Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Regulation of Mating Type in Yeast
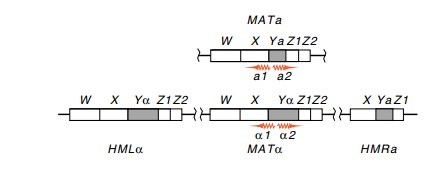
Structure of the Mating Type Loci
Structure of the Mating Type Loci
Cloning the mating-type sequences permitted direct
determination of their structures. DNA-DNA heteroduplexes revealed the overall
struc-tural similarities and differences, while DNA sequencing was used to
examine the detailed aspects of the structures. The a- and α-specific sequences are denoted
by Ya and Yα are relatively small, only about
800 base pairs long. In addition to these regions, the HML, MAT, and HMR loci are flanked by common sequences
W, X, Y, Z1 and Z2.
The RNA transcripts from either of the MAT regions originate from near the
center and extend outward in both directions, giving transcripts a1 and a2 or α1 and α2. These
transcripts were identified by S1 mapping by extracting RNA from cells,
hybridizing it to end-labeled DNA frag-ments, and digesting the remaining
single-stranded RNA and DNA. Measurement of the size of the DNA that was
protected from digestion by the RNA and knowledge of the locations of the
labeled end of the DNA fragment give the transcription start points. On the
basis of genetic complementation tests, the α1, α2, and a1 transcripts are
translated into protein, but the a2 is not translated. Consistent with this
conclusion is
the fact that no mutations have been found in the
a2 region and the a2 transcript lacks a good open reading frame preceded by an
AUG codon.
Related Topics