Chapter: 11th Nursing : Chapter 6 : Nursing - Infection Control
Vaccine: Definition and Types of vaccines
Vaccine:-
Definition:
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease. A vaccine typically contains an agent that resembles a disease causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or killed forms of the microbe, its toxin or one of its surface protein.
The agent stimulates the body’s immune and that it may encounter in the future.
The term vaccine and vaccination were derived from variola vaccine (smallpox of the cow) This term was first discovered by Edward Jenner in 1796.
Types of vaccines:
· Live Attenuated Vaccine
· Inactivated Vaccine
· Subunit Vaccine
· Toxoid Vaccine
· Conjugate Vaccine
· DNA Vaccine
· Recombinant Vector Vaccine
Live attenuated vaccine:
Live microorganism modified to be less deadly or closely related microorganism that induce immune response. The organism can be attenuated by growing it in prolonged culture. Attenuation means the loss of virulence of the pathogen.
e.g. OPV, MMR (mumps, measles, Rubella) BCG, varicella vaccine, yellow fever.
Inactivated vaccine or killed vaccine:
Whole microorganism destroyed by heat, chemicals, radiation, antibiotics.
e.g. Hepatitis A vaccine, Hepatitis B, Pneumococcal polysaccharide, IPV, influenza, Hib, Typhoid.
Toxoid vaccine:
Inactivated toxic compounds is toxoid. [toxins can be inactivated by using formalin]
Toxin +formalin ____________ toxoid
e.g. DPT, Antivenom, TT (tetanus toxoid)
Subunit vaccine:
A Protein component of the microorganism.
e.g. Surface Protein or Synthetic virus like particles lacking viral genetic material [unable to replicate] e.g. Hepatitis –B
Monovalent Vaccine:
Immunize against single strain of microorganism.
Multivalent Vaccine:
Immunize against multiple antigens strains or micro organism
The children with malnutrition have low resistance to fight against infection. Therefore children need timely immunization. All children have a rights to get vaccines, protection against preventable disease. Extremely malnourished children may show severe reaction to certain vaccines because they have low antibodies. e.g. Measles Vaccine.
Advantages of live/killed Vaccine:
Live Vaccine:
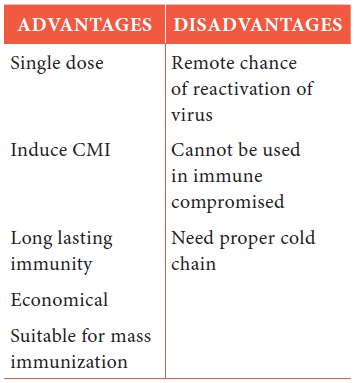
Killed Vaccine:
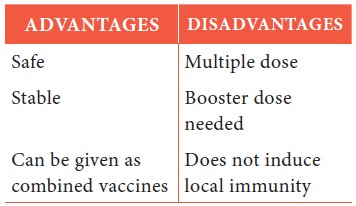
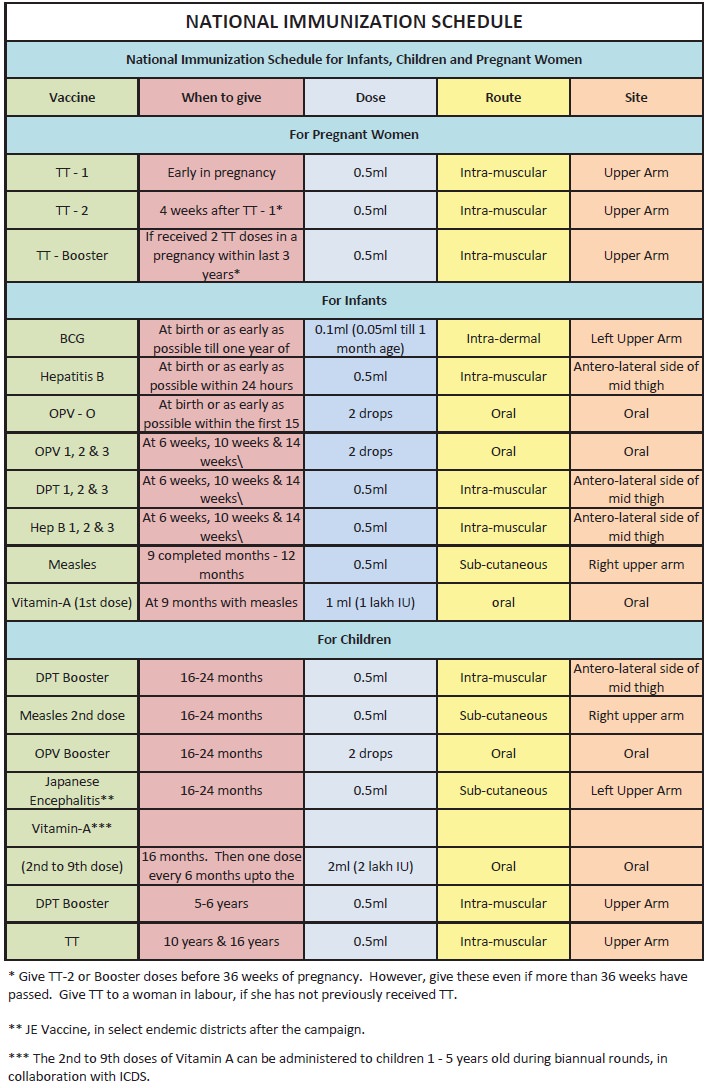
Maintaining a cold chain:
It is essential to maintain the favorable temperature with cold storage, to maintain the potency of vaccines. The temperature should be around 2°C to 8°C. The vaccine should be kept under freezing compartment. The thermometer should be placed in cold place to confirm the validity.
During transportation, the vaccines should be placed in a container maintaining the cited temperature or in a plastic bag in the ice box.
The Vaccines should be arranged according to their expiry dates for the better use.
Contraindications for the immunization:
An acute illness with fever.
When the child is on immune suppressive drug or on radiation.
A child suffering from leukemia, lymphoma, malignancy.
Related Topics