Digestion and Absorption | Zoology - Answer the following questions | 11th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Digestion and Absorption
Chapter: 11th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Digestion and Absorption
Answer the following questions
Zoology
Digestion and Absorption
Evaluation
Answer the following questions
17. Why are villi present in the intestine and not in the stomach?
• The ileal mucosa has numerous vascular
projections called villi
• It is involoved in the process of
absorption and the cells lining the villi produce numerous microscopic projections
called microvilli.
• A brush border appearance increases
the surface area enormously.
• Villi are not present in the stomach,
because absorption doesnot occur and digestion happens with the help of gastric
juices.
18. Bile juice contains no digestive enzymes, yet it is important for digestion. Why?
• The pile contains bile pigments (Bilirubin
and biliverdin)
• The pile pigments are broken down
products of heamoglobin of dead RBC's
• Bile salts, cholesterol and phospho
lipids.
• Bile has no enzyme.
• Bile helps in emulsification of fats.
• Bile salts reduce the surface tension
of fat droplets and break them into small globules. Bile also activates lipase to
digest lipids.
19. List the chemical changes that starch molecule undergoes from the time it reaches the small intestine.
• Maltose ----Maltase→
glucose + glucose
• Sucrose ----Sucrase→
glucose + fructose
• Lactose -----Lactase→
glucose + galactose
20. How do proteins differ from fats in their energy value and their role in the body?
Protein
1.
The caloric value 5.65 Kcal/gram
Q.
Physiological fuel value 4 Kcal/ gram
Lipid
1.
The caloric value 9.45 Kcal/gram
Q. Physiological fuel value 9 Kcal/ gram
21. Digestive secretions are secreted only when needed. Discuss.
• The saliva is secreted by salivary
gland in the mouth
Saliva
• The saliva contains water.
• Electrolytes - Na+, K+,
Cl− , HCo−3
• Salivary amylase (ptyalin)
• Mucus (a glycoprotein)
• Polysaccharides, starch is hydrolyzed
by the salivary amylase enzyme into disaccharides (maltose)
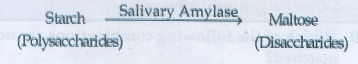
Stomach
• The gastric juice contains HCl and
proenzymes
• Proenzyme pepsinogen on exposure to
HC1 gets converted into active enzyme pepsin.
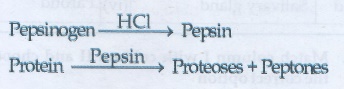
• The HCl provides an acidic medium
(pH=1.8) which is optimum for pepsin, kills bacteria and other harmful organisms
and avoids putrification.
• Proteolytic enzyme found in gastric
juice of Infants is rennin helps in the digestion of milk protein caseinogen to
casein in the presence of calcium.

Small Intestine
• Pancreatic juice:
Enzymes : Trypsinogen, Chymotrypsinogen, Carboxypeptidases,
Pancreatic, Amalyse, Pancreatic Lipase and Nucleases.
• Trypsinogen is activated by an enzyme
enterokinase, secreated by the intestinal mucosa into active trypsin, which in turn
activates the enzyme chymotrypsinogen in the pancreatic juice.

Bile Juice
• The bile contains bile pigment (Bilirubin,
and biliverdin) as the break down product of heamoglobin of dead RBC's, Bile salts,
Cholesterol and phospholipids. But has no enzymes. Bile helps in emulsification
of fats. Bile salts reduce the surface tension of fat droplets and break them into
small globules, bile also activates lipases to digest lipids.
Pancreatic juice action
• Trypsin hydrolyses protein into polypeptides
and peptones. While chymotrypsin hydrolyses peptide bond associated with specific
amino acid.
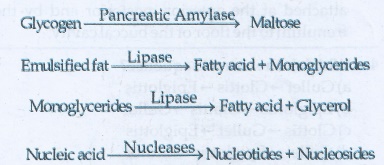
Succus entericus
• The secretions of the Brunner's gland
along with the secretions of the intestinal glands constitute the intestinal juice
or succus entericus.
Enzymes : Maltase, lactase, sucrase (invertase), dipeptidases,
lipases, nucleosidases.

Bicarbonate
ions from the Pancreas provides an alkaline medium (pH=7.8) for the enzymatic action.
All Macromolecules → Micromolecules
Carbohydrate → Monosaccharides
Protein → Aminoacid
Lipids → Fatty acids and Glycerol
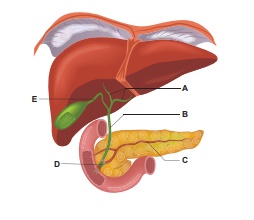
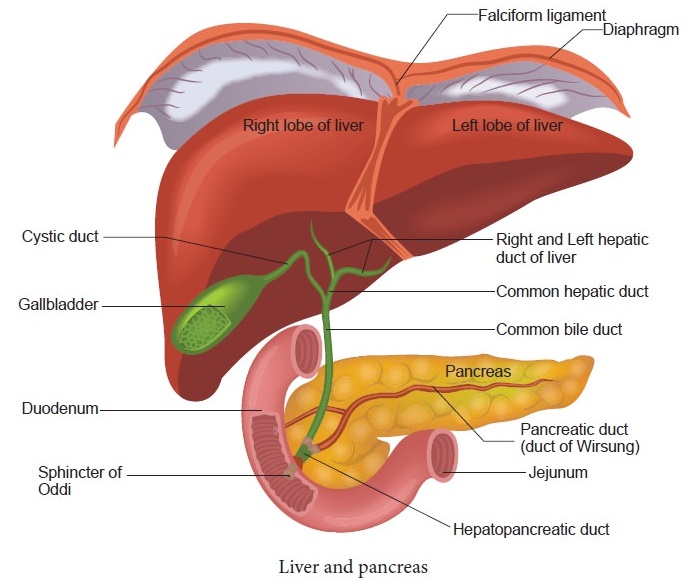
22. Label the given diagram.
Related Topics