Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Geography earth space Higher secondary school College Notes
Cold and Tropical deserts Biomes
Plants and Animals, The Biomes
The plant and animal communities of the biosphere living in a particular territory is called the 'biomes'. These biomes adapt themselves to the prevailing environmental conditions of the surroundings. The biomes help us with a clear understanding that we require of the relationships among the ecosystems. Let us now see the interactions and relationships among the climate, soil, vegetation, animals and humankind. Based on their structural characteristics, the biomes can be classified, as follows: -
1. FOREST BIOMES
a. Coniferous forests
b.Temperate forests
c. Tropical forests
2. GRASSLAND BIOMES
a. Temperate grasslands
b.Tropical grasslands
3. DESERT BIOMES
a. Cold deserts
b.Tropical deserts
4. MOUNTAIN BIOMES
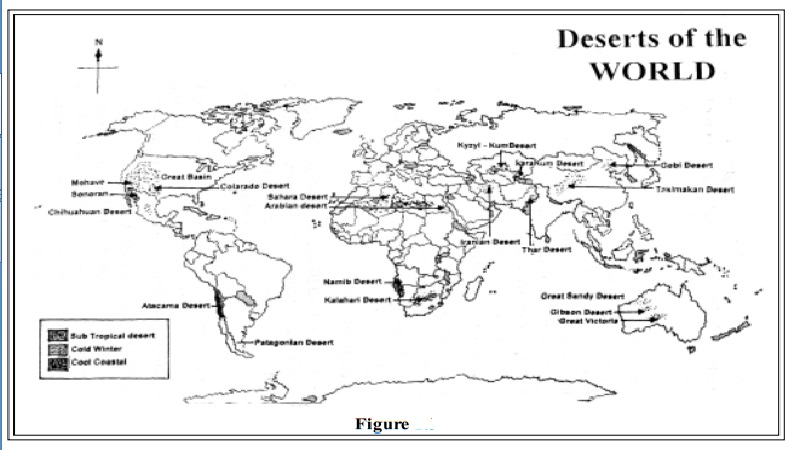
DESERT BIOMES
Desert has an intimate relation with the quantum of rainfall. They are rain deficient regions. They are found in areas with less than 250 mm of rainfall in a year. Deserts are of several types. Using moisture content, they may be classified as arid and semi-arid deserts, hot and cold deserts. All deserts have similar basic characteristics; that is, they all have scanty rains throughout the year .
Cold Desert Biomes: The cold deserts are in the northern hemisphere around the pole and in continuous stretches. In North America, they stretch from Alaska until Labrador and then until the edge of Greenland. In Eurasia, these are found from Scandinavia to the eastern fringe of Siberia. In the southern hemisphere however there are the seas instead of Tundra.
In Tundra, there are hills and highlands, together with gently undulating plains. In the long winters, it is covered with snow, for almost seven long months. For many weeks or months, the sun does not shine here. Due to this, there is a high pressure, characterised by extreme cold and dry winter conditions. The annual rainfall is highly small. In winter, the soil is frozen. When the sun begins to shine, the snow begins to melt. The melting water does not infiltrate the soil, rather it forms the lakes.
The Tundra vegetation varies from place to place. In summer, there are grasses, lichens, mosses and short plants. Although the flora is few in number, there is a great variety of animals. Most animals are herbivores and migratory. Karibou, reindeer, musk oxen, polar rabbits and foxes are some of the cold desert animals. Lemmings live here through the year. The rabbits and foxes change their colour to pure white during the winter. The musk oxen have the skins with grey furs.
Lemmings have a strange life cycle. They breed fairly rapidly and multiply to a great number in about three years. This done, the armies of Lemmings travel towards the sea. They travel by night, until they reach the seas. Then they swim through the water until they die. In these parts, the conditions conducive for human living are but a few. In North America, Eskimos are a people of small numbers. They depend mostly on the sea biomes for their food. Lapps of the Eurasian lands move south during the winter, although their movements are increasingly being restricted to certain pockets.
They get most of their food needs satisfied with the milk and meat and their clothing from the skin of the reindeer.
Hot Deserts. Most important of the hot deserts are the Sahara and its extensions. The Arabian desert, Thar, Kalahari, the West Australian deserts, Atacama and Californian deserts are the other hot deserts. The plants of these deserts are able to withstand the dryness. They are so structured as to adapt to these conditions. Narrow leaves, chlorophyll rich stems, deep and penetrating roots, protective spikes and small thorns are the characteristic features. The plants are spaced out because of the scarce groundwater sources.
In the deserts, like the plants, the animals are also limited in number. They are able to bear the drought and the heat of the deserts. Animals like the camel, mountain goats and other small animals live in the deserts. Camels drink as much water as they get when available and stay without water for long periods. Some rodents of the desert live on dry vegetables and fruits. Some small animals are nocturnal in their search for food and they stay holed up in their burrows to avoid the day temperatures. Smaller insects have wax coating to protect them from the heat.
People are sparsely distributed in the deserts. They do not stay permanently in a place but lead a nomadic life. We find some of the desert tribes in the deserts even today.
Related Topics