Chapter: BIOLOGY (ZOOLOGY) Standard XI first year 11th text book Assignment topics question and answer Explanation Definition
Pests - Pests of Crops : Cotton, Paddy, Sugarcane, Vegetables, Coconut palm, Stored grains, household goods
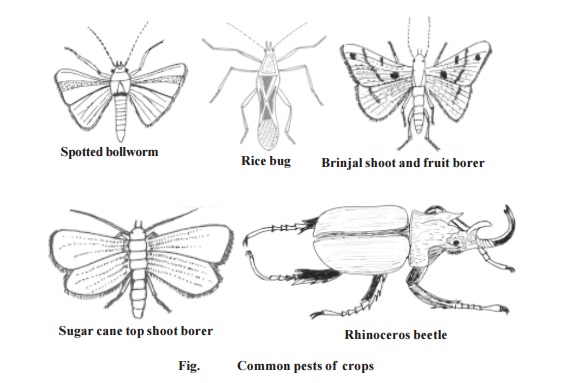
Pests - Pests of Crops : Cotton, Paddy, Sugarcane, Vegetables, Coconut palm, Stored grains, household goods
Pests
Any animal which becomes a source of trouble or loss to human is called a pest. Among insects such pests are numerous and are of different kinds. An insect is usually called as a pest when it causes appreciable damage and loss to the crops or other belongings. The pests may be classified as major or occassional. The insects damaging standing crops cereals, fruits and other plant products of commercial importance are designated as crop pests. Those insects destroying stored grains are called the store pest. Insects causing damage to household articles are called the household pests.
Pests of Crops
I. Pest of Cotton
a. Pink boll worm - Pectinophora gossypiella
This pest causes damage to the buds, flowers and seeds.
b. Red cotton bug - Dysdercus koenigii
This bug sucks the cell sap of green bolls and leaves.
c. Spotted boll worm - Earias vitella, E. insulana
These two species are the most important pests of cotton in India causing heavy losses to the crop every year. E- vitella is abundant in high rainfall areas, where as E- insulana abounds in areas receiving scanty rains. The caterpillars of Earias. bore into the stem portion of young seedlings and apical shoots and later eat into buds, flowers and bolls. The attacked shoots wither, droop and ultimately die.
Control : The attacked shoots and bolls should be collected and destroyed. Avoid growing lady's finger during the offseason in the vicinity of the cotton fields. Insecticidal control of the pest consists of spraying is done every 15 - 20 days of monocrotophos, endosulfan or malathion.
II. Pests of Paddy
a. Rice stem borer - Tryporyza incertulas
This pest bores into the stems of the young mature stages of paddy.
b. Rice bug - Leptocorisa acuta
It is the most important pest of paddy in India. It mainly feeds on paddy but is also found feeding on millets, maize, sugar cane and some grasses. The adults and nymphs feed on the milky juice of the forming grains which as a consequence become chaff.
Control : In nurseries and fields , the leaves of paddy plants containing eggs should be clipped and burnt. As the bugs feed and breed on various types of grasses, removal of such grasses from the fields will help in reducing the population. Collection of bugs with a hand net and their destruction is a usefulmechanical method. Among the insecticides BHC and malathion as dusts and carbaryl and methyl parathion as sprays just before flowering of the plants are effective.
III. Pest of Sugarcane
a. Indian sugarcane leaf hopper - Pyrilla perpusilla. This pest sucks the cell sap of leaves.
b. Sugarcane root borer - Emmalocera depressella.
This pest causes damage to the stem below the soil surface.
c. Sugarcane shoot borer - Chilo infuscatellus. This pest causes damage to the shoot.
d. Sugarcane top shoot borer - Scirpophaga nivella
It is one of the most destructive pests of sugarcane.It is found all over India. The damage by the borer actually starts from the mid-rib of the top leaves into which it bores and makes tiny holes. When the growing point is damaged, side shoots are formed in the young plants and bunchy tops in the olders ones. The quality of the juice is also affected.
Control : Effective control of this pest is possible only by integrating mechanical and chemical control methods. Mechanical methods include the collection and de-struction of egg masses and affected top shoots and sowing of resistant varieties. The chemical methods involve application of 4 % carbaryl or endo sulfan granules in the leaf whorls or spraying of 0.05 % monocrotophos or 0.1 % endrin.
IV. Pests of Vegetables.
a. The red pumpkin beetle - Raphidopalpa foveicollis.
This pest causes damage to the leaves, flowers and buds of younger plants.
b. Cabbage butterfly - Pieris brassicae .
This pest causes damage to the leaves.
c. The Hadda beetle - Epilachna dodecastigma.
This pest causes damage to the leaves of the brinjal, potato and tomatoes.
d. Brinjal shoot and fruit borer - Leucinodes orbonalis.
It is the most important and destructive pest of brinjal and has a country-wide distribution. The pest starts damaging the brinjal plant a few weeks after its transplantation. When the shoot is attacked by the caterpillar it droops and withers , finally drying up. When the petioles of the leaves are bored into by the larva the
leaves wither and drop. The attacked fruits show holes plugged with excreta on them. Upto 70 % loss of crop is caused by this pest.
Control : Prompt collection and destruction of the plant parts harbouring larvae help in reducing the infestation. Insecticides such as carbaryl, endosulfan, Lindane and diazinon, when applied at regular intervals give relief from heavy infestation.
V. Pest of Coconut palm
Rhinoceros beetle - Oryctes rhinoceros. It is distributed throughout South East Asia, Southern China, Philipines and south Pacific Islands. The adult causes infes-tation by feeding the young leaf fronds. They make burrows and throw out a fibrous mass. The infestation is marked by a number of holes on the fronds, when they open out . The attack results in the destruction of growing plant as a result of which the tree dies.
Control : The beetles should be destroyed by inserting specially designed hooked rod. In earlier developmental stages beetles should be destroyed by tackling the breeding places like manure pits near gardens by spraying 0.01% aldrin.
VI. Pests of Stored grains
a. Rice weevil - Sitophilus Oryzae
a. This is a very serious major pest of stored grains in farm storage. It is worldwide in distribution. Generally, infestation starts in grains only during storage which may lead to heat spots in the grain. The grains are hollowed and the weight is reduced.
Control : The weevil is unable to breed at a grain moisture content of 9 % or less. Hence dry storage of grains can aviod infestation by the pest. The larvae and adults are killed by exposing them for 48 hrs to the vapours of ethylene dichloride
- carbon tetra chloride mixture under gas - proof covers. Fumigation of infested grains with methyl bromide is also effective and kills all stages of pest including eggs.
b. Khapra beetle - Trogoderma granarium
Khapra beetle is a very serious pest of wheat and other stored grains all over India. Only the larval stage is destructive, adult beetle being harmless. The grubs attack the germ portion of the grain. In severe infestation the cereals are reduced to mere frass.
Control : Stocks of grains should be stored in thoroughly clean and insect-free stores which are regularly aerated. Before storage of grains, the godown should be properly disinfected with benzene hexachloride smoke or fumigants.
c. Pulse beetle - Callosobruchus Chinensis
This is a very important pest of various pulse crops in India. It affects both in fields and in stores. The pest attacks leguminous pods in the field from where they are carried to godowns. The larvae bore into the pulses and grains. They feed and grow inside. The damaged grains are unfit for human consumption.
Control : Control can be achived by growing suceptible crops atleast a kilometre away from storage godowns which are the main source of infestation.Fumiga-tion with methyl bromide in the godown is very effective but proper care must be taken because of the high toxicity of this compound.
VII. Pests of household goods
a. Termites (white ants) - Odontotermes obesus
There are more than 2000 species of termites. The food of termites con-sists primarily of wood (cellulose). This habit of termites is the cause for very serious losses, particularly in tropical countries. They destroy wood work, furnitures, buildings, fences and other wooden structures that come into contact with the soil. The losses caused by termites to Indian agriculture and other commercial crops are extensive. About 40 species of termites are injurious to economic plants such as wheat, barley, maize, gram, sugarcane, groundnut, several vegetables, fruit trees and coconut in India.
Control : The seriousness of their attack demands immediate control. For termite control, insecticides should be applied to the soil. Emulsions of 1 % chlordane, 0.5 % aldrin and 0.5 % heptachlor are suitable for soil treatment. 5 % pentachlorophe-nol is good for wood preservation. The application of a mixture of BHC and aldrin to soil in the foundations of a building is effective.
b. Silverfish - Lepisma saccharina
It is cosmopolitan in distribution. It is commonly found living in moist warm places and among old books. It is a whitish wingless insect of about 13 mm in length It mostly attacks old books and magazines. It infests starched clothes, rayon fabrics, book labels or bindings where glue has been used.
Control : The books should not be kept in damp places. Books should be exposed to sunlight frequently. Dusting of 5% malathion has proved to be an effective control measure for heavily infested cases.
Related Topics