Meaning, Definitions, Characteristics - Fiscal Economics - Tax Revenue | 12th Economics : Chapter 9 : Fiscal Economics
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 9 : Fiscal Economics
Tax Revenue
Tax Revenue
1. Meaning
Tax is a compulsory payment by the citizens to the government to
meet the public expenditure. It is legally imposed by the government on the tax
payer and in no case tax payer can refuse to pay taxes to the government.

2 Definitions
“A Tax is a compulsory
payment made by a person or a firm to a government without reference to any
benefit the payer may derive from the government.” -Anatol Murad
“A Tax is a compulsory contribution imposed by public authority,
irrespective of the exact amount of service rendered to the tax payer in return
and not imposed as a penalty for any legal offence.” - Dalton
3. Characteristics of Tax
1. A tax is a compulsory payment made to the government. People on
whom a tax is imposed must pay the tax. Refusal to pay the tax is a punishable
offence.
2. There is no quid pro quo between a taxpayer and public
authorities. This means that the tax payer cannot claim any specific benefit
against the payment of a tax.
3. Every tax involves some sacrifice on part of the tax payer.
4. A tax is not levied as a fine or penalty for breaking law.
Some of the tax revenue sources are
❖ Income tax
❖ Corporate tax
❖ Sales tax
❖ Surcharge and
❖ Cess
4. Non-Tax Revenue
The revenue obtained by the government from sources other than tax
is called Non-Tax Revenue. The sources of non-tax revenue are
1. Fees
Fees are another important source of revenue for the government. A
fee is charged by public authorities for rendering a service to the citizens.
Unlike tax, there is no compulsion involved in case of fees. The government
provides certain services and charges certain fees for them. For example, fees
are charged for issuing of passports, driving licenses, etc.
2. Fine
A fine is a penalty imposed on an individual for violation of law.
For example, violation of traffic rules, payment of income tax after the
stipulated time etc.
3. Earnings from Public Enterprises
The Government also gets revenue by way of surplus from public
enterprises. Some of the public sector enterprises do make a good amount of
profits. The profits or dividends which the government gets can be utilized for
public expenditure.
4. Special assessment of betterment levy
It is a kind of special charge levied on certain members of the
community who are beneficiaries of certain government activities or public
projects. For example, due to a public park or due to the construction of a
road, people in that locality may experience an appreciation in the value of
their property or land.
5. Gifts, Grants and Aids
A grant from one government to another is an important source of
revenue in the modern days. The government at the Centre provides grants to
State governments and the State governments provide grants to the local
government to carry out their functions.
Grants from foreign countries are known as Foreign Aid. Developing
countries receive military aid, food aid, technological aid, etc. from other
countries.
6. Escheats
It refers to the claim of the state to the property of persons who
die without legal heirs or documented will.
5. Canons of Taxation:
The characteristics or qualities which a good tax should possess
are described as canons of taxation. It must be noted that canons refer to the
qualities of an isolated tax and not to the tax system as a whole. A good tax
system should have a proper combination of all kinds of taxes having different
canons.
According to Adam Smith, there are four canons or maxims of
taxation. They are as follows:
Canons of Taxation
1. Economical
2. Equitable
3. Convenient
4. Certain
5. (Efficient and Flexible)

1. Canon of Ability
The Government should impose tax in such a way that the people
have to pay taxes according to their ability. In such case a rich person should
pay more tax compared to a middle class person or a poor person.
2. Canon of Certainty
The Government must ensure that there is no uncertainty regarding
the rate of tax or the time of payment. If the Government collects taxes
arbitrarily, then these will adversely affect the efficiency of the people and
their working ability too.
3. Canon of Convenience
The method of tax collection and the timing of the tax payment
should suit the convenience of the people. The Government should make
convenient arrangement for all the tax payers to pay the taxes without
difficulty.
4. Canon of Economy
The Government has to spend money for collecting taxes, for
example, salaries are given to the persons who are responsible for collecting
taxes. The taxes, where collection costs are more are considered as bad taxes.
Hence, according to Smith, the Government should impose only those taxes whose
collection costs are very less and cheap .
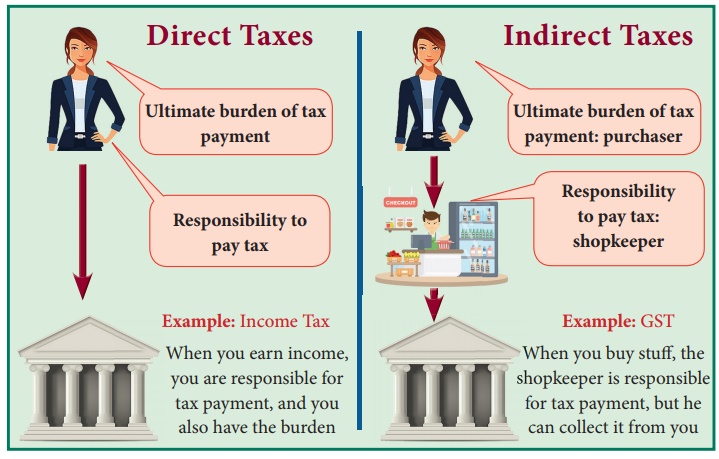
6. Direct Tax and Indirect Tax
Direct Tax
A direct tax is referred to as a tax levied on person’s income and
wealth and is paid directly to the government; the burden of such tax cannot be
shifted. The tax is progressive in nature. It is levied according to the paying
capacity of the person, i.e. the tax is collected more from the rich and less
from the poor people.
The plans and policies of the Direct Taxes are being recommended
by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) which is under the Ministry of
Finance, Government of India.
7. Merits of Direct Taxes
1.Equity
Direct taxes are progressive i.e. rate of tax varies according to
tax base. For example, income tax satisfies the canon of equity.
2.Certainity
Canon of certainty can be ensured by direct taxes. For example, an
income tax payer knows when and at what rate he has to pay income tax.
3. Elasticity:
Direct taxes also satisfy the canon of elasticity. Income tax is
income elastic in nature. As income level increases, the tax revenue to the
Government also increases automatically.
4. Economy
The cost of collection of direct taxes is relatively low. The tax
payers pay the tax directly to the state.
8. Demerits of Direct Taxes
1. Unpopular
Direct taxes are generally unpopular.
It is inconvenient and less flexible.
2. Productivity affected
According to many economists direct tax may adversely affect
productivity. Citizens are not willing to earn more income because in that case
they have to pay more taxes.
3. Inconvenient
The tax payers find it inconvenient to maintain accounts, submit
returns and pay tax in lump sum.
4. Tax Evasion
The burden of direct tax is so heavy that tax-payers always try to
evade taxes. This ultimately leads to the generation of black money, which is
harmful to the economy.
9. Indirect Tax
Indirect Tax is referred to as a tax charged on a person who
purchases the goods and services and it is paid indirectly to the government.
The burden of tax can be easily shifted to the another person. It is levied on
all persons equally whether rich or poor.
There are several types of Indirect Taxes, such as:
Excise Duty: Payable by the manufacturer who shifts the tax burden to
retailers and wholesalers.
Sales Tax: Paid by a shopkeeper or retailer, who then shifts the tax
burden to customers by charging sales tax on goods and services.
Custom Duty: Import duties levied on goods from outside the country,
ultimately paid for by consumers and retailers.
Entertainment Tax: Liability is on the cinema theatre
owners, who transfer the burden to cinema goers.
Service Tax: Charged on services like telephone bill, insurance premium
such as food bill in a restaurant etc.
10. Merits of Indirect Taxes
(1) Wider Coverage
All the consumers, whether they are rich or poor, have to pay
indirect taxes. For this reason, it is said that indirect taxes can cover more
people than direct taxes. For example, in India everybody pays indirect tax as
against just 2 percent paying income tax.
(2) Equitable
The indirect tax satisfies the canon of equity when higher tax is
imposed on luxuries used by rich people.
(3) Economical
Cost of collection is less as producers and retailers collect tax
and pay to the Government. The traders act as honorary tax collectors.
(4) Checks harmful consumption
The Government imposes indirect taxes on those commodities which
are harmful to health e.g. tobacco, liquor etc. They are known as sin taxes.
(5) Convenient
Indirect taxes are levied on commodities and services. Whenever
consumers make purchase, they pay tax along with the price. They do not feel
the pinch of paying tax.
11. Demerits of Indirect Taxes
(1) Higher Cost of Collection
The cost of collection of indirect taxes is higher than the direct
taxes. The Government has to spend huge money to collect indirect taxes.
(2) Inelastic
Indirect taxes are less elastic compared to direct taxes. As
indirect taxes are generally proportional.
(3) Regressive
Indirect taxes are sometimes unjust and regressive in nature since
both rich and poor persons have to pay same amount as taxes irrespective of
their income level.
(4) Uncertainity
The rise in indirect taxes increase the price and reduces the
demand for goods. Therefore, the Government is uncertain about the expected
revenue collection. So Dalton says under indirect taxes 2+2 is not 4 but 3 or
even less than 3.
(5) No civic Consciousness
As the tax is hidden in price, the consumers are not aware of
paying tax.
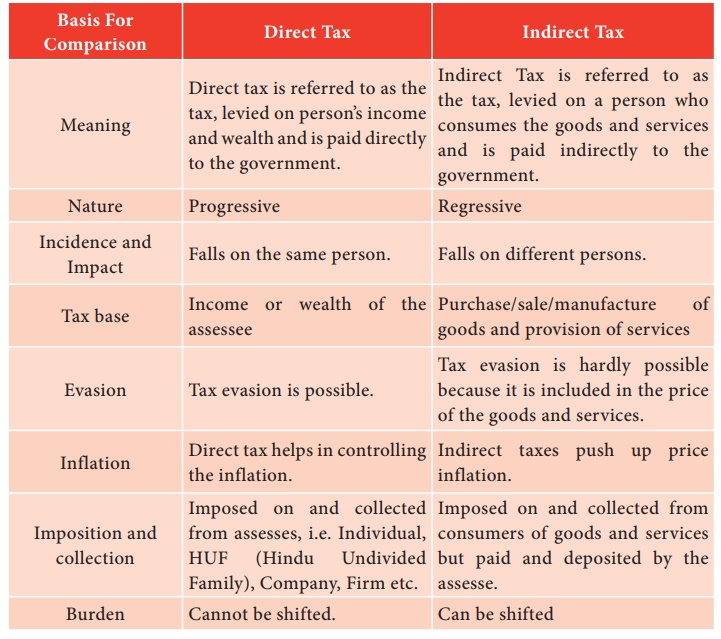
12. Comparison Chart
13. GST (Goods and Service Tax)
GST is an Indirect Tax which has replaced many Indirect Taxes in
India. The Goods and Service Tax Act was passed in the Parliament on 29th March
2017. The Act came into effect on 1st July 2017; Goods & Services Tax in
India is a comprehensive, multi-stage, destination-based tax that
is levied on every value addition.
In simple words, Goods and Service Tax (GST) is an indirect tax
levied on the supply of goods and services. This law has replaced many indirect
tax laws that previously existed in India.
GST is one indirect tax for the entire country.
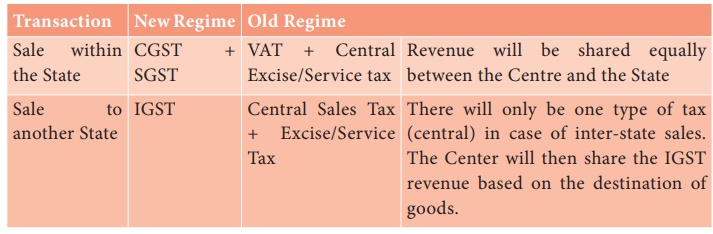
Under the GST regime, the tax will be levied at the final point of
sale. In case of intra-state sales, Central GST and State GST will be charged.
Inter-state sales will be chargeable to Integrated GST.

Destination Based
Consider goods manufactured in Tamil Nadu and are sold to the
final consumer in Karnataka. Since Goods Service Tax is levied at the point of
consumption, in this case, Karnataka, the entire tax revenue will go to
Karnataka and not Tamil Nadu.
Components of GST
The component of GST are of 3 types.
They are: CGST, SGST & IGST.
CGST: Collected by the Central Government on an intra-state sale
(Eg: Within state/ union territory)
SGST: Collected by the State Government on an intra-state sale
(Eg: Within state/ union territory)
IGST: Collected by the Central Government for inter-state sale
(Eg: Maharashtra to Tamil Nadu)
In most cases, the tax structure under the new regime will be as
follows:
Nature of Sales tax, VAT and GST
1. Sales tax was multipoint tax with cascading effect.
2. VAT was multipoint tax without cascading effect.
3. GST is one point tax without cascading effect.
Advantages of GST
1. GST will mainly remove the cascading effect on the sale of
goods and services. Removal of cascading effect will directly impact the cost
of goods. Since tax on tax is eliminated in this regime, the cost of goods
decreases.
2. GST is also mainly technologically driven. All activities like
registration, return filing, application for refund and response to notice need
to be done online on the GST Portal. This will speed up the processes.
Related Topics