Chapter: 12th Nursing : Chapter 1 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
Endocrine System
Endocrine System
The endocrine system provides the body with the hormones that are
needed to sustain life and create life. Hypo and hyper secretion of the
endocrine glands leads to physiological problems.
Physiology
Endocrine system is a control system of ductless glands that
secrete hormones within specific organs. Hormones acts as “messengers” and are
carried by the blood stream to different cells in the body, which interpret
these messages and act on them. It provides an electrochemical connection from
the hypothalamus of the brain to all the organs that control the body
metabolism, growth and development, reproduction and also maintain homeostasis.
The endocrine system regulates its hormones through negative
feedback. Increases in hormones activity decrease the production of that
hormone
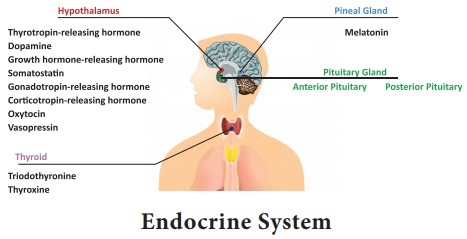
The endocrine system consists of these glands
• Hypothalamus
• Pituitary gland
• Pineal gland
• Thyroid
• Parathyroid
• Adrenal glands
• Pancreas
• Ovaries
• Testes
Hypothalamus
The hypothalamus lies within the cranium which regulates the
homeostasis. The hypothalamus regulates the release or slow down and stop the
release of hormones from other endocrine glands based on the blood levels of
these hormones.
Pituitary Gland
Located at the base of the brain, is the master gland which
controls the secretion of several other glands included in the endocrine
system.
Pineal Gland
The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland that lies close to the
hypothalamus, performs the coordination of circadian rhythm (sleep -
wake cycle).
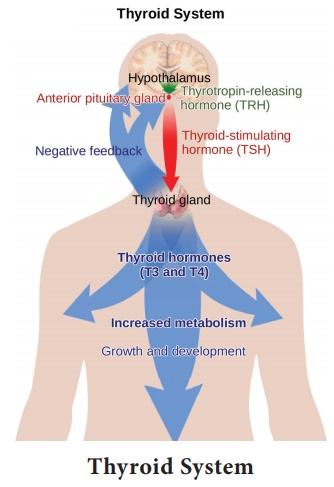
Thyroid Gland
The Thyroid gland shaped like angel wings on each side of the
throat just above the trachea, are connected to each other with a thin
connecting area called the Isthmus.
The Thyroid gland regulates the body’s metabolism, basal metabolic
rate, cardiac system’s function, physical growth and sexual
The parathyroid glands are two pairs of glands found bilaterally
on both sides of the neck just behind the Thyroid gland. The body has four
parathyroid glands which is unique when compared to the other glands of the
endocrine system. The role of the glands is to control the circulating amount
of two electrolytes, calcium and phosphorous with the secretion of parathyroid
hormone.
Adrenal Glands
The adrenal glands, which are in the abdominal area, are located
bilaterally just above each kidney and the diaphragm. The adrenal glands
consist of two layers, the cortex (outer layer) and the medulla (inner core).
The cortex secretes:
·
Androgen - male hormone
·
Aldosterone - controls blood pressure and fluid balance
·
Cortisol - regulates and coordinates metabolism
The medulla secretes stress reaction hormones such as:
• Adrenaline
• Noradrenaline
• Catecholamine
The Pancreas
The pancreas is located behind the stomach. The islets of Langerhans
secrete glucagon, insulin, pancreatic polypeptide and somatostatin. The
pancreas produces and releases digestive enzymes and juices that break down
foods as they enter the small intestine.
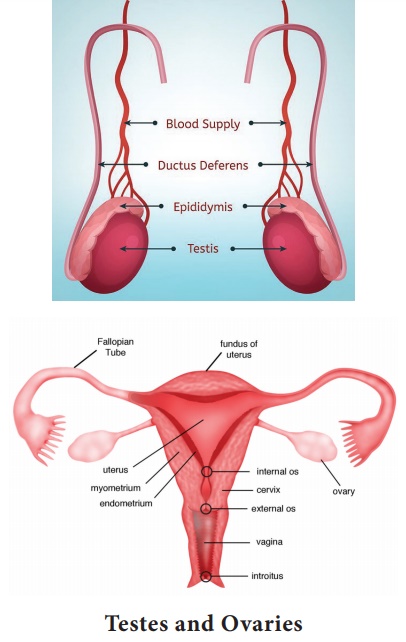
Testes and Ovaries
Ovaries and Testes are the endocrine glands and gonads, which is
called as a sex and reproduction glandular structure.
The ovaries produce progesterone, estrogen, inhibin and
androstenedione. Progesterone regulates menstrual cycle and the preparation of
the uterus for the implantation of the egg. Estrogen regulates the development
of breasts. Inhibin inhibits Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) in females and
in males it inhibits the development of sperm and androstenedione (androgen
that is weaker than testosterone).
The testes produce androgens, testosterone and sperms.
Diseases related to endocrine system
·
Diabetes insipidus
·
Acromegaly
·
Gigantism
·
Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone Secretion (SIADH)
·
Hyperthyroidism
·
Hypothyroidism
·
Cushing’s syndrome
·
Addison’s disease
Related Topics