures, evaluate mined
patterns, and visualize the patterns in different forms.
Related Topics