Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Development, Heredity, and aging
Neural tube and neural Crest Formation - Prenatal Development
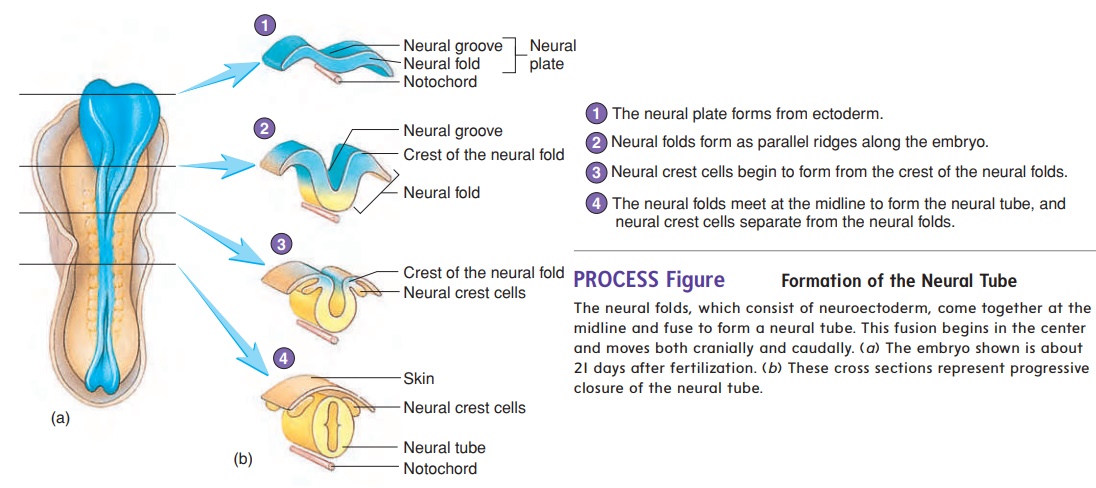
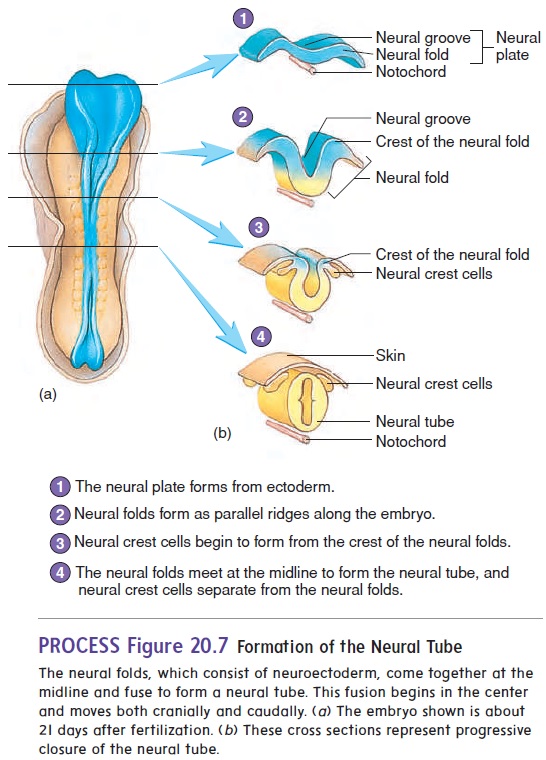
Neural tube and neural Crest Formation
At about 18 days after fertilization, the ectoderm overlying the notochord thickens to form the neural plate. The lateral edges of the plate begin to rise like two ocean waves coming together. These edges are called the neural folds, and between them lies a neural groove. The neural folds begin to meet in the midline and fuse into a neural tube (figure 20.7). The cells of the neural tube are called neuroectoderm (noor-ō -ek′ tō -derm) (table 20.1). Neuroectoderm becomes the brain, the spinal cord, and parts of the peripheral nervous system. The neural tube becomes com-pletely closed by day 26. If the neural tube fails to close, major defects of the central nervous system can result.
Anencephaly (an′en-sef′̆a-l̄e; no brain) is a birth defectwherein much of the brain fails to form because the neural tube did not close in the region of the head. A baby born with anen-cephaly cannot survive. Spina bifida (spı̄ ′ n̆a bif ′ i -d̆a ; split spine) is a general term describing defects of the spinal cord or vertebral column. Spina bifida can range from a simple defect with one or more vertebral spinous processes split or missing but no clinical manifestation to a more severe defect that can result in paralysis of the limbs or the bowels and bladder, depending on where the defect occurs. More severe forms of spina bifida result from failure of the neural tube in the area of the spinal cord to close. It has been demonstrated that adequate amounts of the B vitamin folate, more commonly referred to as folic acid, in the diet during pregnancy can reduce the risk of such defects.
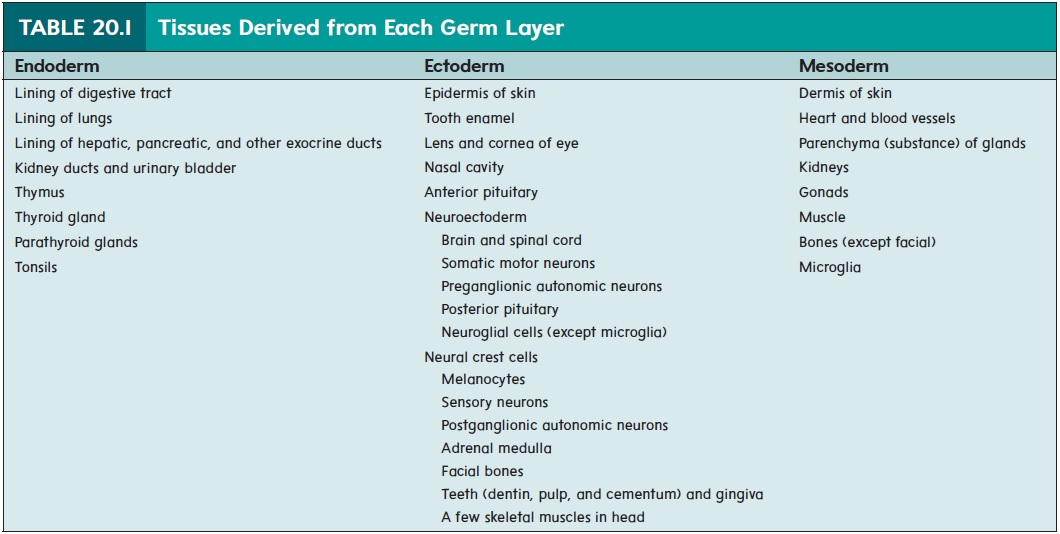
As the neural folds come together and fuse, a population of cells breaks away from the neuroectoderm all along the crests of the folds. Most of these neural crest cells become part of the peripheral nervous system or become melanocytes in the skin. In the head, neural crest cells also contribute to the skull, the dentin of teeth, blood vessels, and general connective tissue.
Related Topics