Chapter: Plant Biochemistry: A large diversity of isoprenoids has multiple functions in plant metabolism
A Prenyl chain renders compounds lipid-soluble
A Prenyl chain renders compounds lipid-soluble
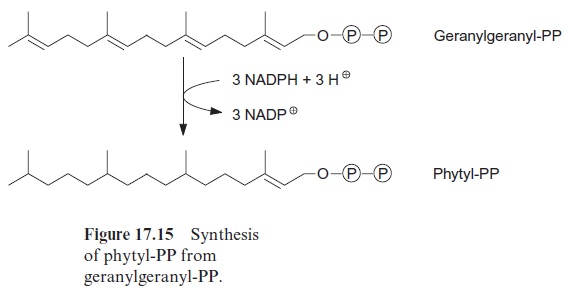
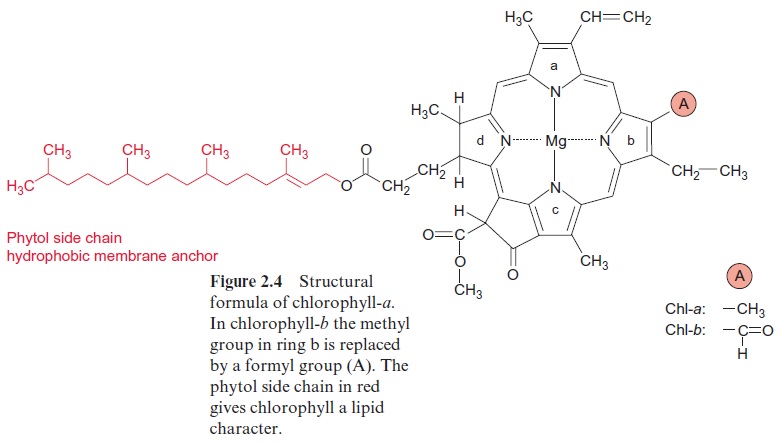
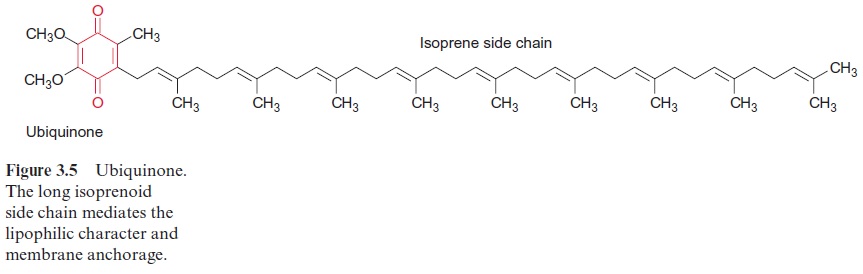
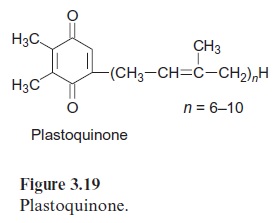
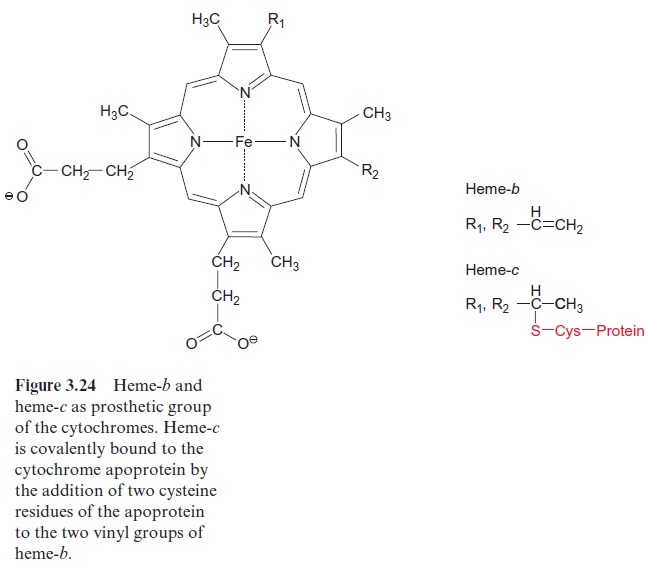
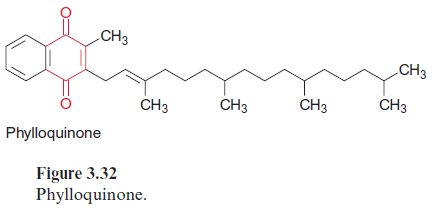
Ubiquinone (Fig. 3.5), plastoquinone (Fig. 3.19), and cytochrome-a (Fig. 3.24) are anchored in membranes by isoprenoid chains of various sizes. At the biosynthesis of these electron carriers, the prenyl chains are introduced from prenyl phosphates by reactions similar to those catalyzed by prenyl transferases. Chlorophyll (Fig. 2.4), tocopherols, and phylloqui-none (Fig. 3.32), on the other hand, contain phytol side chains. These are synthesized from geranylgeranyl-PP by reduction with NADPH and are incorporated correspondingly (Fig. 17.15).
Proteins can be anchored in a membrane by prenylation
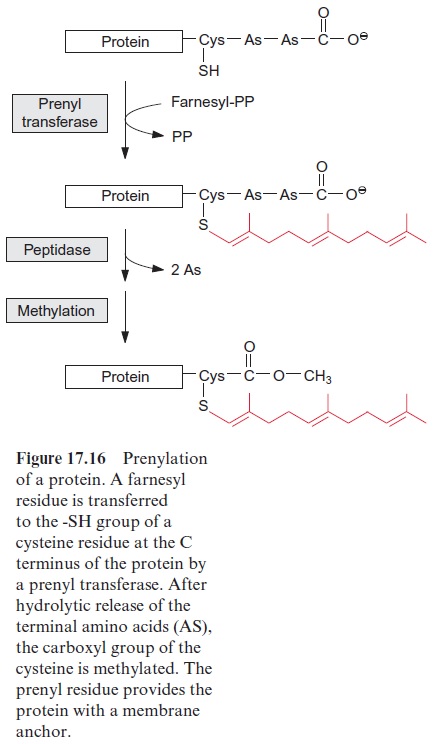
A large number of membrane proteins present in yeast and animals pos-sess a characteristic C terminal sequence with a cysteine, which binds a farnesyl or geranyl residue via a thioether (Fig. 17.16). The connection of these molecules is catalyzed by a specific prenyl transferase. In many cases, the terminal amino acids following the cysteine residue are eliminated after prenylation by a peptidase, and the carboxylic group of the cysteine is methylated. Prenylation and methylation modify the protein so that it becomes lipid-soluble and can be anchored in a membrane. Recent results indicate that this prenylation of proteins plays important roles in plants.
Dolichols mediate the glucosylation of proteins
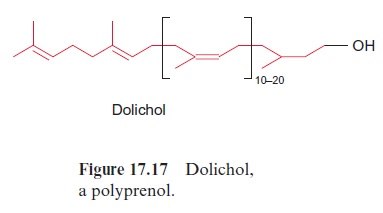
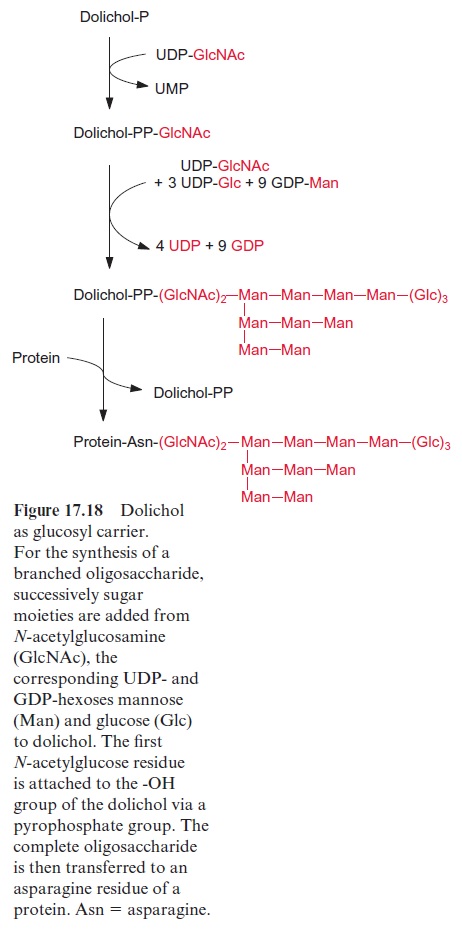
Dolichols (Fig. 17.17) are isoprenoids with a very long chain length, occur-ring in the membranes of the endoplasmatic reticulum and the Golgi net-work. They have an important function in the transfer of oligosaccharides. Many membrane proteins and secretory proteins are N-glucosylated by branched oligosaccharide chains. This glucosylation proceeds in the endo-plasmatic reticulum utilizing membrane-bound dolichol (Fig. 17.18). The oligosaccharide structure is successively synthesized at the dolichol molecule, and after completion it is transferred to an asparagine residue of the pro-tein to be glucosylated. By subsequent modification in the Golgi network, in which certain carbohydrate residues are split off and others are added, a large variety of oligosaccharide structures are generated.
Related Topics