Common keywords, Syntax, Advantages, Disadvantages, Example - Pseudo code | Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
Chapter: Problem Solving and Python Programming : Algorithmic Problem Solving
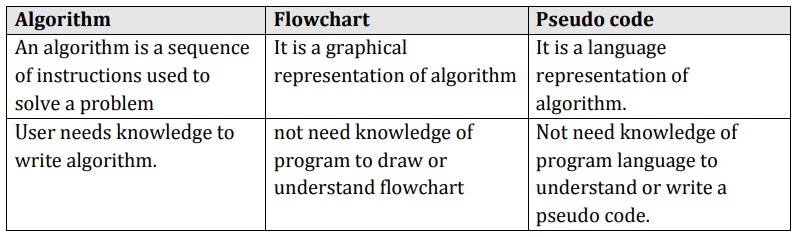
Pseudo code
PSEUDO CODE:
v Pseudo code consists of short, readable and
formally styled English languages used for explain an algorithm.
v It does not include details like variable
declaration, subroutines.
v It is easier to understand for the programmer
or non programmer to understand the general working of the program, because it
is not based on any programming language.
v It gives us the sketch of the program before
actual coding.
v It is not a machine readable
v Pseudo code can’t be compiled and executed.
v There is no standard syntax for pseudo code.
Guidelines for writing pseudo code:
v Write one statement per line
v Capitalize initial keyword
v Indent to hierarchy
v End multiline structure
v Keep statements language independent
Common keywords used in pseudocode
The following
gives common keywords used in pseudocodes.
1. //: This keyword used to represent a
comment.
2. BEGIN,END: Begin is the first statement
and end is the last statement.
3. INPUT, GET, READ: The keyword is used
to inputting data.
4. COMPUTE, CALCULATE: used for calculation
of the result of the given expression. 5.
ADD, SUBTRACT, INITIALIZE used for addition, subtraction and initialization.
6. OUTPUT, PRINT, DISPLAY: It is used to
display the output of the program.
7. IF, ELSE, ENDIF: used to make decision.
8. WHILE, ENDWHILE: used for iterative
statements.
9. FOR, ENDFOR: Another iterative
incremented/decremented tested automatically.
Syntax for if
else:
IF
(condition)THEN
statement
...
ELSE
statement
...
ENDIF
Example: Greates of two numbers
BEGIN
READ a,b
IF (a>b) THEN
DISPLAY a is
greater
ELSE
DISPLAY b is
greater
END IF
END
Syntax for
For:
FOR( start-value
to end-value) DO
statement
...
ENDFOR
Example: Print n natural numbers
BEGIN
GET n
INITIALIZE i=1
FOR (i<=n) DO
PRINT i
i=i+1
ENDFOR
END
Syntax for
While:
WHILE
(condition) DO
statement
...
ENDWHILE
Example: Print n natural numbers
BEGIN
GET n
INITIALIZE i=1
WHILE(i<=n)
DO
PRINT i
i=i+1
ENDWHILE
END
Advantages:
v Pseudo is independent of any language; it can
be used by most programmers.
v It is easy to translate pseudo code into a
programming language.
v It can be easily modified as compared to
flowchart.
v Converting a pseudo code to programming
language is very easy as compared with converting a flowchart to programming
language.
Disadvantages:
v It does not provide visual representation of
the program’s logic.
v There are no accepted standards for writing
pseudo codes.
v It cannot be compiled nor executed.
v For a beginner, It is more difficult to follow
the logic or write pseudo code as compared to flowchart.
Example:
Addition of two numbers:
BEGIN
GET a,b
ADD c=a+b
PRINT c
END
Related Topics