Functions of SHRC - State Human Rights Commission(SHRC) | 9th Social Science : Civics: Human Rights
Chapter: 9th Social Science : Civics: Human Rights
State Human Rights Commission(SHRC)
State Human Rights Commission(SHRC)

Every state in India has
a State Human Rights Commission established in accordance
with the power conferred on the state under section 21of the Protection of
Human Rights Act, 1993. The protection and promotion of human rights constitute
the principal concern of the Commission. Moreover, the procedures adopted by
the Commission to conduct its proceedings, the suo motu actions taken on
complaints regardless of the sources received and the transparency of the
proceedings of the SHRC add strength to its functioning in a state.
Functions of SHRC
·
The SHRC shall enquire into violation of human rights in respect
of matters specified in the state and concurrent lists.
·
Its objectives and duties are the same as NHRC, but confined only
to the state. It has a chairman and two members.
·
It has the power of a civil court and can take cognizance of cases
if received or in suo motu.
·
It can also recommend compensation to victims.
Child Rights
Apart from the
fundamental rights described by the Constitution, we have to ensure certain
other rights.
A child is a person who
has not completed the age of 18 years i.e. a minor as per UNO. This principle
is exhibited in Articles 25 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Based
on these principles, the declaration of the Rights of the child was accepted
and adopted in the UN General Assembly on 20th November, 1989.
·
Right to life
·
Right to family environment
·
Right to Education
·
Right to benefit from Social security
·
Right against sexual exploitation
·
Right against sale or trafficking
·
Right against other forms of exploitation like Child labour.
· Right to life
A child has the right to
survive even before its birth. The right to survival also includes the right to
be born, the right to basic needs of food, shelter and clothing and a dignified
living.
· Right to Family Environment
A child has the right to
live a normal childhood in a family environment. Children who have been left
destitute, abandoned or orphaned also have the right to live. These children
can be given for adoption to caring families.
· Right to benefit from Social security
Children should get
financial support from the country when their parents or guardians are unable
to provide them with a good standard of living by themselves, due to any
illness, disability or old age.
· Right to Education
Right to Education Act
is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted in 2009 for free and compulsory
education for children from 6 to 14 years of age as under Article 21A of the
Constitution.
The Right of children
To free and compulsory Education (RTE) Act, 2009, means that every child has a
right to formal Elementary Education. This right of children provides free and
compulsory education till the completion of elementary education in a
neighbourhood school. The child need not pay any kind of fee for completing
elementary education.
Malala - Nobel Peace
prize laureate says
"I loved school.
But everything changed when the fundamentalist took control of our town in Swat
Valley.

They said girls could
no longer go to school. I spoke out publicly on behalf of girls and our right
to learn. And this made me a target.
In October 2012, on my
way home from school, a masked gunman boarded my school bus and asked, “Who is
Malala?” He shot me on the left side of my head. I woke up 10 days later
in a hospital in Birmingham, England. After months of surgeries and
rehabilitation, I joined my family in our new home in the U.K. I
determined to continue my fight until every girl could go to school.
Every day I fight to
ensure all girls receive 12 years of free, safe, quality education. With more
than 130 million girls out of school today, there is more work to be done. I
hope you will join my fight for education and equality. Together, we can create
a world where all girls can learn and lead.
If you were Malala,
what would you have done?
Is Malala's fight
necessary?
Are girl children
treated and given education equally?
· Right against sale or trafficking
Children should be
treated as individuals with fundamental human rights. Children are vulnerable.
There are root causes such as poverty, gender discrimination, broken families
etc., behind the sale or trafficking of children.
Children are subjected
to sale or trafficking for various reasons – economic exploitation, sexual
exploitation, sexual abuse, drug trafficking and child labour.
· Right against sexual exploitation
The state should protect
children from sexual exploitation and abuse, when they are forced or persuaded
to take part in sexual activities physically or mentally.
· Right against other forms of exploitation like Child labour
Children are often
employed in several industries. These children are deprived of their childhood,
health and education. This will lead to a life of poverty and want. These
children are made to work in glass, match-box, lock-making factories,
rag-picking, carpet – making industry, beedi - rolling, mining, stone quarrying,
brick kilns and tea gardens etc.
Work is mostly gender –
specific, with girls performing more home – based work, while boys are employed
as waged labour. Since these children work in agricultural fields, restaurants,
motor repair workshops and home – based industries, elimination of child labour
remains a challenge.

The findings of an
international survey reveals that children with disabilities are 3.4% more
sexually abused than normal children.
Child Rights in the
Indian Constitution
Article 24 – No child
below the age of 14 must be employed in hazardous employment. Article 45 – Free
and compulsory education for all children until they attain the age of 14
years.
Women Rights
The National Commission
for Women (NCW) is constituted in India to review the Constitutional and
legal safeguards for women, recommends remedial measures and advises the
government on all matters of policy affecting the welfare and development of
women in the country.
In modern India, women
have held high offices including that of the President, Prime Minister, Speaker
of the Lok Sabha, Leader of the Opposition, Union Ministers, Chief Ministers
and Governors.
In Tamil Nadu,
ancestral property rights were given to women through Hindu Succession (Tamil
Nadu Amendment) Act 1989.
The Central Government
amended the Hindu Succession Act in 2005. By this amendment, women are now
given equal shares in inheritance of the undivided property.
Women's rights under the Constitution of India mainly include equality, dignity, and freedom from discrimination; additionally, India has various statutes governing the rights of women.
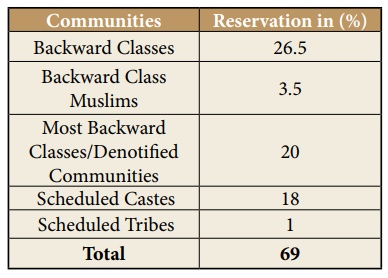
Reservations
The state of Tamil Nadu
provides 69% of reservation to the Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Most
Backward Classes / Denotified Communities and Backward Classes in public
employment and in educational institutions. Backward class Muslims are granted
separate reservation.
The following table
gives us a very clear picture of the percentage of reservation for various communities
by the Government of Tamil Nadu.
Under each reserved
category andin General category 30% is reserved for women and 4% is reserved
for differently abled persons.
Special reservation to
Arunthathiyars has been granted by preferential allotment of seats with in the
seats reserved for Scheduled castes. For persons studied in Tamil medium 20%
seats are offered under each category on priority basis.
In Tamil Nadu
Transgenders has been classified under Most Backward Classes.
Right to Information Act (RTI)
The Right to Information
Act is a revolutionary act that aims to promote transparency in the government
institutions in India. This act was enacted in October 2005.
A common man can demand
any government organization to provide information. The information must be
provided within thirty days. If not, a fee will be collected as penalty from
the concerned official.
It is one of the most powerful laws of the country. This act is people friendly; even an illiterate person can ask any Public Information Officer to write it down for him. All government agencies like Municipal Corporations, Government departments, Government Schools, Road Authorities, etc., come under this Act.
RTI Activists

of government documents
such as records, reports, papers, etc., Personal information
of
individuals and
organisations related to the country’s defence and intelligence,
such as BSF, CRPF,
Intelligence Bureau are exempted from the RTI.
·
Sign the Application form with your full name and address along
with the date and send it through a registered post to the office of the
concerned authority.
·
If a reply is not received within 30 days, an appeal can be filed
with the Appellate Authority.
Labour Rights
The Constitution ensures right to equality, equality of opportunity in public employment, right to form associations and unions, right to livelihood, prohibits trafficking, forced labour and child labour. Article 39(d) ensures equal wages to male and female workers for equal work.
“The rights of every man
are diminished when the rights of one man are threatened” said John F. Kennedy.
Civilized nations of the world insist on equality. Nations pay more attention
on human rights to ensure equality. This helps in maintaining peace, harmony
and development of the country.
Contribution of Dr.B.R. Ambedkar

Dr.B.R. Ambedkar's
contribution to labourers.
• Reduction in Factory Working Hours
(8 hours a day)
• Compulsory Recognition of Trade Unions
• Employment Exchange in India
• Employees State Insurance (ESI)
• Minimum Wages
• Coal and Mica Mines Provident Fund
Related Topics