Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Morphology and Physiology of Bacteria
Fluorescence microscopy
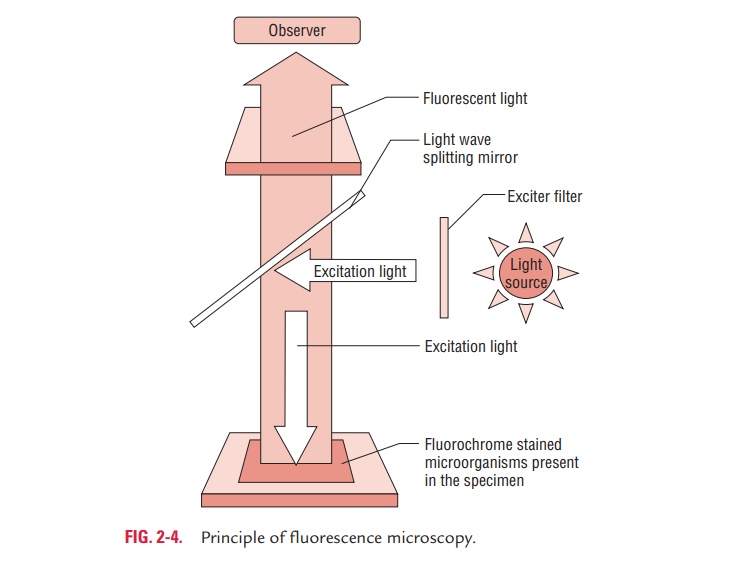
Fluorescence microscopy
Fluorescence microscopy is based on the principle that the spec-imens stained with fluorescent dye when exposed to ultraviolet light result in emission of longer wavelength of light (i.e., vis-ible light) (Fig. 2-4). The bacteria stained with fluorescent dye appear as a brightly glowing object against a dark background.
Fluorescence microscopy needs a fluorescence microscope fitted with an ultraviolet light source. Auramine O, acridine orange, and rhodamine are fluorescent dyes used to visualize bacteria. The resolving power of a fluorescence microscope is increased due to the short wavelength of ultraviolet light. Auramine O, acridine orange, and rhodamine are fluorescent dyes used to visualize bacteria. Fluorescence microscopy is widely used in diagnostic microbiology in the following ways:
· It is used for direct demonstration of antigen of a patho-gen in clinical specimens by direct fluorescent antibody test (e.g., direct detection of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Corynebacteriumdiphtheriae, etc. directly in clinical specimens).
· It is also used for the estimation of antibodies in the serum by indirect fluorescent antibody test (IFA) (e.g., IFA in lepto-spirosis, syphilis, brucellosis, etc.).
Related Topics