Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Regulation of Mating Type in Yeast
DNA Strand Inheritance and Switching in Fission Yeast
DNA Strand Inheritance and Switching in Fission
Yeast
A yeast other than Saccharomyces cerevisiae is also widely
studied. This is Schizosaccharomyces
pombe, schizo meaning divide, and
pombe an African word for beer. These
are rod-shaped cells that elongate and divide by fission into two equal-sized
cells, in contrast to budding. Some of the processes like mRNA splicing in S. pombe are more similar to those found
in higher eukaryotic cells than the corresponding functions in S. cerevisiae.
The two
mating types in S. pombe are called P for plus, and M, for minus. The mating-type conversion occurs by transposition of
copies of genetic information derived from reference locations, mat2 and mat3, into the expression locus mat1,
much like that found in S. cerevisiae.
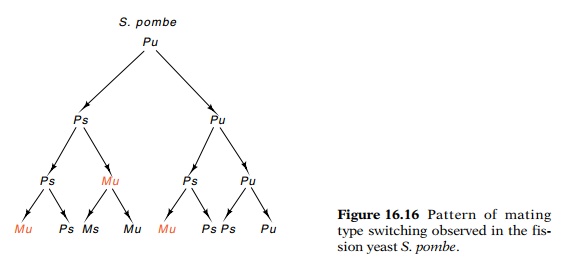
The
pedigree of switching is much different between the two yeasts, however.
Instead of mother and daughter switching together as in S.cerevisiae, only a single sister switches in pombe. That is, only one offour granddaughters of an originally
unswitchable Pu cell switches (Fig.
16.16).
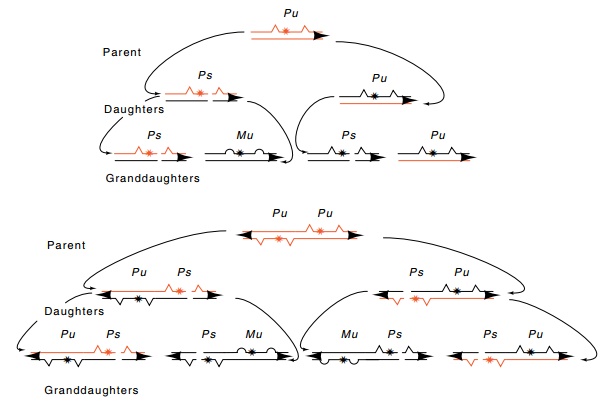
Figure 16.17 A strand
marking mechanism of determining the developmentalfate of daughter cells. The
two cell types are denoted by M and P with curved and angular symbols.
Switchable and unswitchable are indicated by s and u.
What
mechanism directs just one of the two sisters of a Ps cell to switch? We might expect that some molecule in the
cytoplasm or nucleus is unequally expressed, distributed, or stabilized in the
two daughters, and therefore controls their different behavior. Instead, the
marking system appears to use strand-specific marking of the DNA. One of the
strands in a Pu is marked. After
replication, only the chromatid inheriting the marked strand is cleaved. This
cell is then competent to switch and is denoted Ps, and it produces one switched sister in the next generation.
An
elegant experiment led to the proposal of the strand marking mechanism. A
strain was constructed to contain an inverted duplication of mat1 (Fig. 16.17). Thus, each of the two
strands of the DNA duplex contain a copy of the site that is marked for
eventual cutting. Hence, in the Pu
cell, both strands are marked, and both sister cells derived from the cell
should be switchable, and indeed, both are. Southern blot analysis to
quantitate the level of cleavage also fits expectations. Thus, for S. pombe, inheritance of parental DNA
strands, which are comple-mentary and not identical, confers developmental
asymmetry to daughter cells.
Related Topics