Chapter: 10th Science : Chapter 11 : Carbon and its Compounds
Classes of Organic Compounds (Based on the Kind of Atoms)
CLASSES OF ORGANIC COMPOUNDS (BASED ON THE KIND OF ATOMS)
Other than carbon,
organic compounds contain atoms like hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, etc., bonded
to the carbon. Combination of these kinds of atoms with carbon gives different
classes of organic compounds. In the following section, let us discuss various
classes of organic compounds.
1. Hydrocarbons
The organic compounds
that are composed of only carbon and hydrogen atoms are called hydrocarbons.
The carbon atoms join together to form the framework of the
compounds. These are regarded as the parent organic compounds and all other
compounds are considered to be derived from hydrocarbons by replacing one or
more hydrogen atoms with other atoms or group of atoms. Hydrocarbons are,
further, sub divided into three classes such as:
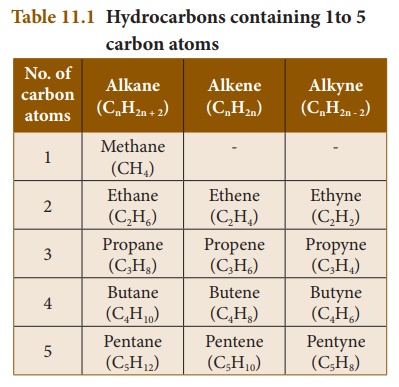
(a) Alkanes: These are hydrocarbons,
which contain only single bonds. They are represented by the general
formula CnH2n + 2 (where n = 1,2, 3, ……). The
simplest alkane (for n=1) is methane (CH4). Since, all are single
bonds in alkanes, they are saturated compounds.
(b) Alkenes: The hydrocarbons, which contain one or more C=C bonds are
called alkenes. These are unsaturated compounds. They are represented by the
general formula CnH2n. The simplest alkene
contains two carbon atoms (n=2) and is called ethylene (C2H4).
(c) Alkynes: The hydrocarbons
containing carbon to carbon triple bond are called alkynes. They
are also unsaturated as they contain triple bond between carbon atoms. They
have the general formula CnH2n – 2. Acetylene (C2H2)
is the simplest alkyne, which contains two carbon atoms. Table 11.1 lists the
first five hydrocarbons of each class:
2. Characteristics of hydrocarbons:
� Lower hydrocarbons are
gases at room temperature E.g. methane, ethane are gases.
� They are colourless and
odourless.
� The boiling point of
hydrocarbons increases with an increase in the number of carbon atoms.
� They undergo combustion
reaction with oxygen to form CO2 and water.
� Alkanes are least
reactive when compared to other classes of hydrocarbons.
� Alkynes are the most
reactive due to the presence of the triple bond.
� Alkanes are saturated
whereas alkenes and alkynes are unsaturated.
� They are insoluble in
water.
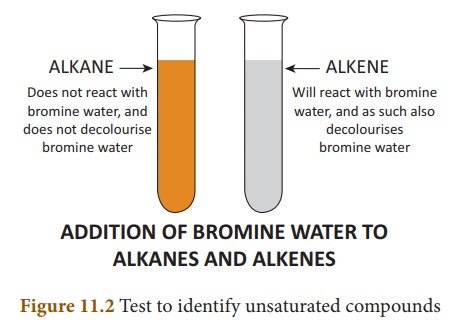
Test to identify saturated and unsaturated compounds:
� Take the given sample
solution in a test tube.
� Add a few drops of
bromine water and observe any characteristic change in colour.
� If the given compound
is unsaturated, it will decolourise bromine water.
� Saturated compounds do
not decolourise bromine.
3. Classification of organic compounds based on functional groups
The structural
frameworks of organic compounds are made of carbon and hydrogen, which are
relatively less reactive. But, the presence of some other atoms or group of
atoms makes the compounds more reactive and thus determines the chemical
properties of the compound. These groups are called functional groups.
A functional group is
an atom or group of atoms in a molecule, which gives its characteristic
chemical properties.
The chemical properties
of an organic compound depend on its functional group whereas its physical
properties rely on remaining part of the structure. Carbon to carbon multiple
bonds (C=C, C![]() C) also are considered as functional groups
as many of the properties are influenced by these bonds. Other functional
groups include atoms of halogens, –OH, –CHO, –COOH, etc.
C) also are considered as functional groups
as many of the properties are influenced by these bonds. Other functional
groups include atoms of halogens, –OH, –CHO, –COOH, etc.
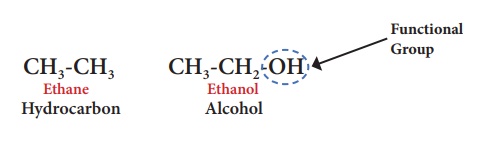
For example, ethane is a
hydrocarbon having molecular formula C2H6. If one of its
hydrogen is replaced by –OH group, you will get an alcohol. Leaving the
functional group, the rest of the structure is represented by ‘R’.
Thus an alcohol is
represented by ‘R-OH’
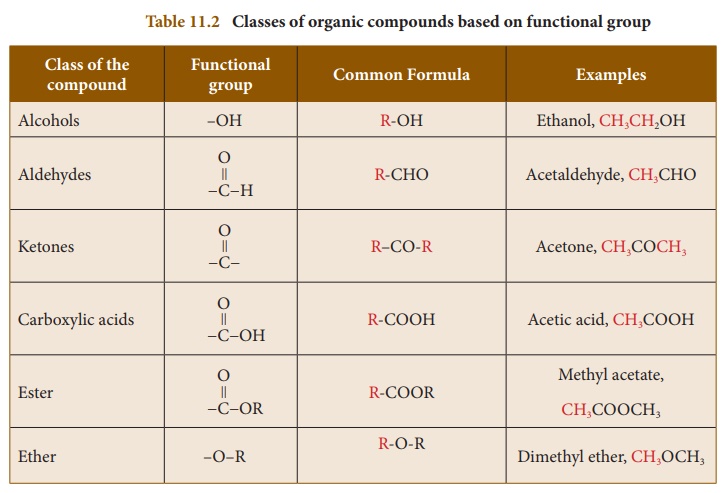
A series of compounds
containing the same functional group is called a class of organic
compounds. Table 11.2 shows various classes or families of organic
compounds and their functional groups:
Related Topics