Coordination Chemistry | Chemistry - Stability of metal complexes | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Coordination Chemistry
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Coordination Chemistry
Stability of metal complexes
Stability
of metal complexes:
The stability of
coordination complexes can be interpreted in two different ways. The first one
is thermodynamic stability and second one is kinetic stability. Thermodynamic
stability of a coordination complex refers to the free energy change (∆G) of a
complex formation reaction. Kinetic stability of a coordination complex refers
to the ligand substitution. In some cases, complexes can undergo rapid ligand
substitution; such complexes are called labile complexes. However, some
complexes undergo ligand substitution very slowly (or sometimes no
substitution), such complexes are called inert complexes.
Stability constant:(β)
The stability of a
coordination complex is a measure of its resistance to the replacement of one
ligand by another. The stability of a complex refers to the degree of
association between two species involved in an equilibrium. Let us consider the
following complex formation reaction
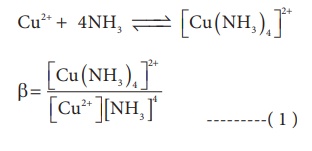
So, as the concentration
of [Cu (NH3)4]2+ increases the value of
stability complexes also increases. Therefore the greater the value of
stability constant greater is the stability of the complex.
Generally coordination
complexes are stable in their solutions; however, the complex ion can undergo
dissociation to a small extent. Extent of dissociation depends on the strength
of the metal ligand bond, thus Stronger the M ← L , lesser is the dissociation.
In aqueous solutions,
when complex ion dissociates, there will be equilibrium between undissociated
complex ion and dissociated ions. Hence the stability of the metal complex can
be expressed in terms of dissociation equilibrium constant or instability
constant α . For example let us
consider the dissociation of [Cu (NH3)4 ]2+ in aqueous solution.
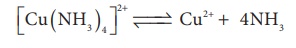
The dissociation
equilibrium constant or instability constant is represented as follows,
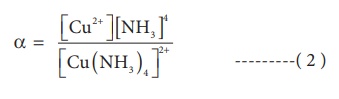
From (1) and (2) we can
say that, the reciprocal of dissociation equilibrium constant ( α) is called as formation
equilibrium constant or stability constant (
β) .
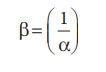
Significance of stability constants
The stability of
coordination complex is measured in terms of its stability constant ( β) . Higher the value of
stability constant for a complex ion, greater is the stability of the complex
ion. Stability constant values of some important complexes are listed in table
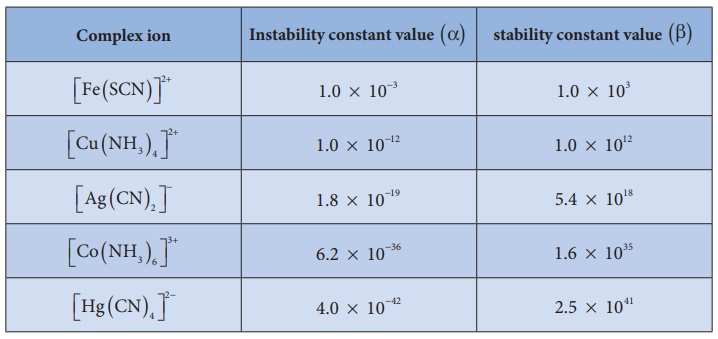
By comparing stability
constant values in the above table, we can say that among the five complexes
listed, [Hg ( CN)4 ]2− is most stable complex
ion and [ Fe ( SCN)]2+ is least stable.
1. Stepwise formation constants and overall formation constants
When a free metal ion is
in aqueous medium, it is surrounded by (coordinated with) water molecules. It
is represented as [MS6]. If ligands which are stronger than water
are added to this metal salt solution, coordinated water molecules are replaced
by strong ligands.
Let us consider the
formation of a metal complex ML6 in aqueous medium.(Charge on the
metal ion is ignored) complex formation may occur in single step or step by
step.
If ligands added to the
metal ion in single step, then
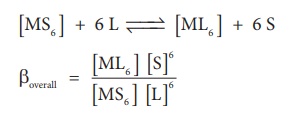
βoverall is
called as overall stability constant. As solvent is present in large excess,
its concentration in the above equation can be ignored.
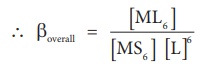
If these six ligands are
added to the metal ion one by one, then the formation of complex [ML6]
can be supposed to take place through six different steps as shown below.
Generally step wise stability constants are represented by the symbol k.
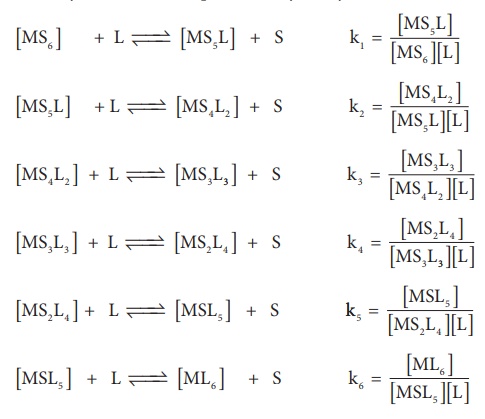
In the above
equilibrium, the values k1 , k2 , k3 , k4
, k5 and k6 are called step wise stability constants. By
carrying out small a mathematical manipulation, we can show that overall
stability constant β
is the product of all step wise stability constants k1 , k2
, k3 , k4 , k5 and k6 .
β = k1 × k2 × k3 × k4 × k5 × k6
On taking logarithm both
sides
log ( β) = log ( k1 ) + log ( k2 ) + log ( k3 ) + log ( k4 ) + log ( k5 ) + log ( k6 )
2. Importance and applications of coordination complexes:
The coordination
complexes are of great importance. These compounds present in many plants,
animals and in minerals. Some Important applications of coordination complexes
are described below.
1.
Phthalo blue – a bright blue pigment is a complex of Copper (II)
ion and it is used in printing ink and in the packaging industry.
2. Purification of Nickel
by Mond’s process involves formation [Ni(CO)4], which Yields 99.5%
pure Nickel on decomposition.
3. EDTA is used as a
chelating ligand for the separation of lanthanides,in softening of hard water
and also in removing lead poisoning.
4. Coordination complexes
are used in the extraction of silver and gold from their ores by forming
soluble cyano complex. These cyano complexes are reduced by zinc to yield
metals. This process is called as Mac-Arthur –Forrest cyanide process.
5. Some metal ions are
estimated more accurately by complex formation. For example, Ni2+ ions present
in Nickel chloride solution is estimated accurately for forming an insoluble
complex called [Ni(DMG)2]
6.
Many of the complexes are used as catalysts in organic and
inorganic reactions. For example,
(i) Wilkinson’s catalyst
– [( PPh3 )3 RhCl] is used for
hydrogenation of alkenes.
(ii) Ziegler-Natta catalyst - [TiCl4
]+ Al ( C2H5
)3 is used in the
polymerization of ethene.
7.
In order to get a fine and uniform deposit of superior metals (Ag,
Au, Pt etc.,) over base metals, Coordination complexes [Ag ( CN)2 ] and [Au ( CN)2 ] etc., are used in
electrolytic bath.
8. Many complexes are used
as medicines for the treatment of various diseases. For example,
(i) Ca-EDTA chelate, is used in the treatment of lead and
radioactive poisoning. That is for removing lead and radioactive metal ions
from the body.
(ii) Cis-platin is used as an antitumor drug in cancer treatment.
9. In photography, when the
developed film is washed with sodium thio sulphatesolution (hypo), the negative
film gets fixed. Undecomposed AgBr forms a soluble complex called
sodiumdithiosulphatoargentate(I) which can be easily removed by washing the
film with water.
AgBr + 2 Na2
S2O3 → Na3 [Ag ( S 2O3 )2 ] + 2 NaBr
10. Many biological systems
contain metal complexes. For example,
·
A red blood corpuscles (RBC) is composed of heme group, which is
Fe2+- Porphyrin complex.it plays an important role in carrying
oxygen from lungs to tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs.
·
Chlorophyll, a green pigment present in green plants and algae, is
a coordination complex containing Mg2+ as central metal ion
surrounded by a modified Porphyrin ligand called corrin ring. It plays an
important role in photosynthesis, by which plants converts CO2 and
water into carbohydrates and oxygen.
·
Vitamin B12(cyanocobalamine) is the only vitamin
consist of metal ion. it is a coordination complex in which the central metal
ion is Co+ surrounded by Porphyrin
like ligand.
·
Many enzymes are known to be metal complexes, they regulate
biological processes. For example, Carboxypeptidase is a protease enzyme that
hydrolytic enzyme important in digestion, contains a zinc ion coordinated to
the protein.
Related Topics